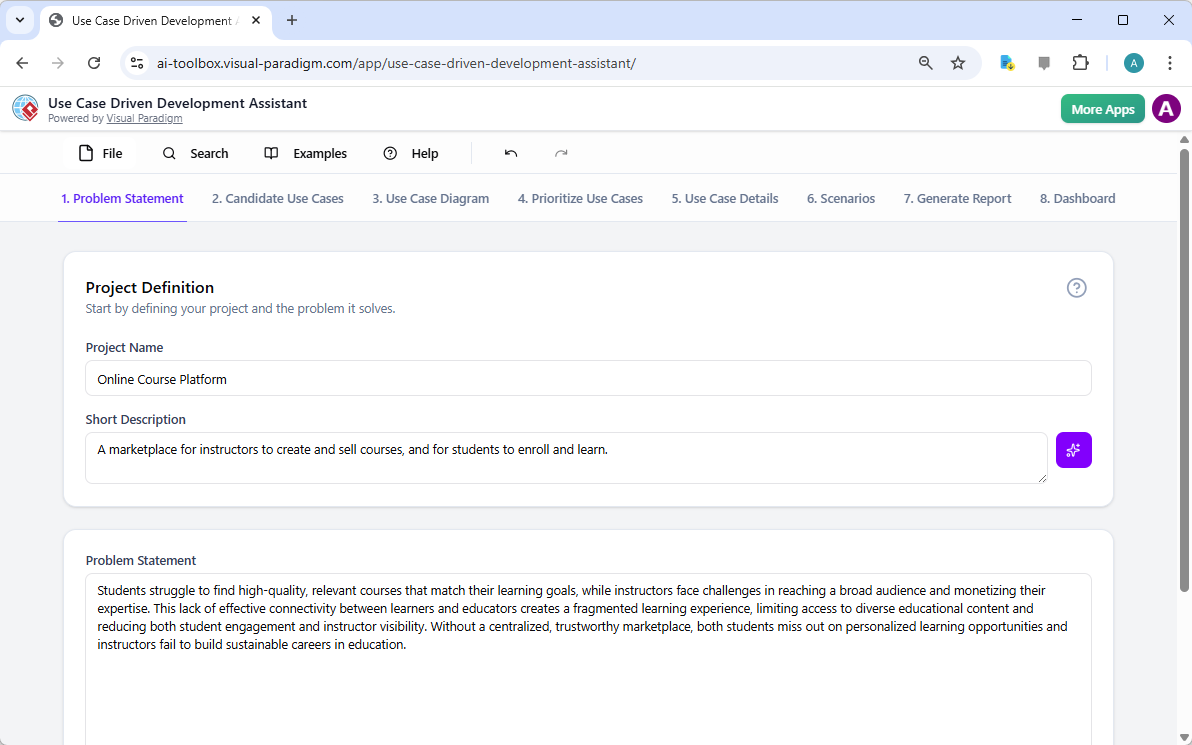
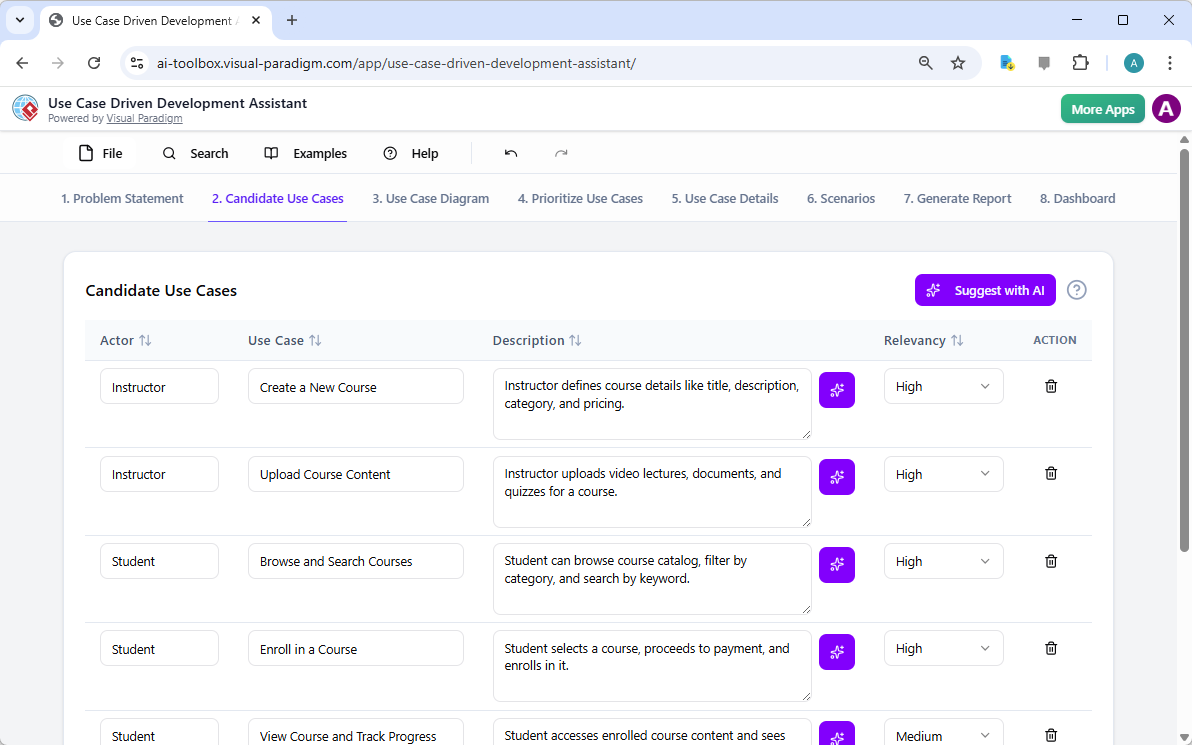
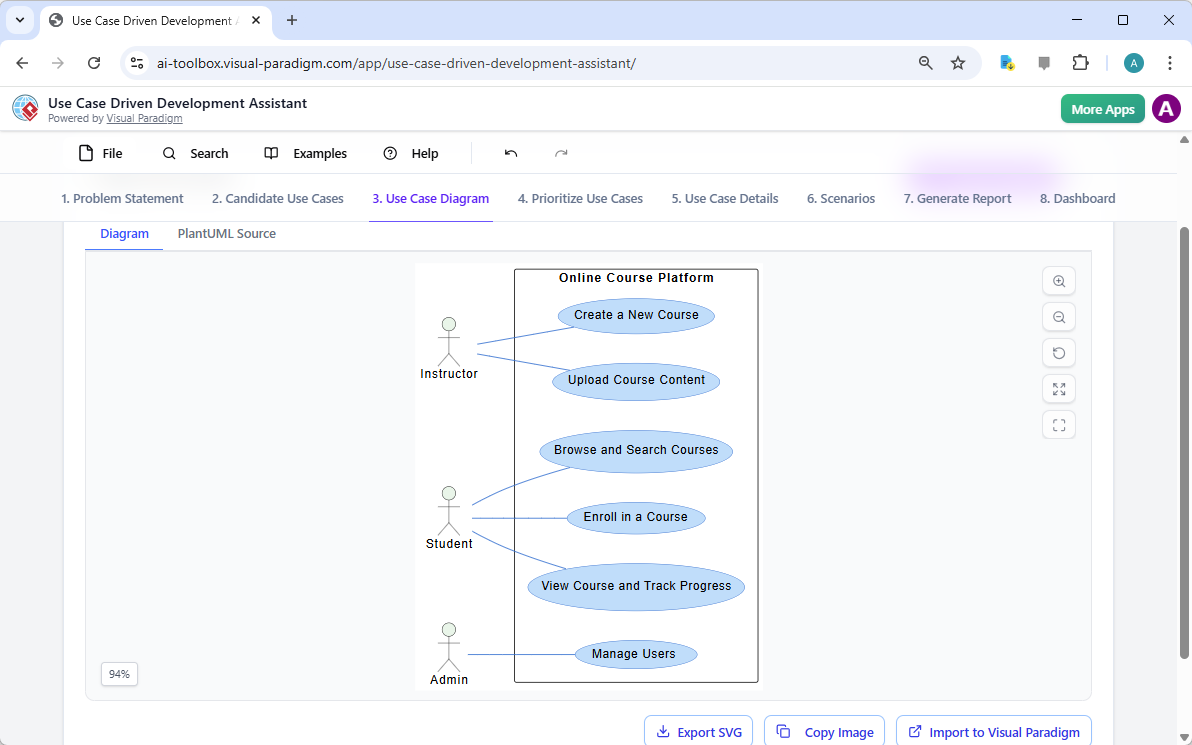
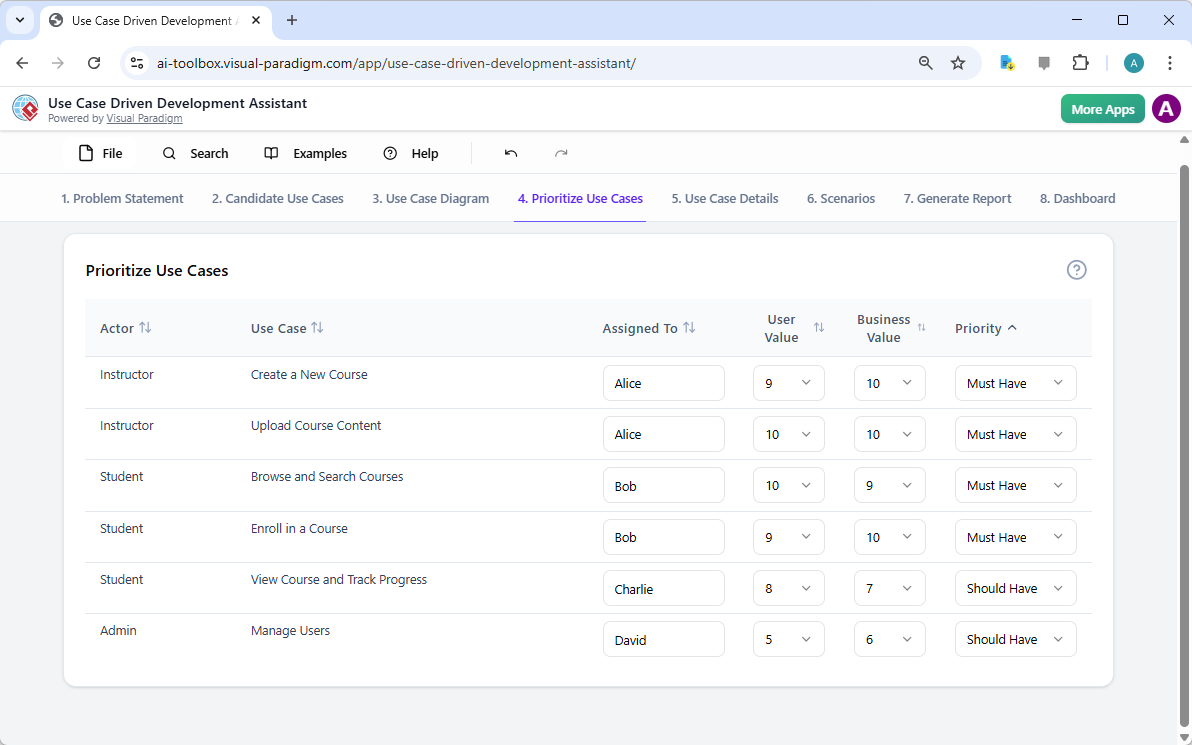
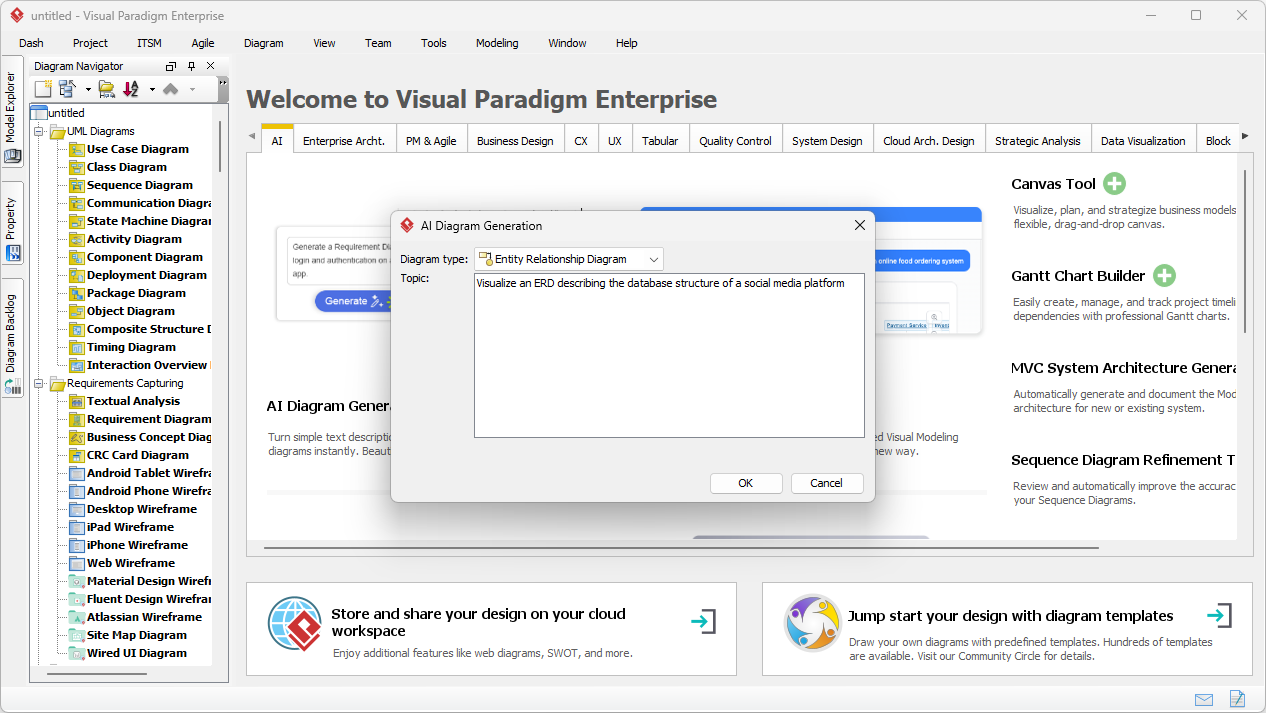
