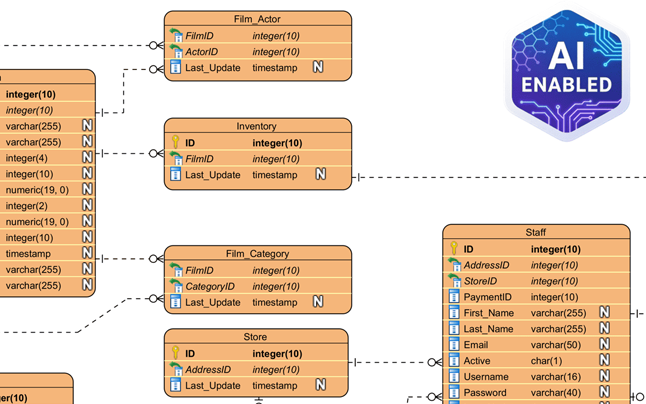
Pengantar Normalisasi yang Didorong oleh Kecerdasan Buatan
Normalisasi basis data adalah proses kritis dalam mengatur data untuk menjamin integritas dan menghilangkan redundansi. Meskipun secara tradisional merupakan tugas yang kompleks dan rentan kesalahan, alat modern telah berkembang untuk mengotomatisasi pekerjaan berat ini. Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler berperan sebagai jembatan cerdas, mengubah konsep abstrak menjadi implementasi yang dioptimalkan secara teknis dan siap produksi.
Untuk memahami nilai alat ini, pertimbangkan analogi pembuatan mobil. Jika Diagram Kelas adalah gambaran awal dan sebuah Diagram Hubungan Entitas (ERD) adalah gambaran teknis, maka normalisasiadalah proses penyetelan mesin untuk memastikan tidak ada baut longgar atau beban berlebihan. AI DB Modeler berfungsi sebagai ‘pabrik otomatis’ yang melaksanakan penyetelan ini untuk efisiensi maksimal. Tutorial ini memandu Anda melalui proses menggunakan AI DB Modeler untuk normalisasi skema basis data Anda secara efektif.

Langkah 1: Mengakses Alur Kerja yang Dipandu
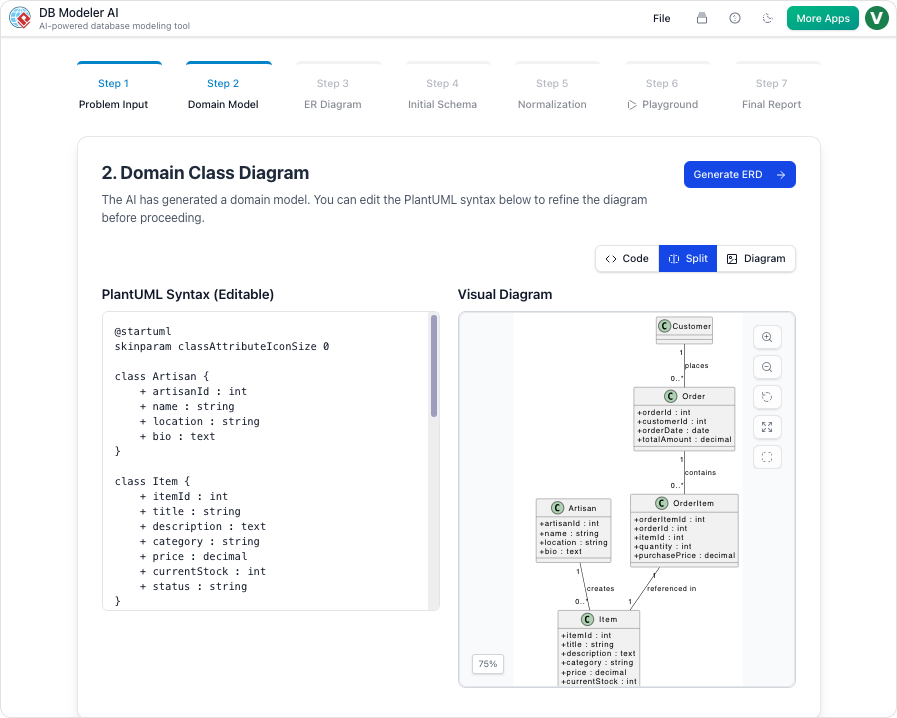
AI DB Modeler beroperasi menggunakan alur kerja khusus 7 langkah alur kerja yang dipandu. Normalisasi menjadi fokus utama pada Langkah 5. Sebelum mencapai tahap ini, alat ini memungkinkan Anda memasukkan kelas konseptual tingkat tinggi. Dari sana, alat ini menggunakan algoritma cerdas untuk mempersiapkan struktur agar siap dioptimalkan, memungkinkan pengguna beralih dari konsep ke tabel tanpa usaha manual.
Langkah 2: Melangkah Melalui Bentuk Normal
Setelah Anda mencapai tahap normalisasi, AI secara iteratif mengoptimalkan skema basis datamelalui tiga tahap utama kematangan arsitektur. Progresi bertahap ini memastikan bahwa basis data Anda memenuhi standar industri dalam hal keandalan.
Mencapai Bentuk Normal Pertama (1NF)
Tingkat optimasi pertama berfokus pada sifat atomik data Anda. AI menganalisis skema Anda untuk memastikan bahwa:
- Setiap sel tabel berisi satu nilai atomik.
- Setiap catatan dalam tabel bersifat unik.
