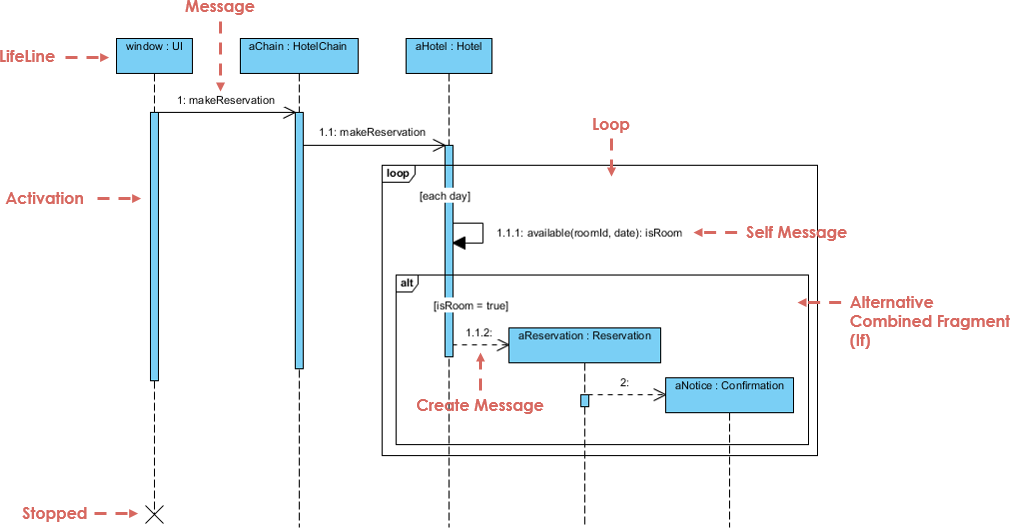
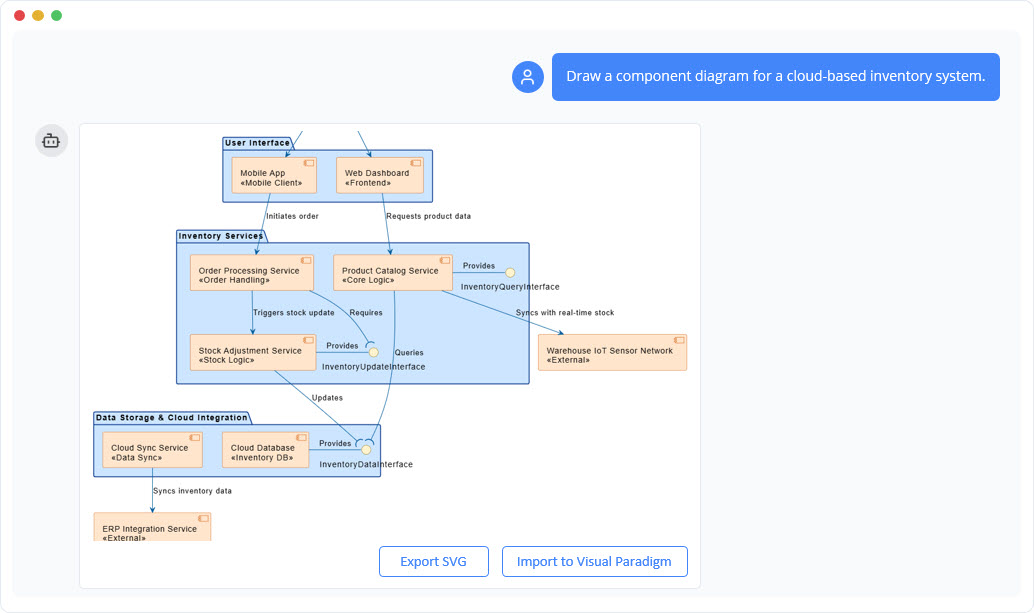
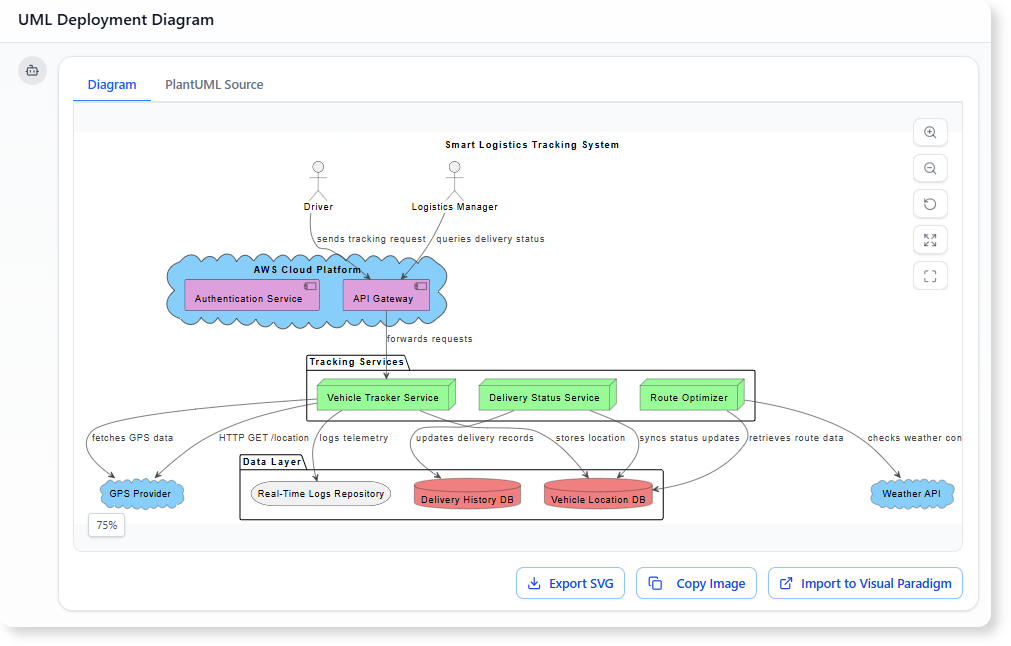
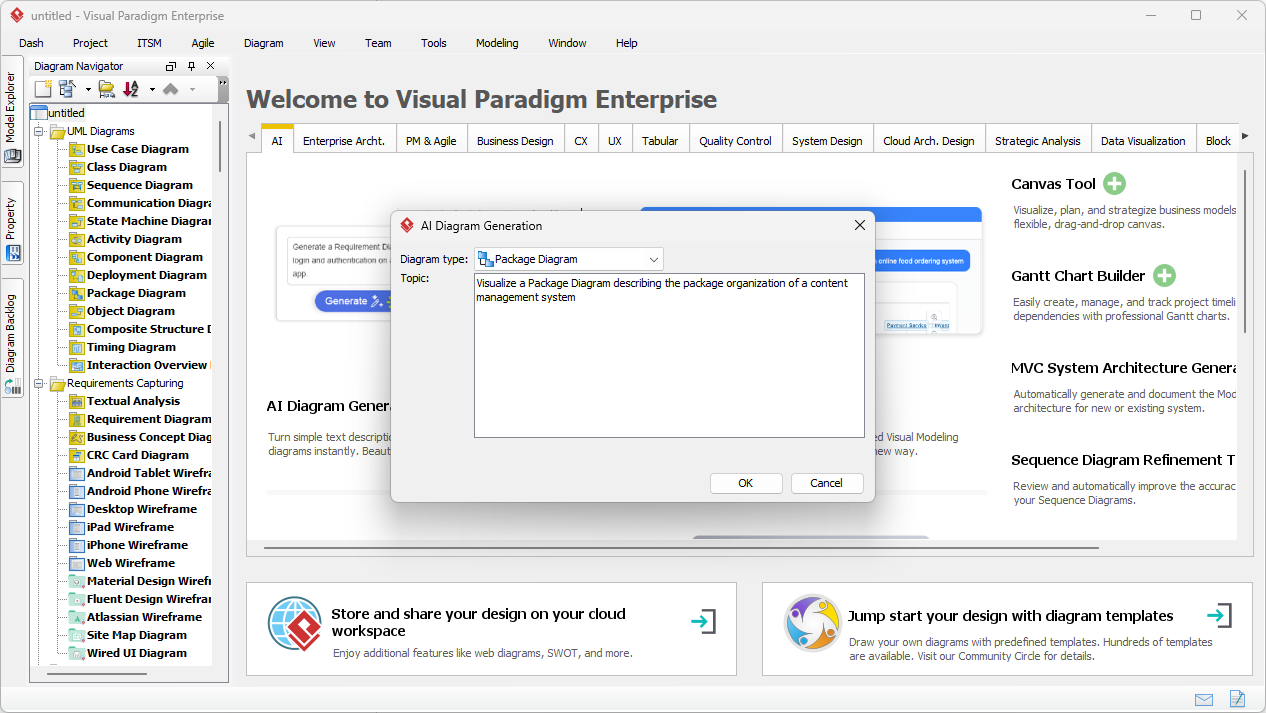
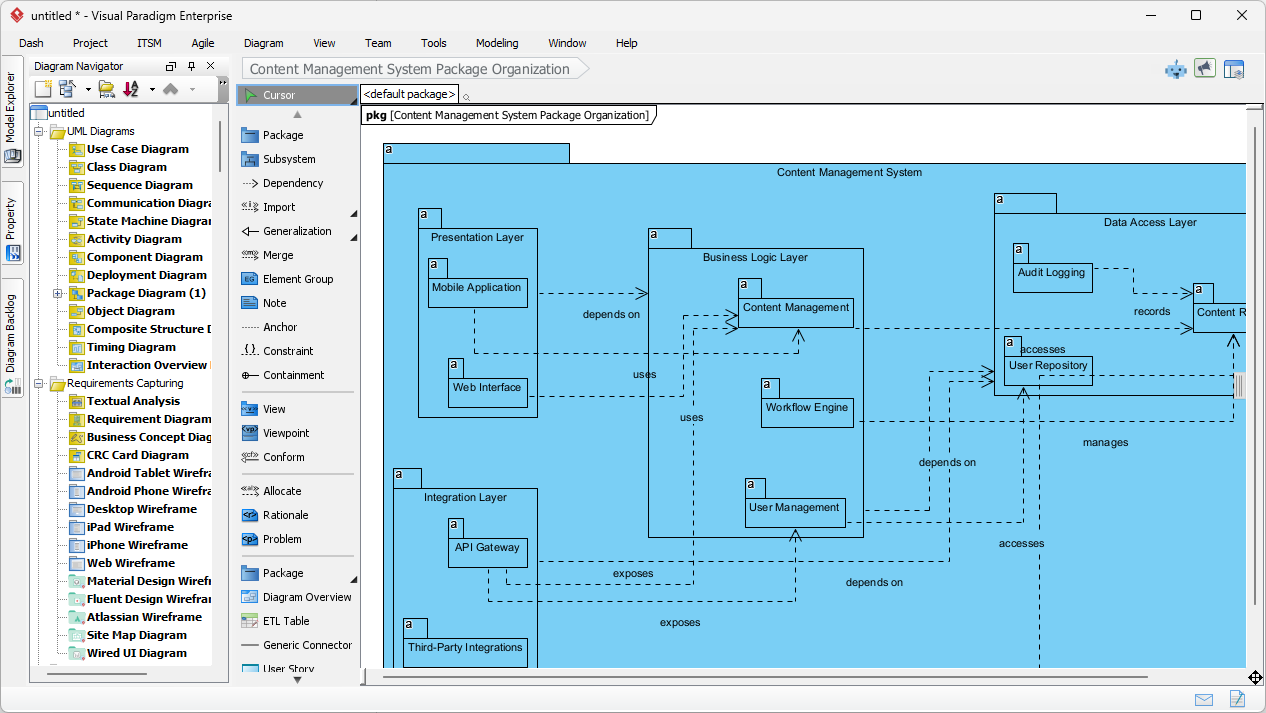
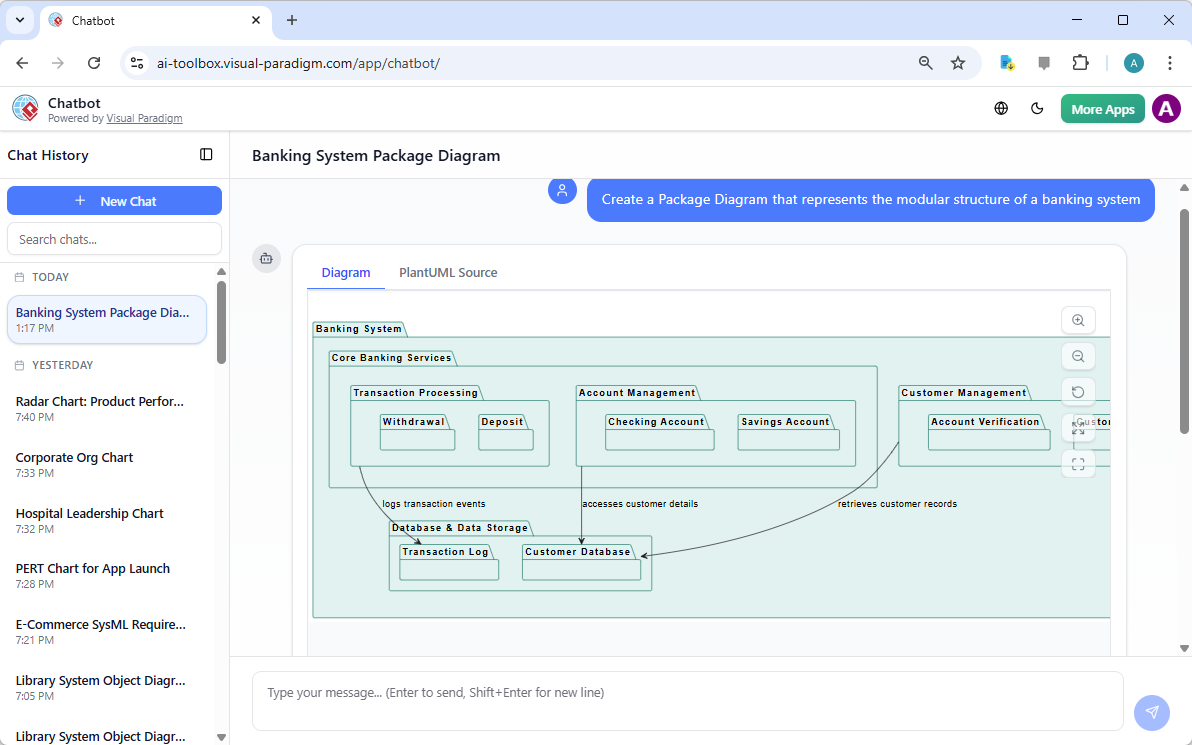
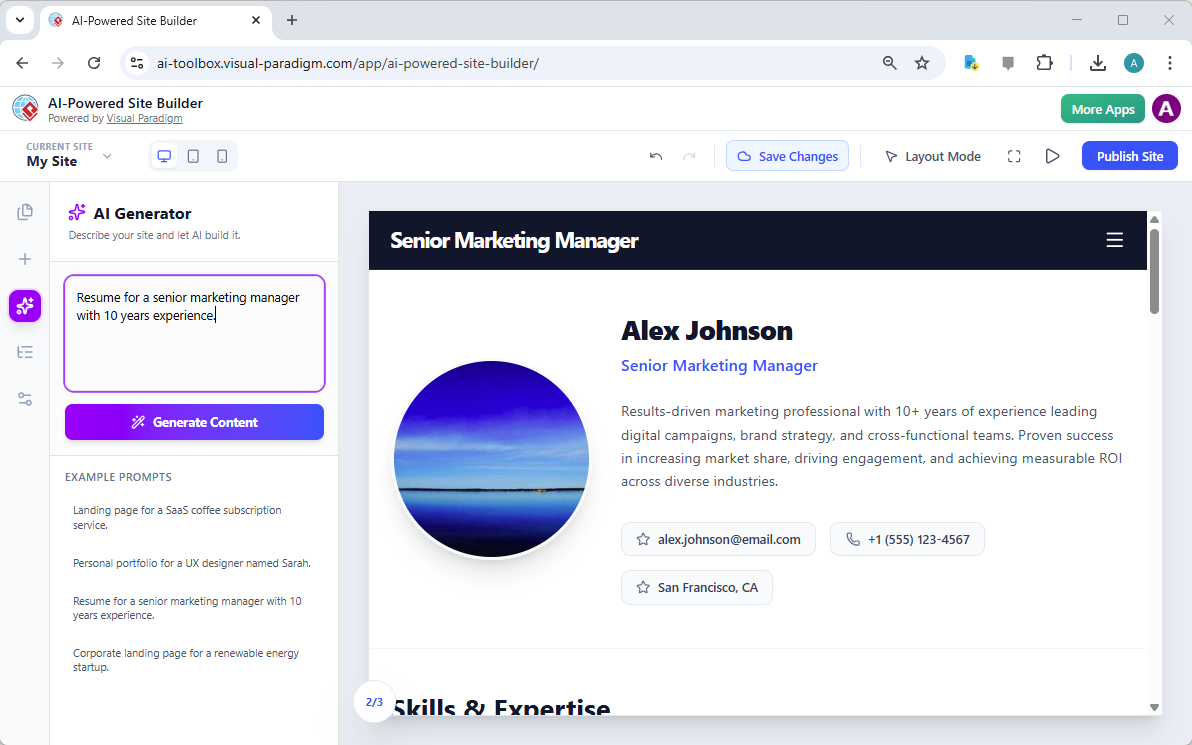
W nowoczesnym środowisku inżynierii oprogramowania przejście od abstrakcyjnych idei do konkretnych projektów systemów często wydaje się rozwiązaniem „labiryntu bez mapy”. Choć ogólne modele językowe (LLM) przełamały nowoczesne podejście do tworzenia treści, znacznie zawiodły w zastosowaniach do profesjonalnego modelowania wizualnego. Niniejszy artykuł bada brakujące elementy generowania diagramów przez przypadkowe AI oraz jak ekosystem AI Visual Paradigm (VP)przekształca te wyzwania w szybki silnik sukcesu architektonicznego.
1. Problem „artysty szkiców”: Co brakuje w przypadkowych AI LLM
Podstawowa ograniczoność ogólnych LLM w modelowaniu wynika z różnicy międzygenerowaniem tekstów istandardowym modelowaniem wizualnym. Źródła charakteryzują ogólne LLM jako„artystów szkiców”, którzy nie posiadają„kodów budowlanych” i„systemów CAD”potrzebnych do profesjonalnej inżynierii.
- Brak silników renderowania:Ogólne LLM są przede wszystkim zaprojektowane do przetwarzania i generowania tekstu. Choć mogą generować „kod diagramów” (np. Mermaid lub PlantUML), nie posiadają wbudowanychsilników renderowaniaw celu przekształcenia tego kodu w wysokiej jakości, edytowalne grafiki wektorowe, takie jak SVG.
