In the modern era of software engineering, bridging the gap between abstract business requirements and concrete technical implementation remains one of the most significant challenges. The Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler addresses this by transforming database design into a structured, automated engineering process. By leveraging artificial intelligence, this tool facilitates the journey from plain language concepts to production-ready SQL schemas, emphasizing “architectural maturity” at every stage of the lifecycle.
The Core Philosophy: A 7-Step Guided Workflow
Unlike traditional modeling tools that require manual drag-and-drop from the start, the AI DB Modeler utilizes a linear, seven-step workflow. This process ensures that data integrity, relationship logic, and physical constraints are handled systematically.
Phase 1: Requirement Analysis and Conceptual Modeling
The design process begins with understanding the user’s intent. This phase focuses on high-level abstraction before diving into technical details.
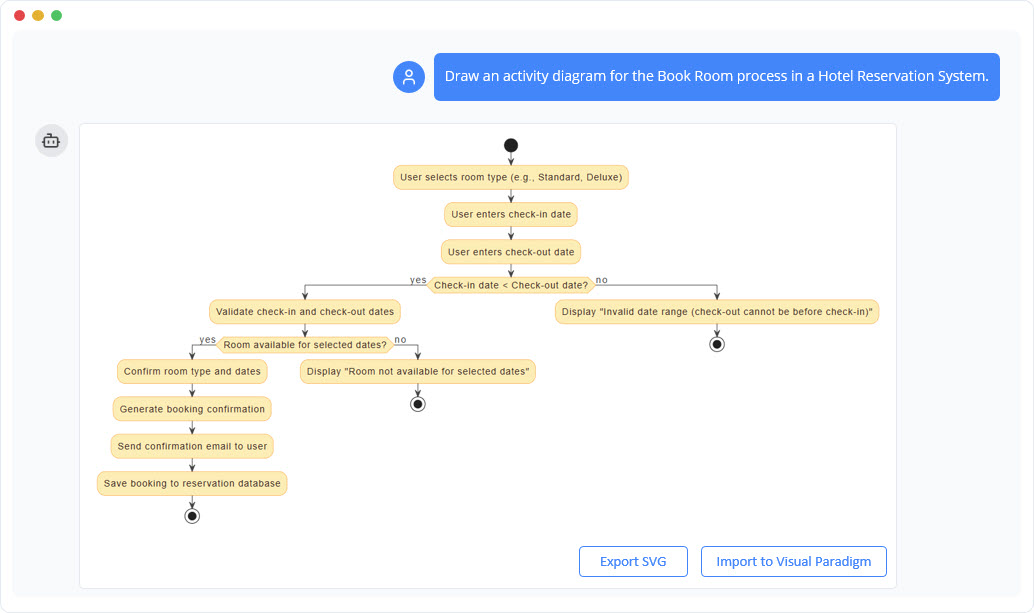
- Step 1: Problem Input: Users interact with the system using natural language. By inputting a simple description, such as “Design a hospital management system,” the AI analyzes the request and expands it into a comprehensive set of technical requirements, ensuring no critical functionality is overlooked.
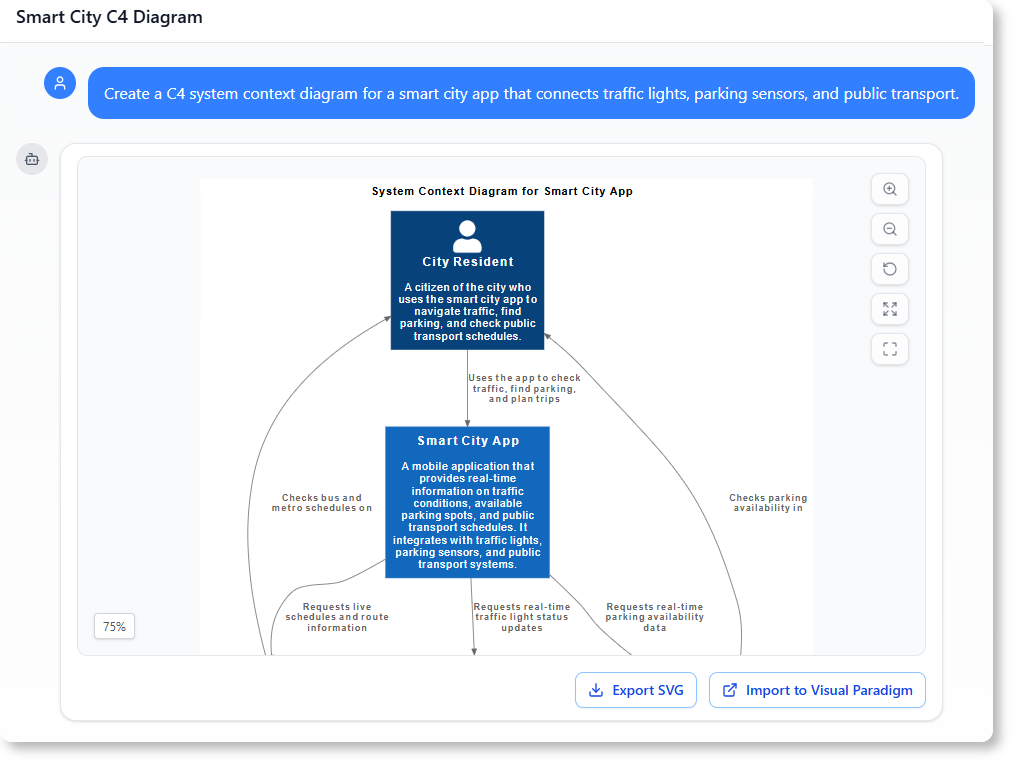
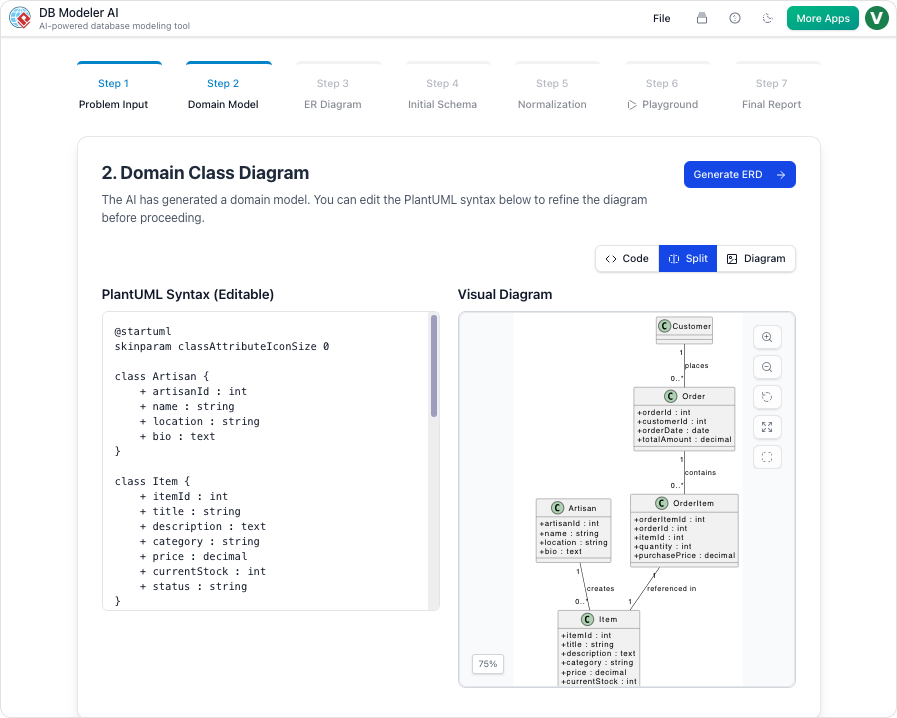
- Step 2: Domain Class Diagram: Once requirements are established, the AI translates them into a visual blueprint known as the Domain Model Diagram. This is rendered using editable PlantUML syntax, which allows architects to visualize objects and attributes instantly without the need for manual drawing.
Phase 2: Logical and Physical Design Automation
Moving from concept to execution requires rigorous structural definition. The tool automates the “heavy lifting” of database architecture during this phase.