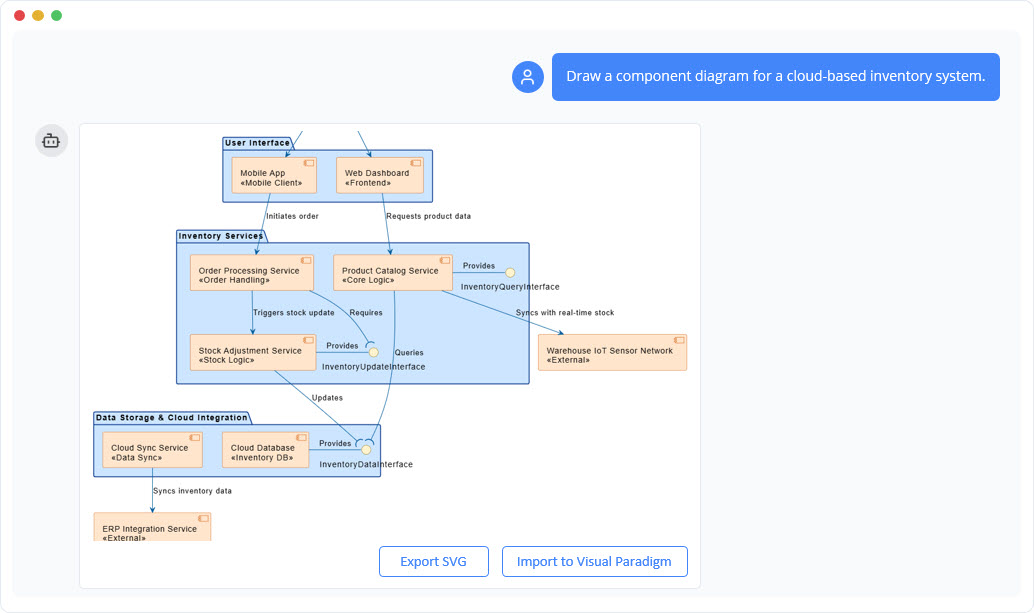
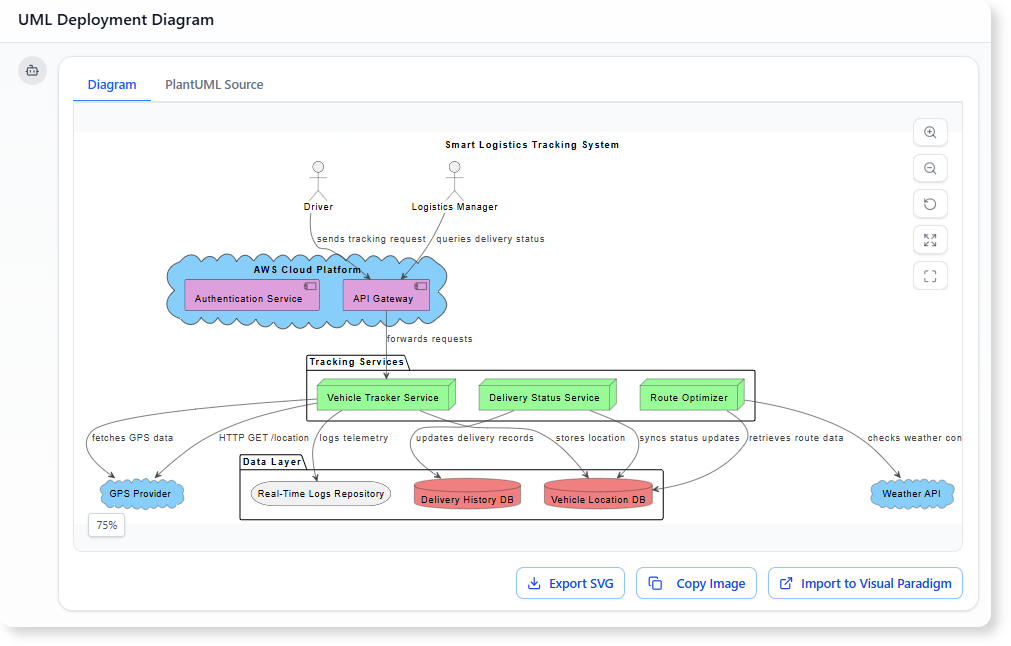
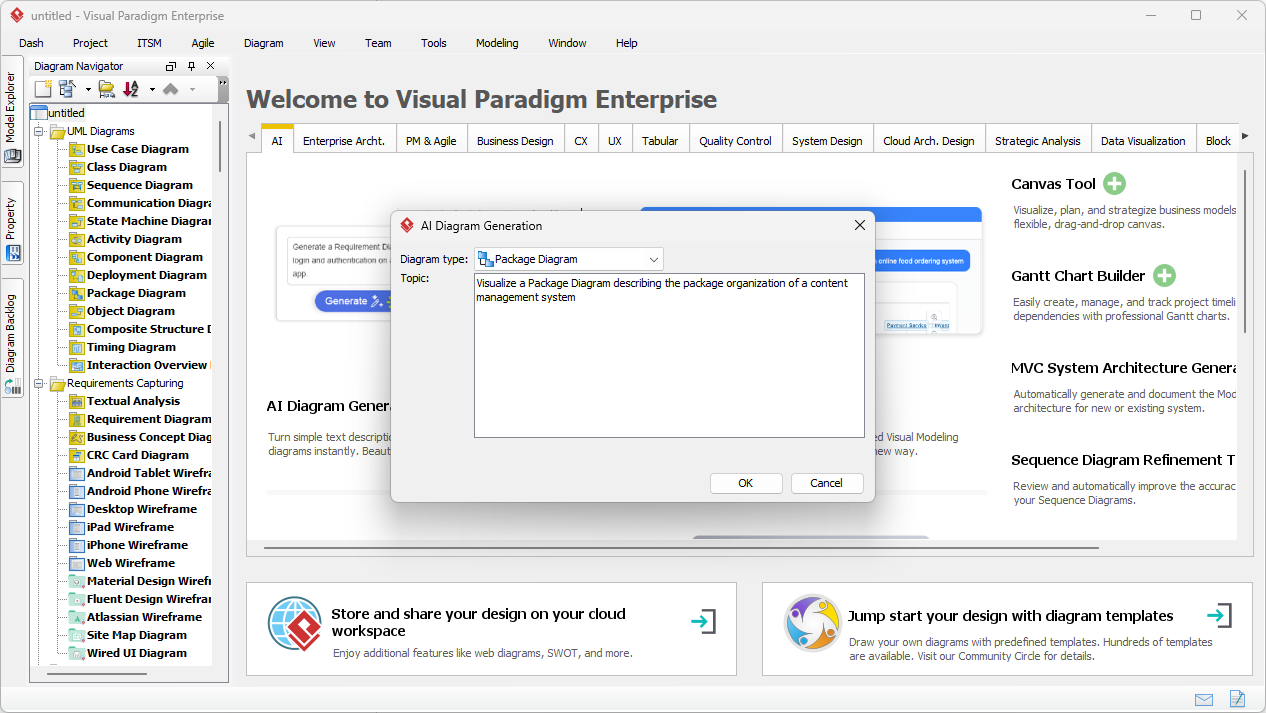
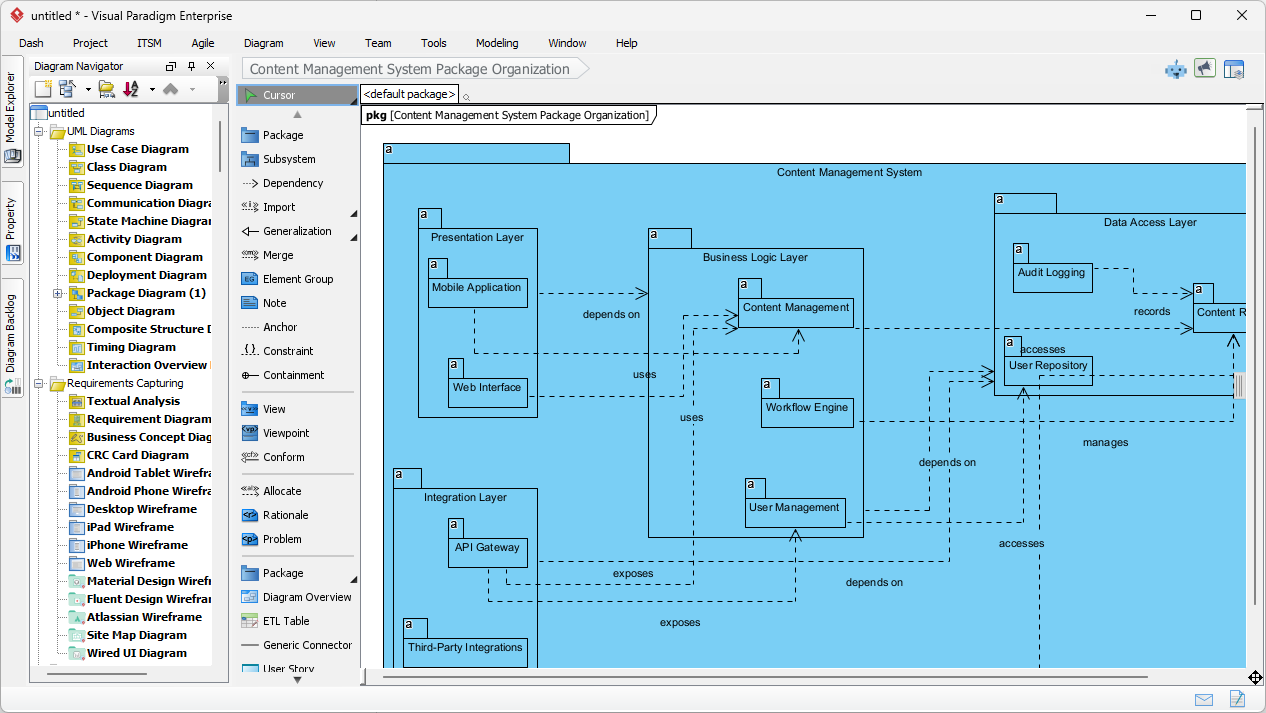
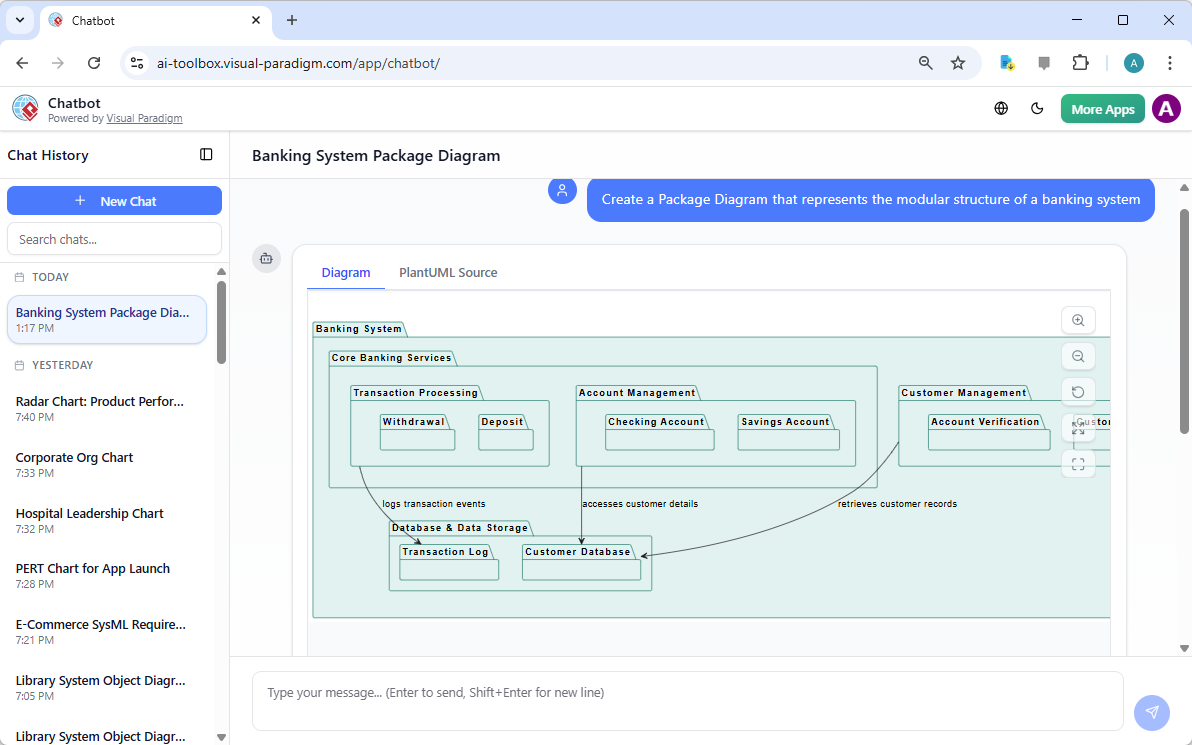