- Naruszenia semantyczne i standardów:Zwykłe modele AI często generują „ładne szkice”, którenaruszają zasady techniczneformalnego modelowania. Często niepoprawnie interpretują skomplikowane terminy techniczne, takie jak„agregacja,” „kompozycja,”lub„polimorfizm,”co prowadzi do dekoracyjnych rysunków zamiast funkcjonalnych artefaktów inżynierskich.
- Brak zarządzania stanem:Zwykłe LLM nie mają trwałej struktury wizualnej. Jeśli użytkownik poprosi AI opartą na tekście o zmianę pojedynczego szczegółu, model często musiprzegenerować całą diagram, co prowadzi do uszkodzonych połączeń, niezgodnych układów lub całkowitej utraty poprzednich szczegółów.
2. Problemy napotykane podczas casualnego tworzenia diagramów przez AI
Opieranie się na casualnym generowaniu przez AI wprowadza kilka ryzyk, które mogą naruszyć integralność projektu:
- Pęknięcie „projektowanie-realizacja”:Bez rygorystycznego wizualnego projektu logika pozostaje „rozproszona” i „niejasna”, często prowadząc do kodu, który jest „chaos”, oraz spotkań kończących się bez wspólnego zrozumienia.
- Barierę wiedzy syntaktycznej:Jeśli AI generuje kod surowy, użytkownik musi posiadaćgłęboką wiedzę technicznąw tej konkretnej składni (np. PlantUML), aby dokonać modyfikacji ręcznych, co niszczy cel „łatwej” narzędzia AI.
