Wprowadzenie do normalizacji sterowanej sztuczną inteligencją
Normalizacja bazy danych to kluczowy proces organizowania danych w celuzapewnienia integralności i eliminacji nadmiarowości. Choć tradycyjnie jest to skomplikowane i podatne na błędy zadanie, nowoczesne narzędzia ewoluowały w kierunku automatyzacji tej „ciężkiej pracy”. Modeler bazy danych AI Visual Paradigm działa jak inteligentny most, przekształcając abstrakcyjne koncepcje w technicznie zoptymalizowane, gotowe do wdrożenia implementacje.
Aby zrozumieć wartość tego narzędzia, rozważ analogię produkcji samochodu. JeśliDiagram klas to początkowy szkic, aDiagram relacji encji (ERD) to projekt mechaniczny, tonormalizacjato proces dopasowania silnika, aby nie było luźnych śrub ani nadmiarowej masy. Modeler bazy danych AI działa jak „fabryka automatyczna”, która wykonuje to dopasowanie w celu maksymalnej efektywności. Ten samouczek prowadzi Cię przez proces używania modelera bazy danych AI w celu skutecznej normalizacji schematu bazy danych.

Krok 1: Dostęp do przewodnika krok po kroku
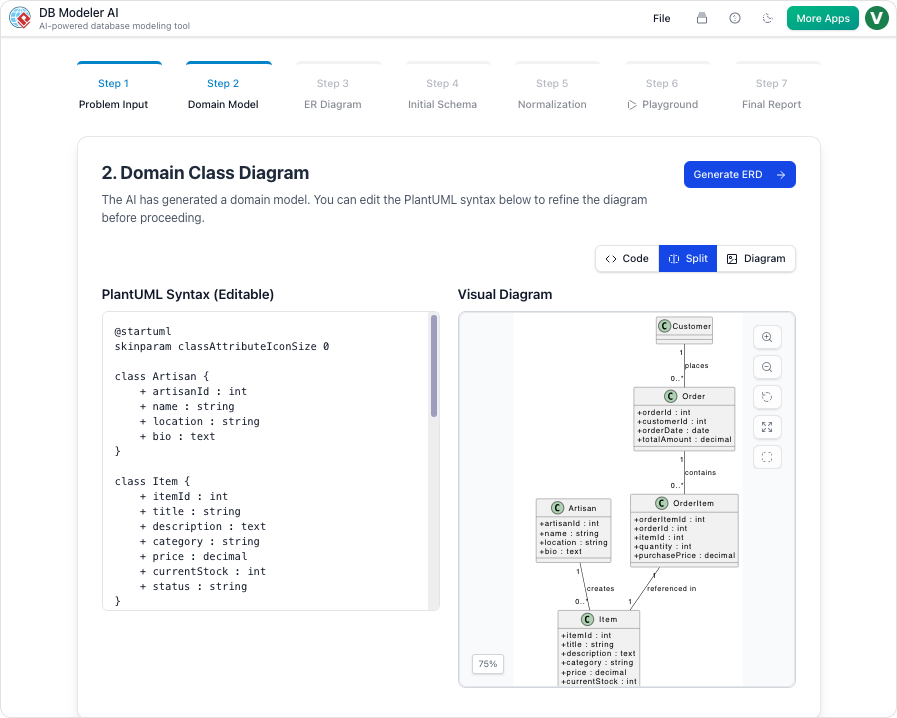
Modeler bazy danych AI działa przy użyciu specjalistycznego przewodnika krok po kroku składającego się z 7 krokówprzewodnika krok po kroku. Normalizacja zajmuje centrum uwagi wKroku 5. Zanim osiągniesz ten etap, narzędzie pozwala Ci wprowadzić pojęciowe klasy najwyższego poziomu. Następnie wykorzystuje inteligentne algorytmy do przygotowania struktury do optymalizacji, umożliwiając użytkownikom przejście od koncepcji do tabel bez konieczności ręcznej pracy.
Krok 2: Przechodzenie przez formy normalne
Gdy osiągniesz fazę normalizacji, AI iteracyjnie optymalizujeschemat bazy danychpoprzez trzy główne etapy dojrzałości architektonicznej. Ta krok po kroku postępująca optymalizacja zapewnia, że Twoja baza danych spełnia standardy branżowe pod względem niezawodności.
Osiąganie pierwszej formy normalnej (1NF)
Pierwszy poziom optymalizacji skupia się na atomowej naturze Twoich danych. AI analizuje Twój schemat, aby upewnić się, że:
- Każde pole tabeli zawiera pojedynczą, atomową wartość.
- Każdy rekord w tabeli jest unikalny.
Przechodzenie do drugiej formy normalnej (2NF)
Opierając się na strukturze 1NF, AI przeprowadza dalszą analizę, aby ustalić silne relacje między kluczami a atrybutami. W tym kroku narzędzie zapewnia, że wszystkie atrybuty niekluczowe są pełnymi funkcjonalnie i zależne od klucza głównego, efektywnie usuwając zależności częściowe.
Zakończenie trzecią formą normalną (3NF)
Aby osiągnąć standardowy poziom profesjonalnej optymalizacji, AI prowadzi schemat do 3NF. Obejmuje to zapewnienie, że wszystkie atrybuty są zależnetylko na kluczu głównym. Dzięki temu narzędzie usuwa zależności przechodnie, które są częstym źródłem anomalii danych.
