The Era of AI in Software Architecture
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software engineering and enterprise architecture, the ability to transform abstract requirements into precise, actionable designs is a critical skill. General-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Claude have revolutionized how we brainstorm and generate text. However, when it comes to professional visual modeling, these tools often fall short. They produce what can best be described as “sketches”—rough approximations that lack the rigor of engineered blueprints.
This comprehensive guide explores the significant gap between casual AI diagramming and professional needs, and how the Visual Paradigm (VP) AI ecosystem bridges this divide by delivering standards-aware, persistent, and iterative diagramming capabilities.
1. The “Sketch Artist” Problem: Limitations of Casual AI LLMs
Casual AI tools treat diagramming primarily as an extension of text generation. When prompted to create a diagram, they typically output code in formats like Mermaid or PlantUML. While impressive for quick visualizations, this approach lacks the depth required for professional engineering contexts.
No Native Rendering or Editing Engine
LLMs generate text-based syntax (e.g., Mermaid flowchart code) but offer no built-in viewer or editor for high-quality vector graphics (SVG). Users are forced to paste code into external renderers, instantly losing interactivity. If a change is needed, the user must request a full regeneration of the code, often resulting in a completely different layout.
Semantic Inaccuracies and Standard Violations
Generic models frequently misinterpret strict modeling standards like UML or ArchiMate. Common errors include:
- Confusing aggregation (shared ownership) with composition (exclusive ownership).
- Drawing invalid inheritance arrows or relationship directions.
- Creating bidirectional associations where unidirectional ones are technically correct.
While the results may look aesthetically pleasing, they fail as engineering artifacts because they do not adhere to the semantic rules that govern system architecture.
Lack of Persistent State
Perhaps the most frustrating limitation is the lack of memory regarding visual structure. Each prompt regenerates the diagram from scratch. For example, asking an LLM to “add error handling to this sequence diagram” often breaks the existing layout, disconnects connectors, or forgets prior elements entirely. There is no persistent state to track the evolution of the model.
2. Real-World Risks of Relying on Casual AI Diagramming
Using general LLMs for serious architectural work introduces risks that can undermine project quality and timeline.
The Design-Implementation Gap
Vague or semantically incorrect visuals lead to misaligned code. Development teams waste valuable time in meetings trying to clarify the intent behind a diagram that lacks precision. A “pretty picture” that is technically wrong is worse than no diagram at all.
Syntax Dependency
Ironically, using “AI-assisted” tools like ChatGPT for diagrams often requires the user to learn specialized syntax (Mermaid/PlantUML) to manually fix errors. This creates an expertise barrier that negates the efficiency gains of using AI.
Workflow Isolation
Diagrams generated by LLMs are static images or code snippets. They are disconnected from version control, collaboration platforms, and downstream tasks like code generation or database schema creation. They exist in a silo, unable to evolve with the project.
3. How Visual Paradigm AI Delivers Professional-Grade Modeling
Visual Paradigm has transformed diagramming into a conversational, standards-driven, and integrated process. Unlike text-based LLMs, VP AI understands the underlying meta-models of UML 2.5,ArchiMate3, C4, BPMN, and SysML, producing compliant and editable models.
Persistent Structure with “Diagram Touch-Up” Technology
Visual Paradigm maintains diagrams as living objects rather than disposable scripts. Users can issue natural language commands to update specific parts of a diagram without triggering a full regeneration.
For example, a user can command: “Add a two-factor authentication step after login” or “Rename the Customer actor to User.” The system instantly adjusts the layout, connectors, and semantics while preserving the integrity of the rest of the model. This eliminates the broken links and layout chaos common in casual tools.
Standards-Compliant Intelligence
Trained on formal notations, VP AI actively enforces rules, ensuring:
- Correct multiplicity in associations.
- Proper use of stereotypes.
- Valid ArchiMate viewpoints (e.g., Capability Maps, Technology Usage).
This results in technically sound blueprints that can be trusted by developers and architects alike.