- Odizolowanie od procesu pracy:Fragmenty tekstu z ogólnych LLM są odizolowane od rzeczywistego procesu inżynierskiego, wymagając ręcznego kopiowania i wklejania oraz nie oferując kontroli wersji ani integracji z innymi typami modeli.
- Niepowodzenie „jednokrotnych” promptów:Jeden prompt rzadko jest wystarczający, aby spełnić 100% wymagań użytkownika dotyczącego szczegółowego systemu. Początkowe pomysły są często „rozproszone”, a użytkownicy często dopiero po zobaczeniu pierwszego szkicu uświadamiają sobie, że pominęli kluczowe detale – takie jak balansery obciążenia lub stany obsługi błędów.
3. Jak Visual Paradigm AI osiąga profesjonalną integralność
Visual Paradigm AI rozwiązuje te kwestie dziedziczne, przekształcając modelowanie z „ciężkiej pracy rysowania” wintuicyjny, rozmowny i automatyzowany proces pracy.
A. „Dokładanie diagramu” i trwała struktura
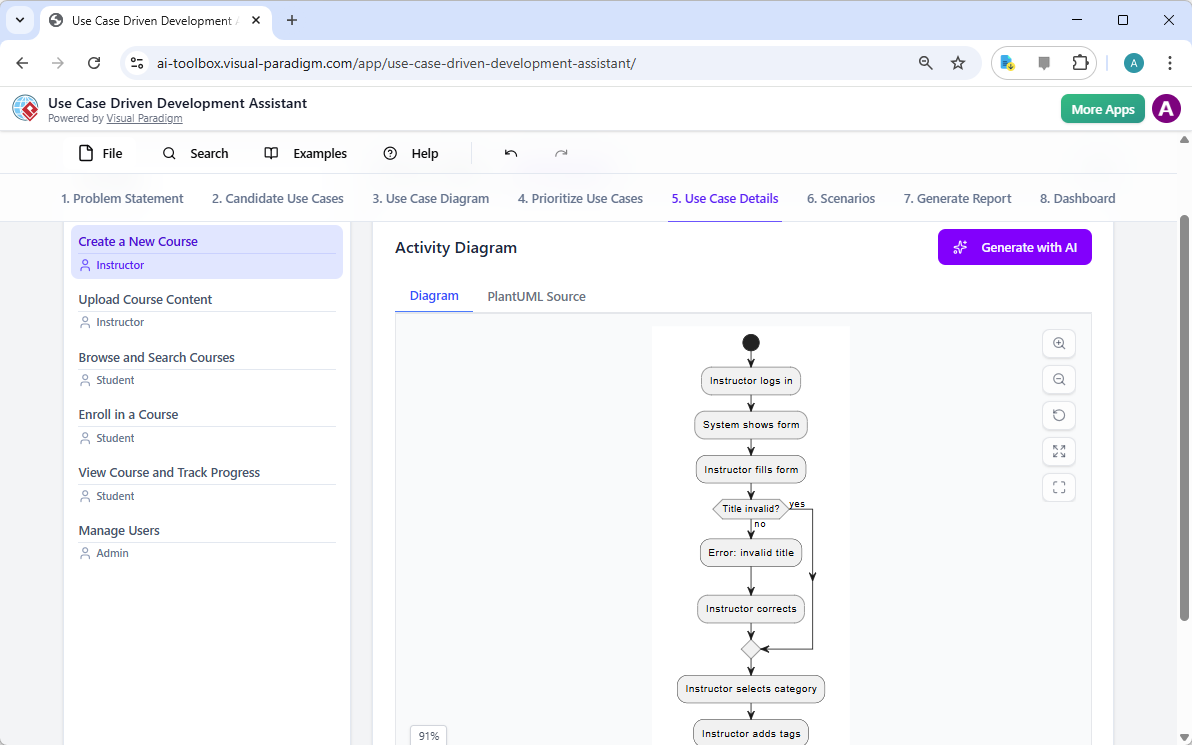
W przeciwieństwie do ogólnych narzędzi, VP AI utrzymuje diagram jakotrwały obiekt. Poprzez własnątechnologię „Dokładania diagramu”, użytkownicy mogą wysyłać rozmowne polecenia, takie jak „dodaj krok uwierzytelniania dwuetapowego” lub „zmień nazwę tego aktora”, a AI aktualizujestrukturę wizualnąod razu, przy jednoczesnymutrzymując integralność układu.