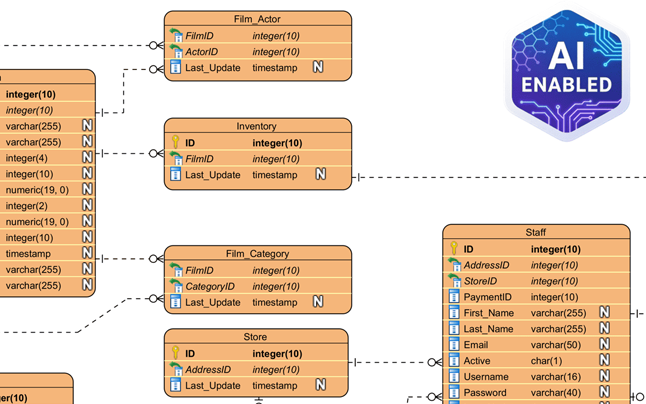
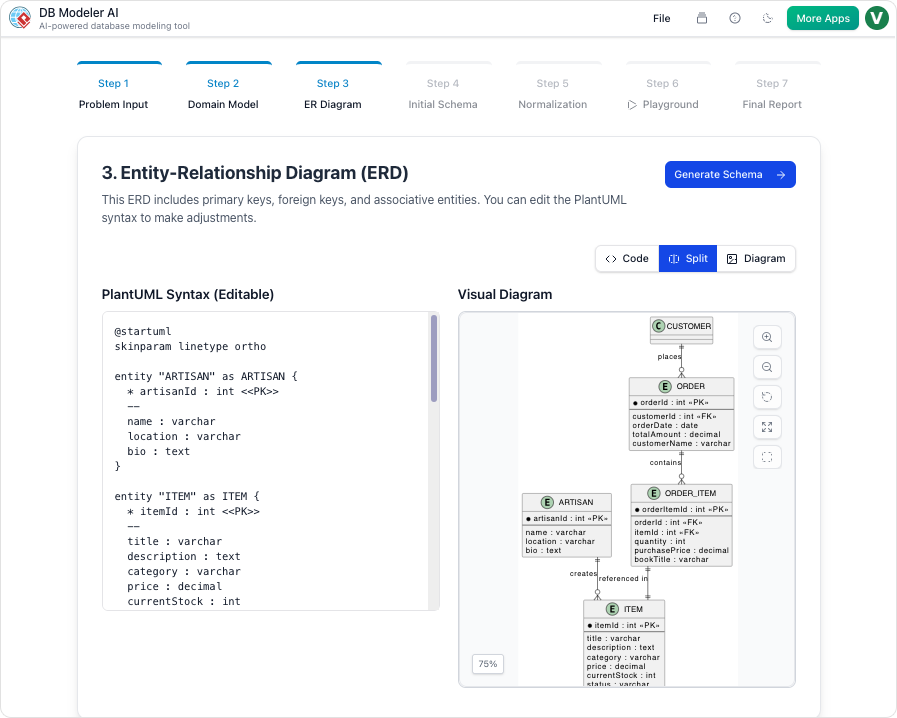
- Step 3: ER Diagram Creation: The conceptual model is converted into a database-specific Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD). Crucially, the AI automatically defines the relationships between entities, handling Primary Keys (PKs), Foreign Keys (FKs), and complex cardinalities (such as 1:1, 1:N, or M:N) to ensure referential integrity.
- Step 4: Initial Schema Generation: With the logical structure in place, the tool translates the visual ERD into executable SQL DDL statements. These scripts are compatible with PostgreSQL and include all necessary table definitions, column types, and constraints.
Phase 3: Optimization and Educational Guidance
One of the standout features of the AI DB Modeler is its approach to database normalization, a process often considered complex and error-prone for human designers.
- Step 5: Intelligent Normalization: The AI acts as an expert DBA, guiding the schema through First (1NF), Second (2NF), and Third Normal Forms (3NF). This process eliminates data redundancy and anomalies.
- Educational Rationales: The tool does more than just fix the schema; it educates the user. It provides detailed explanations for every structural change made during the normalization process, offering transparency on how data integrity is being preserved.
Phase 4: Validation and Documentation
Before any code is deployed to a production environment, the design must be rigorously tested and documented.
- Step 6: Interactive SQL Playground: The tool features an in-browser SQL client for immediate validation. To make this testing meaningful, the environment is automatically seeded with realistic, AI-generated sample data. This allows users to run queries, verify performance, and test logic without installing local software.
- Step 7: Final Report and Export: The lifecycle concludes with the generation of a professional report. Available in PDF, JSON, or Markdown formats, this documentation includes diagrams, SQL scripts, and design rationales, making it ideal for project hand-offs or archiving.
Advanced Assistance Features
Beyond the core workflow, the platform includes several auxiliary features designed to streamline the user experience and enhance collaboration.
- Conversational Refinement: Users can utilize an integrated AI Chatbot to modify diagrams using natural language commands. Instructions like “Add payment gateway” or “Rename Customer to Buyer” are executed instantly.
- Model Traceability: The platform ensures consistency across the entire project. It maintains automatic synchronization between conceptual, logical, and physical models, so a change at the abstract level is immediately reflected in the SQL code.
- Multi-Language Support: To support global teams, the AI is capable of processing prompts and generating diagram content in over 40 languages.
Understanding the Process: An Analogy
To fully grasp the capabilities of the AI DB Modeler, it is helpful to visualize it as an automated car factory.
When you provide a high-level description of the car you want, you are completing Step 1. The AI then draws an artist’s sketch of the vehicle (Step 2) before engineering detailed mechanical blueprints that show how every part connects (Step 3). Next, it writes the manufacturing code for the assembly robots (Step 4) and fine-tunes the engine to ensure maximum fuel efficiency (Step 5). Finally, before the car is built, the system allows you to take it for a “virtual test drive” with simulated passengers to ensure it runs perfectly (Step 6).
Conclusion
The Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler represents a shift in how databases are architected. By automating the transition from requirements to normalized SQL schemas, it reduces the technical barrier to entry while ensuring that the final output adheres to strict industry standards for data integrity and performance.