Krok 3: Przeglądanie automatycznego wykrywania błędów
W trakcie całego procesu normalizacji AI DB Modeler wykorzystujeinteligentne algorytmy do wykrywania błędów projektowych, które często atakują słabo zaprojektowane systemy. Szczególnie szuka anomalii, które mogą prowadzić do:
- Błędy aktualizacji
- Błędy wstawiania
- Błędy usuwania
Automatyzując to wykrywanie, narzędzie eliminuje obciążenie ręczne związane z poszukiwaniem potencjalnych problemów integralności, zapewniając solidne podstawy dla Twoich aplikacji.
Krok 4: Zrozumienie zmian architektonicznych
Jedną z charakterystycznych cech AI DB Modeler jest jego przejrzystość. W przeciwieństwie do tradycyjnych narzędzi, które po prostu przekształcają tabele na wstępie, to narzędzie działa jako zasób edukacyjny.
Dla każdej zmiany dokonanej w trakcie kroków 1NF, 2NF i 3NF, AI dostarczaedytoryczne uzasadnienia i wyjaśnienia. Te wgląd pomagają użytkownikom zrozumieć konkretne zmiany architektoniczne wymagane do zmniejszenia nadmiarowości, działając jako cenny narzędzie do opanowania najlepszych praktyk w zakresieprojektowania baz danych.
Krok 5: Weryfikacja za pomocą interaktywnego playgroundu
Po tym, jak AI zoptymalizuje schemat do 3NF, przepływ pracy przechodzi doKroku 6, gdzie możesz zweryfikować projekt przed rzeczywistymwdrożeniem. Narzędzie oferuje unikalny interaktywny playground do końcowej weryfikacji.
| Funkcja | Opis |
|---|---|
| Testowanie na żywo | Użytkownicy mogą uruchomić instancję bazy danych w przeglądarce opartą na wybranym poziomie normalizacji (Początkowy, 1NF, 2NF lub 3NF). |
| Realistyczne zasiewanie danych | Środowisko jest wypełnionerealistycznymi, wygenerowanymi przez AI danymi przykładowymi, w tym instrukcje INSERT i skrypty DML. |
Ten środowisko pozwala na testowanie zapytań i sprawdzanie wydajności w stosunku do struktury znormalizowanej od razu. Poprzez interakcję z danymi początkowymi możesz potwierdzić, że schemat poprawnie i efektywnie obsługuje informacje, zapewniając, że „silnik” jest idealnie dopasowany, zanim samochód wjechał na drogę.
-
Kompleksowa recenzja DBModeler AI do projektowania schematów: szczegółowa analiza, jak DBModeler AI przekształca projektowanie schematów baz danych poprzez automatyzację i inteligencję.
-
DBModeler AI: inteligentny narzędzie do modelowania baz danych: uzyskaj dostęp do narzędzia opartego na AI do automatycznego modelowania baz danych i generowania schematów w Visual Paradigm.
-
DBModeler AI: narzędzie do projektowania baz danych z wykorzystaniem AI z siedmiokrokowym przepływem pracy. Generuj modele dziedziny, diagramy ER, znormalizowane schematy i pełne raporty projektowe. Uruchom interaktywną platformę baz danych w przeglądarce, aby natychmiast przetestować zapytania.
-
Analiza tekstowa z wykorzystaniem AI – automatyczne przekształcanie tekstów w modele wizualne: użyj AI do analizy dokumentów tekstowych i automatycznego generowania diagramów, takich jak UML, BPMN i ERD, aby przyspieszyć modelowanie i dokumentację.
-
Narzędzie Visual Paradigm ERD – tworzenie diagramów encji-relacji online: potężne narzędzie ERD oparte na przeglądarce, które pozwala użytkownikom na łatwe projektowanie i wizualizację schematów baz danych za pomocą intuicyjnych funkcji przeciągania i upuszczania.
-
Projektowanie baz danych za pomocą narzędzi ERD – przewodnik Visual Paradigm: kompleksowy przewodnik dotyczący używania narzędzi ERD do projektowania solidnych, skalowalnych baz danych z wykorzystaniem najlepszych praktyk modelowania danych i projektowania schematów.
-
Co to jest diagram encji-relacji (ERD)? – przewodnik Visual Paradigm: szczegółowe wyjaśnienie ERD, ich składników i ich znaczenia w projektowaniu baz danych i modelowaniu danych.
-
Bezpłatne narzędzie ERD – projektowanie baz danych online za pomocą Visual Paradigm: uzyskaj dostęp do bezpłatnego narzędzia ERD online do tworzenia profesjonalnych diagramów encji-relacji bez instalacji i subskrypcji.
-
Jak rysować encje w narzędziu ERD Visual Paradigm: krok po kroku przewodnik użytkownika dotyczącego tworzenia i dostosowywania encji w narzędziu ERD Visual Paradigm do dokładnego modelowania baz danych.
-
Jak modelować bazę danych relacyjną za pomocą ERD – tutorial Visual Paradigm: praktyczny tutorial pokazujący, jak używać ERD do modelowania baz danych relacyjnych od koncepcji po wdrożenie.