B. Znormalizowana inteligencja
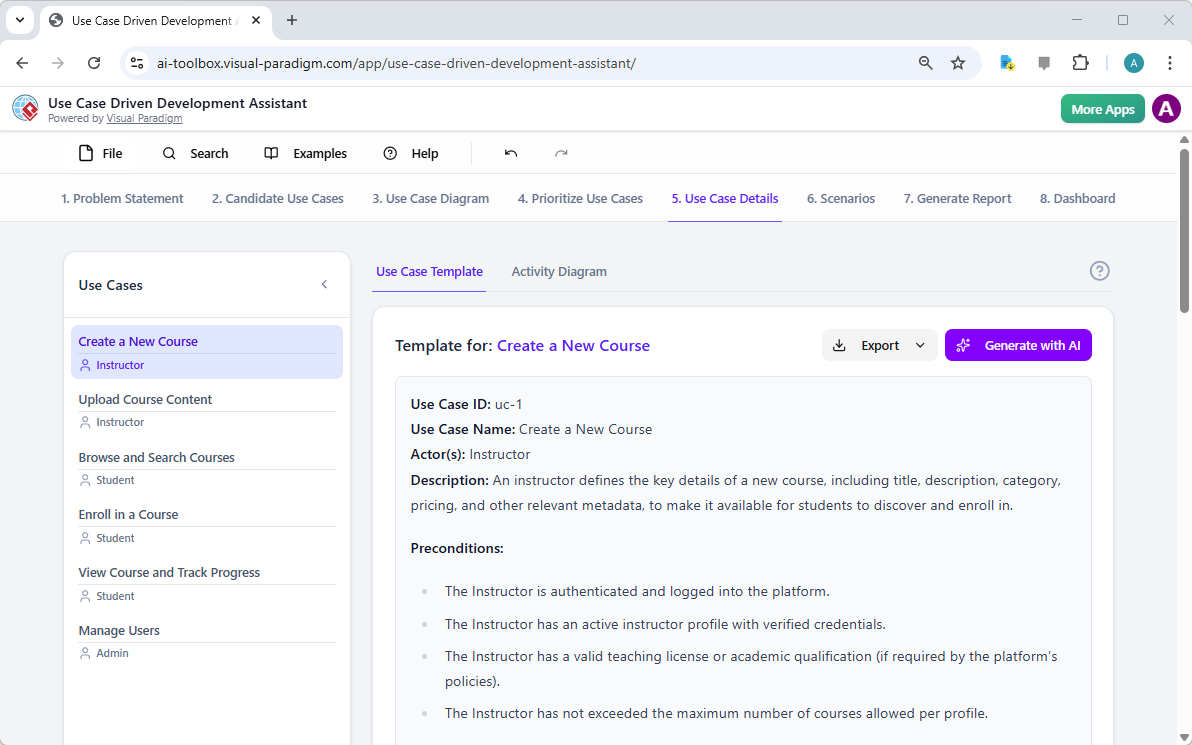
Visual Paradigm AI tounikalnie szkolony na ustanowionych standardach modelowania, w tym UML 2.5, ArchiMate 3 i C4. Rozumiereguły semantyczne i strukturęza słowami, zapewniając, że relacje i konwencje nazewnictwa są technicznie poprawnymi projektami gotowymi do budowy.
C. Specjalistyczna analiza oparta na krokach