在當今快速變化的軟體工程與企業架構領域,將抽象需求轉化為精確且可執行的設計仍然具有挑戰性。通用型大語言模型(LLM)擅長腦力激盪與文字生成,但在專業視覺建模方面卻表現不佳。它們產生的僅是「草圖」,而非工程化的藍圖。視覺範式(Visual Paradigm)的AI驅動生態系統改變了這一現狀,提供符合標準、具備持久性與迭代性的圖示繪製功能,從構想到實作加速架構工作流程。
1. 「草圖畫家」問題:隨意AI大語言模型的限制
隨意的AI工具(例如 ChatGPT、Claude)將圖示繪製視為文字生成的延伸。它們輸出以如Mermaid 或 PlantUML等格式的程式碼,但在專業用途上缺乏深度。
主要限制包括:
- 缺乏原生渲染或編輯引擎LLM產生的是基於文字的語法(例如 Mermaid 流程圖程式碼),但並未提供內建的檢視器或編輯器來呈現高品質的向量圖形(SVG)。使用者需將程式碼貼入外部渲染工具,導致失去互動性。任何修改都需重新完整生成。
- 語義錯誤與標準違規通用模型會誤解 UML/ArchiMate 的概念。例如,它們會混淆聚合(共用擁有權)與組合(獨佔擁有權),或繪製無效的繼承箭頭。結果看似美觀,卻無法作為工程實體——例如,類圖可能顯示雙向關聯,而實際上應為單向關聯。
- 缺乏持久狀態與增量更新每次提示都需從頭重新生成圖示。