-
AI-Powered Visual Modeling and Design Solutions by Visual Paradigm: Explore cutting-edge AI-driven tools for visual modeling, diagramming, and software design, enabling faster, smarter development workflows.
-
Visual Paradigm – All-in-One Visual Development Platform: A comprehensive platform for visual modeling, software design, business process modeling, and AI-powered development tools.
-
AI Chatbot Feature – Intelligent Assistance for Visual Paradigm Users: Leverage AI-powered chatbot functionality to get instant guidance, automate tasks, and enhance productivity within Visual Paradigm.
-
Visual Paradigm Chat – AI-Powered Interactive Design Assistant: An interactive AI chat interface that helps users generate diagrams, write code, and solve design challenges in real time.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: Use AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML, BPMN, and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
-
Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot Enhances Multi-Language Support …: 7 hours ago · Discover the latest updates to Visual Paradigm ‘s AI -Powered visual modeling software, including multi-language UI and improved chat content localization. Experience seamless AI diagram generation in languages like Spanish, French, Chinese, and more with our AI chatbot for UML and other diagrams.
-
AI -Powered BI Analytics by Visual Paradigm – ArchiMetric: Get started in under a minute at ai . visual – paradigm .com/tool/ ai -powered-bi-analytics. No installation, no signup required for most features.
-
Discover the Power of Visual Paradigm ’s AI -Powered… – Visualize AI: While tools like Google’s AI Image Translator (via Google Lens and Google Translate) offer convenience, Visual Paradigm ’s AI -Powered Image Translator takes the lead with…
-
AI Chatbot for Diagramming: How It Works with Visual Paradigm: The Visual Paradigm AI chatbot is an AI -powered modeling assistant that turns natural language into diagrams. It doesn’t require users to learn specific modeling standards or syntax.
-
AI Brainstorming Features – Visual Paradigm: Discover how Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered brainstorming tools enhance idea generation with intelligent suggestions and collaborative workflows.
-
AI Brainstorming Tool – Visual Paradigm AI: Use the AI Brainstorming tool from Visual Paradigm to rapidly generate and organize ideas with AI-driven insights and smart templates.
-
AI-Powered Use Case Diagram Refinement Tool – Smart Diagram Enhancement: Leverage AI to automatically refine and optimize your use case diagrams for clarity, consistency, and completeness.
-
Convert Use Case to Activity Diagram – AI-Powered Transformation: Automatically convert use case diagrams into detailed activity diagrams using AI to visualize system workflows.
-
AI-Assisted UML Class Diagram Generator – Visual Paradigm: An interactive, step-by-step tool to help users create UML class diagrams with AI-powered suggestions, validation, PlantUML export, and design analysis.
-
Mastering UML Activity Diagrams with AI | Visual Paradigm Blog: A blog post exploring how AI-powered features in Visual Paradigm enhance the creation and optimization of UML activity diagrams for developers and analysts.
-
Revolutionize Your Slides: Meet Visual Paradigm’s AI Markdown Presentation Maker!: 9 Dec 2025 · Introducing Visual Paradigm’s AI Markdown Presentation Maker – the game-changing tool that turns your raw ideas into stunning, animated …
-
Lumina AI: Generate AI-Powered Video Slideshows Instantly: Create dynamic video presentations from text using AI, perfect for storytelling, marketing, and rapid content creation.
-
Lumina AI Slideshow Maker: Create Stunning Presentations with AI: Use artificial intelligence to generate professional-quality slides from simple text input, saving time and enhancing creativity.
-
Illumy AI Slideshow Maker: Instant AI-Powered Presentation Creation: Generate visually rich, professional slides in seconds using AI, ideal for marketers, educators, and business professionals.
-
AI Animated Presentation Studio: Create Dynamic, Animated Slides with Ease: Design engaging, animated presentations with AI assistance, combining storytelling with motion and visual effects.
-
How to Structure Your Jira Backlog Instantly with Agilien AI: Learn how Agilien AI automates Jira backlog structuring by analyzing user stories and generating well-organized sprints and epics.
-
Agilien AI-Powered Jira Backlog Planner – Visual Paradigm: Automate and enhance your Jira backlog planning with Agilien AI, which intelligently structures user stories and epics for efficient sprint planning.
-
How to Create Stunning Animated Presentations with Visual Paradigm’s AI Markdown Presentation Maker: A step-by-step guide on leveraging AI-powered Markdown tools within Visual Paradigm to design visually engaging and dynamic presentations effortlessly.
-
Introducing AI Animated Presentation Studio – A New Era in Visual Storytelling: Visual Paradigm launches its AI Animated Presentation Studio, enabling users to generate dynamic, AI-enhanced presentations with minimal effort.