Aby zlikwidować lukę między wymaganiami a projektem, ekosystem oferuje systematyczne aplikacje:
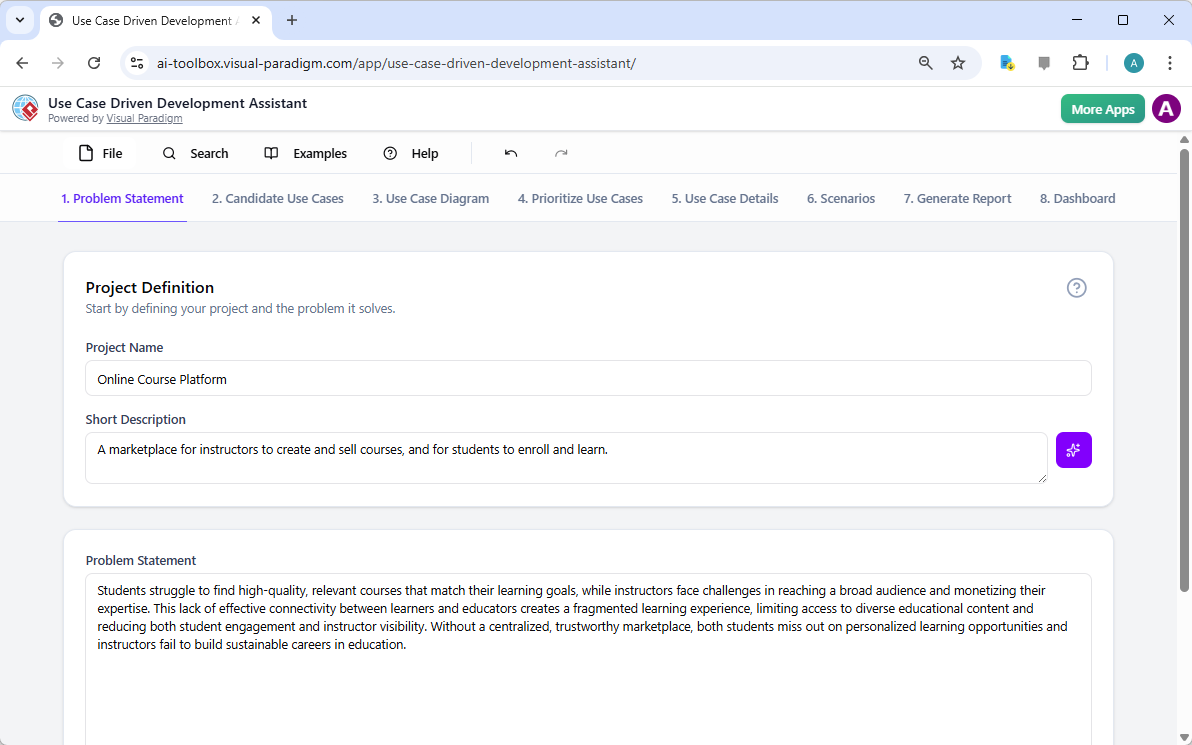
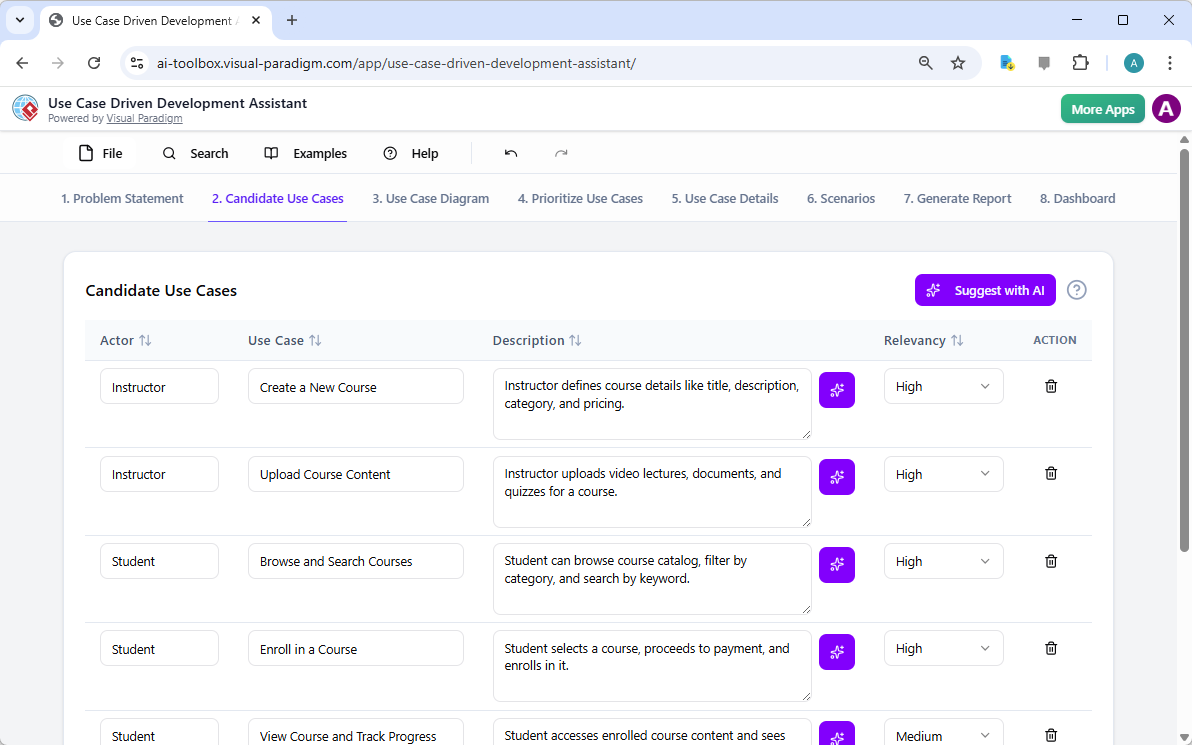
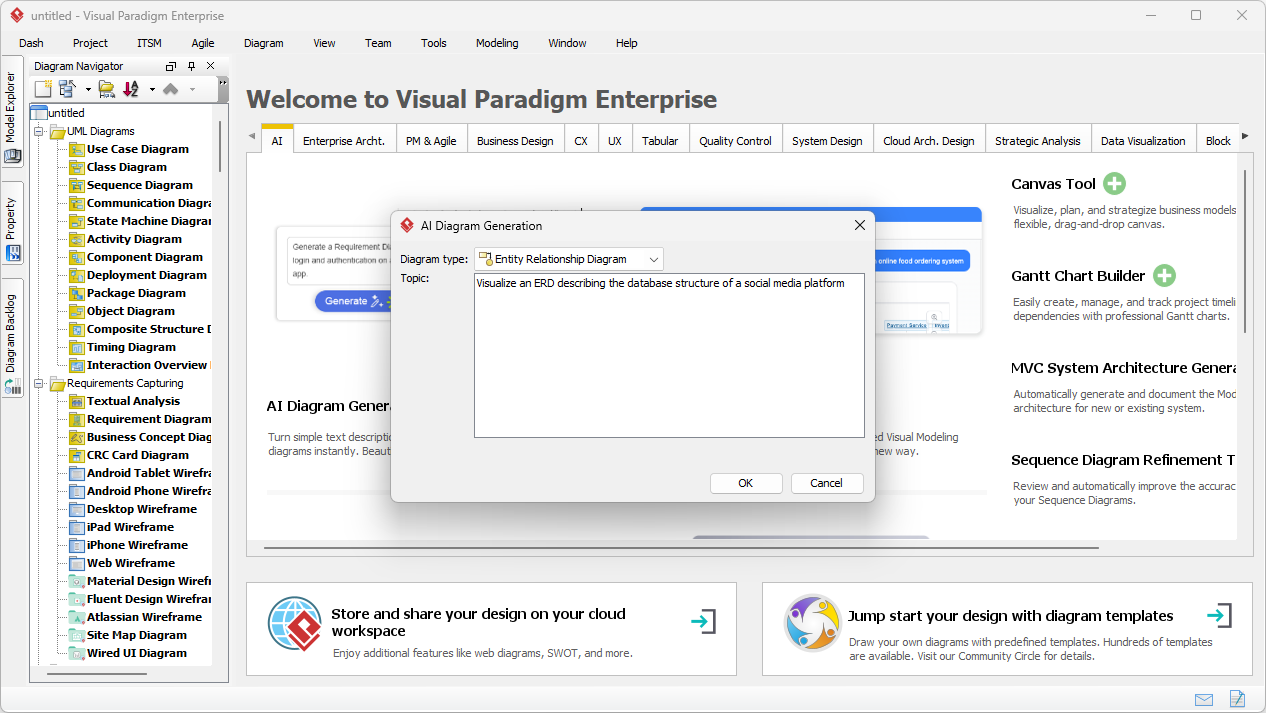
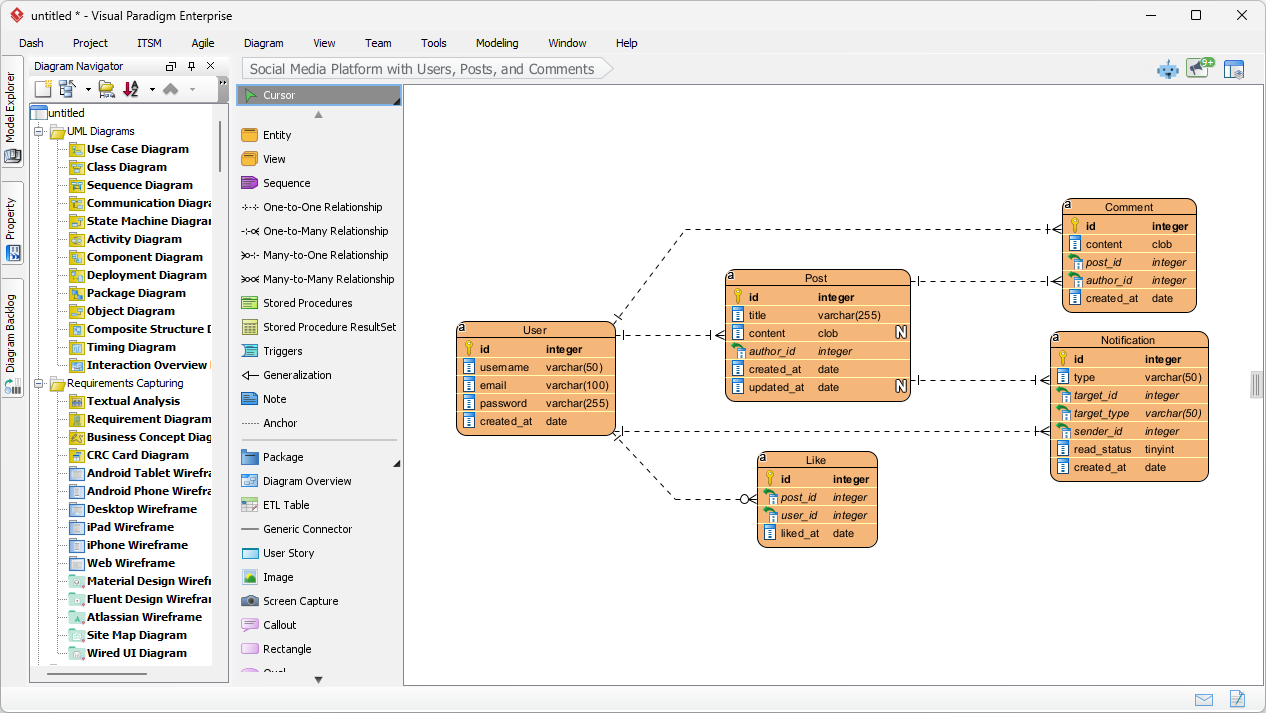
- Analiza tekstowa z wykorzystaniem AI:Automatycznie wyodrębniakandydatów do klas dziedziny, atrybutów i relacjiz nieuporządkowanych opisów problemówprzednarysowaniem jednej linii.