4. Bridging Requirements to Design: Advanced AI Workflows
Visual Paradigm goes beyond simple generation by providing structured applications that guide users from abstract ideas to concrete designs.
AI-Powered Textual Analysis
This feature analyzes unstructured text—such as requirements documents or user stories—to extract candidate classes, attributes, operations, and relationships. It can generate an initial class diagram automatically based on the analysis.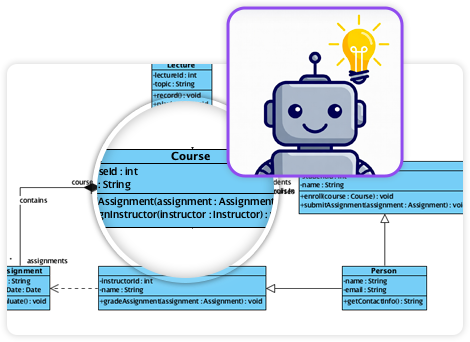
Example Scenario: Input a description like “An e-commerce platform allows customers to browse products, add to cart, checkout with payment gateway, and track orders.” The AI identifies classes (Customer, Product, Cart, Order, PaymentGateway), attributes (price, quantity), and associations (Customer places Order).
The 10-Step AI Wizard
For complex diagrams like UML Class models, VP offers a guided wizard. This tool leads users through a logical progression: Define Purpose → Scope → Classes → Attributes → Relationships → Operations → Review → Generate. This human-in-the-loop approach validates the design at every step, preventing the “one-shot” errors common in prompt-based generation.
5. Comparison: Casual LLMs vs. Visual Paradigm AI
| Feature | Casual LLMs (ChatGPT, Claude) | Visual Paradigm AI |
|---|---|---|
| Output Format | Text-based code (Mermaid, PlantUML) | Editable Native Models & Vector Graphics |
| State & Persistence | None (Regenerates from scratch) | Persistent (Supports incremental updates) |
| Standards Compliance | Low (Hallucinates syntax/rules) | High (Enforces UML/BPMN/ArchiMate rules) |
| Editability | Requires manual code edits | Conversational UI & Drag-and-Drop |
| Integration | Isolated Snippets | Full Lifecycle (Code Gen, DB Schema, Teamwork) |
Conclusion: From Manual Chiseling to Intelligent Engineering
Traditional diagramming often feels like chiseling marble—slow, error-prone, and irreversible. Casual AI LLMs improved the speed of sketching but remain limited by their inability to produce consistent, persistent, and engineered visuals.
Visual Paradigm AI acts like a high-precision 3D printer for software architecture. It allows users to input plain English specifications and receive standards-compliant, editable structures. It supports conversational iteration and drives implementation directly through code generation and database integration.
For software architects, enterprise teams, and developers tired of regenerating broken Mermaid snippets, Visual Paradigm represents the next evolution: intelligent modeling that respects standards, preserves intent, and accelerates delivery.
-
AI-Powered Visual Modeling and Design Solutions by Visual Paradigm: AI-driven tools for visual modeling, diagramming, and software design that accelerate development workflows.
-
Visual Paradigm – All-in-One Visual Development Platform: A unified platform for visual modeling, software and business process design, and AI-powered development tools.
-
AI Chatbot Feature – Intelligent Assistance for Visual Paradigm Users: AI-powered chatbot that delivers instant guidance, automates tasks, and boosts productivity in Visual Paradigm.
-
Visual Paradigm Chat – AI-Powered Interactive Design Assistant: An interactive AI interface for generating diagrams, writing code, and solving design challenges in real time.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: AI analyzes text documents to automatically generate UML, BPMN, and ERD diagrams for faster modeling and documentation.
-
Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot Enhances Multi-Language Support …: AI chatbot supports multiple languages, enabling seamless diagram generation in Spanish, French, Chinese, and more.
-
AI -Powered BI Analytics by Visual Paradigm – ArchiMetric: Start using AI-powered BI analytics in under a minute—no installation or signup required for most features.