Melangkah ke Bentuk Normal Kedua (2NF)
Membangun atas struktur 1NF, AI melakukan analisis lebih lanjut untuk membangun hubungan kuat antara kunci dan atribut. Pada langkah ini, alat ini memastikan bahwa semua atribut non-kunci sepenuhnya fungsional dan tergantung pada kunci utama, secara efektif menghilangkan ketergantungan parsial.
Menyelesaikan dengan Bentuk Normal Ketiga (3NF)
Untuk mencapai tingkat optimalisasi profesional standar, AI mengembangkan skema hingga 3NF. Ini melibatkan memastikan bahwa semua atribut tergantung hanya pada kunci utama. Dengan melakukan hal tersebut, alat ini menghilangkan ketergantungan transitif, yang merupakan sumber umum dari anomali data.
Langkah 3: Meninjau Deteksi Kesalahan Otomatis
Sepanjang proses normalisasi, AI DB Modeler menggunakanalgoritma cerdasuntuk mendeteksi kekurangan desain yang sering menghantui sistem yang dirancang buruk. Secara khusus, alat ini mencari anomali yang dapat menyebabkan:
- kesalahan pembaruan
- kesalahan penyisipan
- kesalahan penghapusan
Dengan mengotomatisasi deteksi ini, alat ini menghilangkan beban manual dalam mencari masalah integritas potensial, memastikan fondasi yang kuat untuk aplikasi Anda.
Langkah 4: Memahami Perubahan Arsitektur
Salah satu fitur khas dari AI DB Modeler adalah transparansinya. Berbeda dengan alat tradisional yang hanya mengatur ulang tabel di latar belakang, alat ini berfungsi sebagai sumber pembelajaran.
Untuk setiap perubahan yang dibuat selama langkah 1NF, 2NF, dan 3NF, AI memberikanalasan dan penjelasan edukatif. Wawasan ini membantu pengguna memahami perubahan arsitektur khusus yang diperlukan untuk mengurangi redundansi, berfungsi sebagai alat pembelajaran berharga untuk menguasai praktik terbaik dalamdesain basis data.
Langkah 5: Validasi melalui Playground Interaktif
Setelah AI mengoptimalkan skema hingga 3NF, alur kerja berpindah keLangkah 6, di mana Anda dapat memverifikasi desain sebelum pelaksanaan nyatapenempatan. Alat ini menawarkan playground interaktif unik untuk validasi akhir.
| Fitur | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| Uji Coba Langsung | Pengguna dapat memulai instance basis data di browser berdasarkan tingkat normalisasi yang dipilih (Awal, 1NF, 2NF, atau 3NF). |
| Penyemaian Data Realistis | Lingkungan diisi dengandata sampel realistis yang dihasilkan oleh AI, termasuk pernyataan INSERT dan skrip DML. |
Lingkungan ini memungkinkan Anda menguji query dan memverifikasi kinerja terhadap struktur yang dinormalisasi secara langsung. Dengan berinteraksi dengan data yang telah diisi, Anda dapat memastikan bahwa skema memproses informasi dengan benar dan efisien, memastikan bahwa ‘mesin’ disesuaikan secara sempurna sebelum mobil melaju.
-
Ulasan Komprehensif tentang DBModeler AI untuk Desain Skema: Analisis mendalam tentang bagaimana DBModeler AI mengubah desain skema basis data melalui otomatisasi dan kecerdasan.
-
DBModeler AI: Alat Pemodelan Basis Data Cerdas: Akses alat yang didorong oleh AI untuk pemodelan basis data otomatis dan generasi skema di Visual Paradigm.
-
DBModeler AI: Alat desain basis data berbasis AI dengan alur kerja 7 langkah. Hasilkan model domain, diagram ER, skema yang dinormalisasi, dan laporan desain lengkap. Jalankan lingkungan basis data langsung di browser untuk menguji query secara instan.
-
Analisis Teks Berbasis AI – Ubah Teks menjadi Model Visual Secara Otomatis: Gunakan AI untuk menganalisis dokumen teks dan secara otomatis menghasilkan diagram seperti UML, BPMN, dan ERD untuk pemodelan dan dokumentasi yang lebih cepat.
-
Alat ERD Visual Paradigm – Buat Diagram Entitas-Relasi Secara Online: Alat ERD berbasis web yang kuat yang memungkinkan pengguna merancang dan memvisualisasikan skema basis data dengan mudah menggunakan fitur seret dan lepas yang intuitif.
-
Desain Basis Data dengan Alat ERD – Panduan Visual Paradigm: Panduan komprehensif tentang penggunaan alat ERD untuk merancang basis data yang kuat dan skalabel dengan praktik terbaik dalam pemodelan data dan desain skema.
-
Apa itu Diagram Entitas-Relasi (ERD)? – Panduan Visual Paradigm: Penjelasan mendalam tentang ERD, komponen-komponennya, dan pentingnya dalam desain basis data dan pemodelan data.
-
Alat ERD Gratis – Rancang Basis Data Secara Online dengan Visual Paradigm: Akses alat ERD gratis secara online untuk membuat diagram entitas-relasi profesional tanpa instalasi atau langganan.
-
Cara Menggambar Entitas di ERD Visual Paradigm: Panduan langkah demi langkah untuk membuat dan menyesuaikan entitas di alat ERD Visual Paradigm untuk pemodelan basis data yang akurat.
-
Cara Memodelkan Basis Data Relasional dengan ERD – Tutorial Visual Paradigm: Tutorial praktis yang menunjukkan cara menggunakan ERD untuk memodelkan basis data relasional dari konsep hingga implementasi.