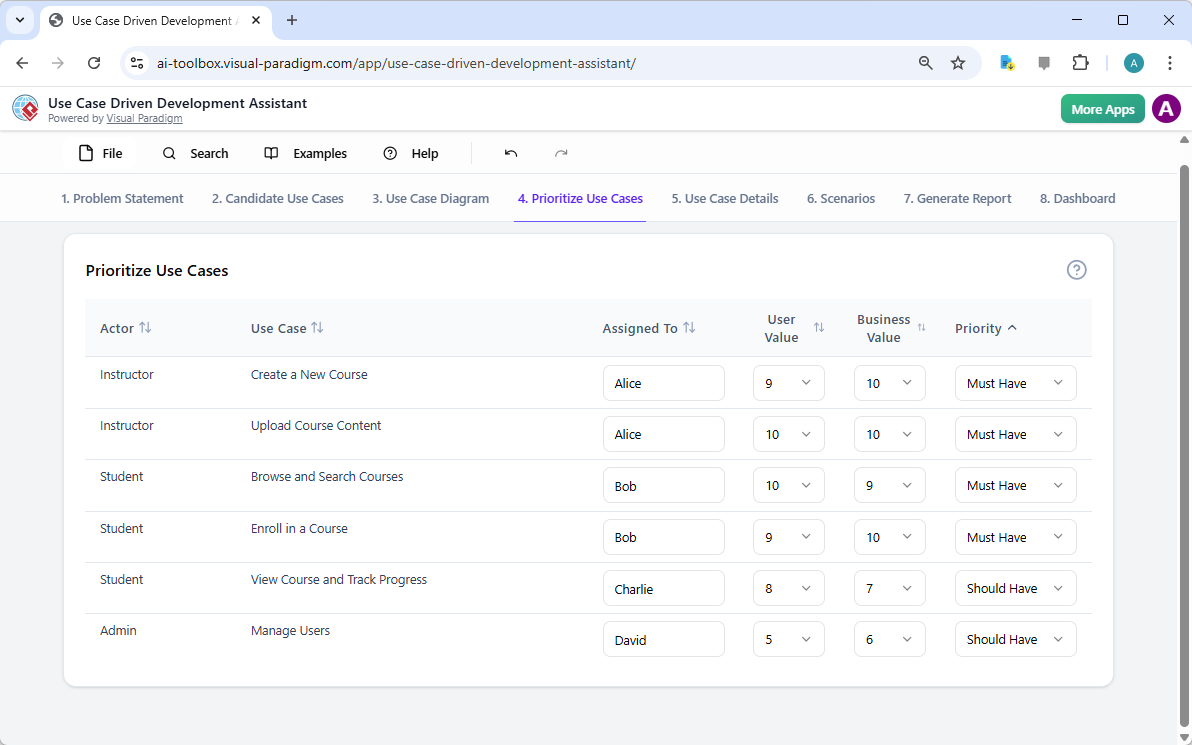
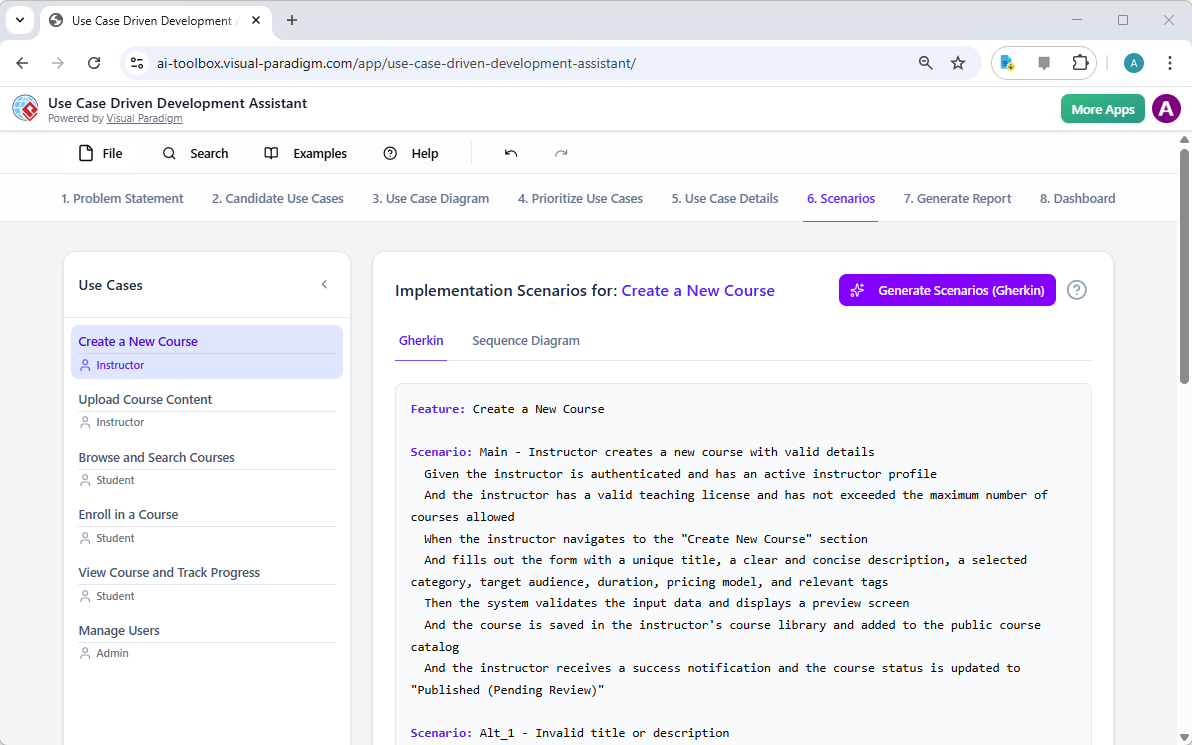
- 10-krokowy czarodziej AI:prowadzi użytkowników przez logiczny ciąg — od definiowania celu po identyfikację operacji — zapewniającweryfikację „człowiek w pętli”aby zapobiec błędom typowym dla generowania AI „w jednym kroku”.
D. Krytyka architektoniczna jako konsultant
Poza prostym generowaniem, AI działa jakosystematyczny asystent projektowy. Może analizować istniejące projekty w celu wykryciajedynych punktów awarii, luk w logice lub sugerować standardowe wzorce branżowe, takie jakMVC (Model-View-Controller)w celu poprawy jakości systemu.
E. Bezproblemowa integracja z ekosystemem
Modele generowane przez AI tofunkcjonalne artefakty, a nie izolowane obrazy. Mogą być importowane doVisual Paradigm Desktop lub Online zestawy do zaawansowanego edytowania, zarządzania wersjami i inżynieria kodu (w tym generowanie bazy danych i integracja z Hibernate ORM), zapewniając, że projekt wizualny bezpośrednio kieruje implementacją oprogramowania.
Wnioski: od dłutowania ręcznego do druku 3D
Tradycyjne modelowanie to jakdłutowanie marmurowej statuy, gdzie każdy ruch to wysokie ryzyko ręcznej pracy. W przeciwieństwie do tego,Visual Paradigm AI to jak korzystanie z zaawansowanego drukarka 3D: podajesz specyfikacje po prostu po języku angielskim, a system precyzyjnie buduje strukturę technicznie poprawną, pozwalając Ci skupić się nadecyzjach strategicznych projektowania. Poprzez połączenie strategii, modelowania biznesowego i projektowania technicznego w jednej platformie wspomaganej AI, Visual Paradigm eliminuje problem „pustej płótna” i zapewnia, że wszyscy uczestnicy pracują na tej samejpodstawie koncepcyjnej.
-
Samouczek: przekształcanie przypadków użycia w diagramy działań za pomocą Visual Paradigm z wykorzystaniem AI: Przewodnik krok po kroku dotyczący automatycznego przekształcania opisów przypadków użycia w szczegółowe diagramy działań przy użyciu AI Visual Paradigm.
-
Przyszłość modelowania: jak AI transformuje generowanie diagramów UML: Analiza, jak sztuczna inteligencja ułatwia i poprawia tworzenie diagramów UML w nowoczesnej inżynierii oprogramowania.
-
Wprowadzamy narzędzie analizy tekstowej z wykorzystaniem AI od Visual Paradigm: Nowe wydanie Visual Paradigm wprowadza analizę tekstową opartą na AI, aby tworzyć diagramy sprytniej i szybciej.
-
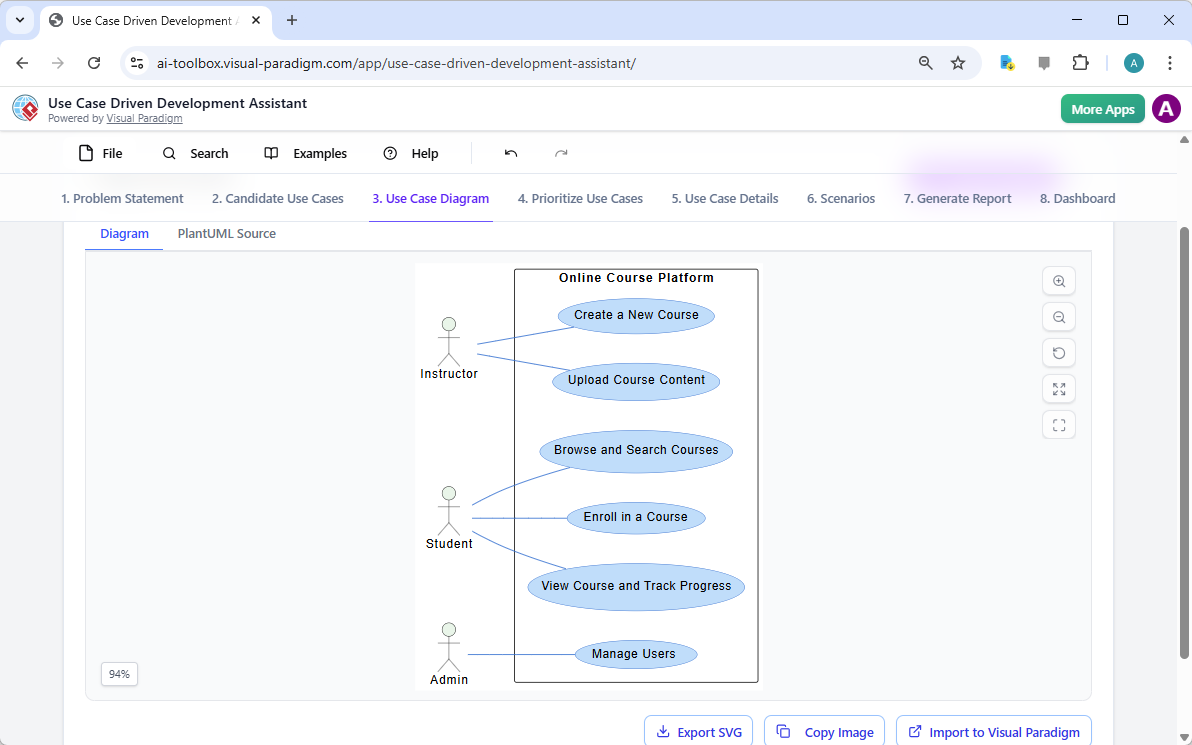
Przykład diagramu przypadków użycia z wykorzystaniem AI dla systemu domu inteligentnego: Diagram przypadków użycia wygenerowany przez AI, udostępniony przez społeczność, pokazujący interakcje użytkownika z systemem domu inteligentnego.
-
Narzędzie do doskonalenia diagramów przypadków użycia z wykorzystaniem AI od Visual Paradigm: Narzędzie AI, które poprawia diagramy przypadków użycia poprzez sugerowanie ulepszeń, identyfikację brakujących aktorów i optymalizację struktury.
-
Generator opisów przypadków użycia z wykorzystaniem AI od Visual Paradigm: Narzędzie wspomagane AI, które generuje szczegółowe opisy przypadków użycia na podstawie wprowadzonych danych użytkownika, aby przyspieszyć dokumentację.
-
Opanuj diagramy przypadków użycia sterowane AI: krótki samouczek: Zwięzły samouczek dotyczący korzystania z AI do tworzenia, doskonalenia i automatyzacji rozwoju diagramów przypadków użycia.
-
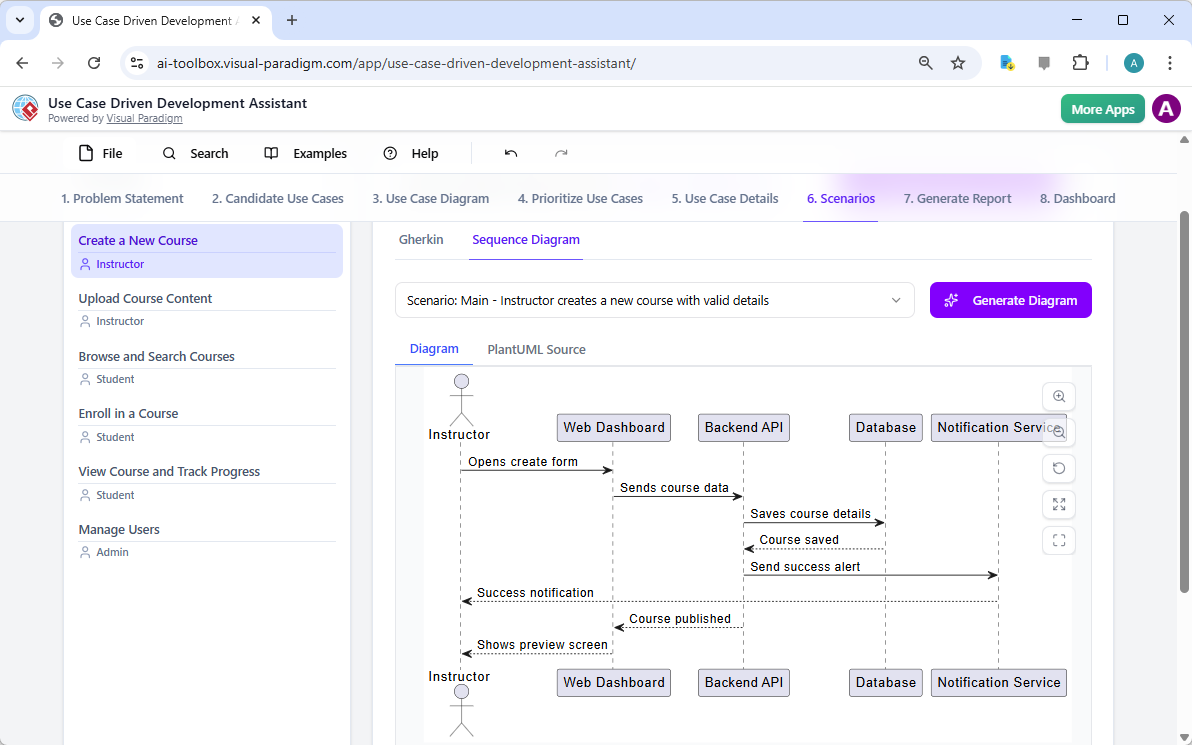
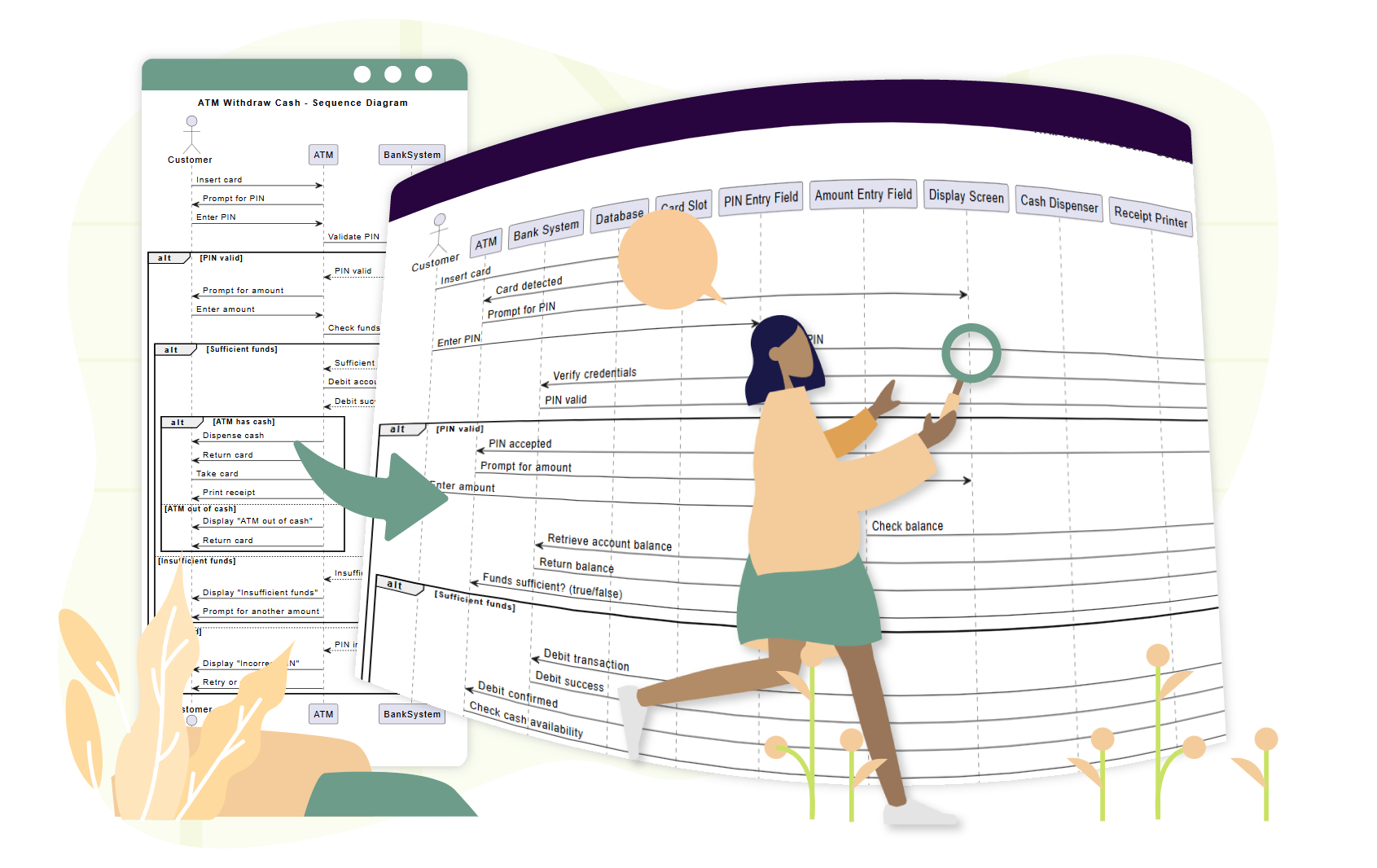
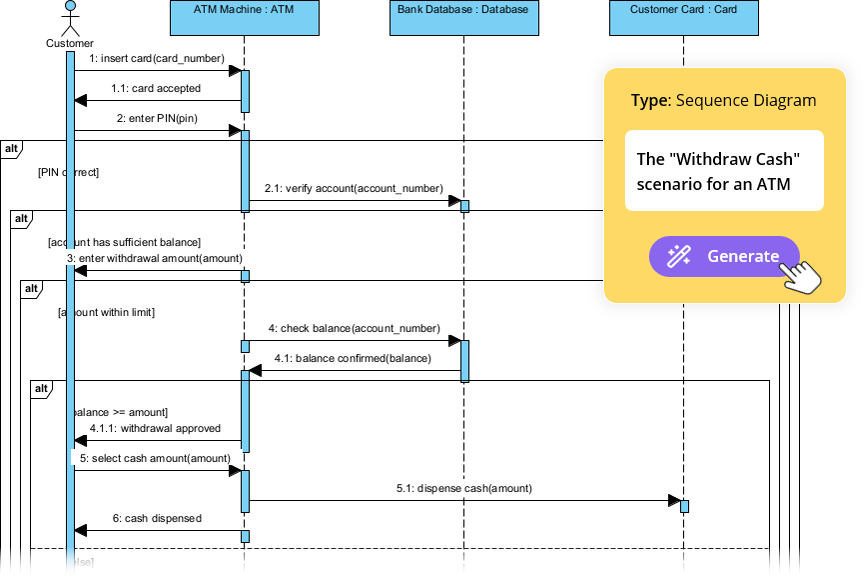
Narzędzie do doskonalenia diagramów sekwencji z wykorzystaniem AI | Visual Paradigm: Narzędzie AI, które poprawia diagramy sekwencji poprzez inteligentne sugestie zwiększające dokładność i przejrzystość.
-
Kompletny przewodnik: korzystanie z narzędzia do doskonalenia diagramów sekwencji z AI: Przewodnik krok po kroku dotyczący korzystania z narzędzia do doskonalenia diagramów sekwencji z AI w celu poprawy jakości i spójności diagramów.
-
Uprość złożone przepływy pracy za pomocą narzędzia do diagramów sekwencji z AI firmy Visual Paradigm: Narzędzie z AI firmy Visual Paradigm ułatwia modelowanie złożonych interakcji systemów i przepływów pracy.
-
Narzędzie do doskonalenia diagramów sekwencji z AI | Visual Paradigm: Doskonalenie diagramów sekwencji z wykorzystaniem AI w celu poprawy czytelności, poprawności i spójności.
-
Przewodnik dla początkujących: stwórz swój pierwszy profesjonalny diagram sekwencji w kilka minut: Przyjazny dla początkujących przewodnik tworzenia profesjonalnych diagramów sekwencji w szybki sposób za pomocą czatbotu z AI firmy Visual Paradigm.
-
Od prostych do zaawansowanych: narzędzie do doskonalenia diagramów sekwencji z AI: Narzędzie z AI firmy Visual Paradigm przekształca podstawowe diagramy sekwencji w wy refined, dokładne modele przy minimalnym wprowadzeniu danych.
-
Doskonalenie diagramów sekwencji z AI: inteligentny sposób projektowania systemów: AI poprawia projektowanie diagramów sekwencji poprzez inteligentne doskonalenie modeli w celu zwiększenia przejrzystości i dokładności systemu.