例如要求「在此序列圖中加入錯誤處理」,經常會導致版面崩潰、連接線遺失,或遺忘先前的元件。圖示結構完全沒有記憶。
範例:向 ChatGPT 要求「一個包含帳戶、交易與雙因素驗證的線上銀行系統的 UML 類圖」,會產生 Mermaid 程式碼。若再加入「包含詐欺偵測模組」,則會重新生成全部內容——可能重新排列類別、遺失關聯,或引入語法錯誤。
這些問題導致產生的僅是「漂亮圖片」,而非可維護的模型。
2. 依賴隨意AI圖示繪製所產生的實際問題
使用通用型 LLM 會帶來風險,進而影響專案品質:
- 設計與實作之間的落差模糊或錯誤的視覺呈現會導致程式碼不一致。團隊需花費大量時間在會議中釐清意圖,因為圖示缺乏精確性。
- 語法依賴與專業門檻編輯 Mermaid/PlantUML 需要學習專門語法——這對於「AI輔助」工具而言實屬諷刺。非專業人士在手動修正時會感到困難。
- 工作流程隔離圖示僅為靜態影像或程式碼片段,與版本控制、協作或下游任務(例如程式碼產生、資料庫結構)完全脫節。
- 「一次性」提示失敗複雜系統需要迭代。使用者只有在首次輸出後才會發現遺漏(例如缺少負載平衡器、快取層或例外流程),但重新生成會導致進度丟失。
範例:在系統設計面試或早期架構會議中,開發人員使用 ChatGPT 透過 Mermaid 生成 C4 模型圖。初始輸出常遺漏關鍵邊界或關係。反覆提示產生不一致的版本,令團隊感到挫折並延遲決策。
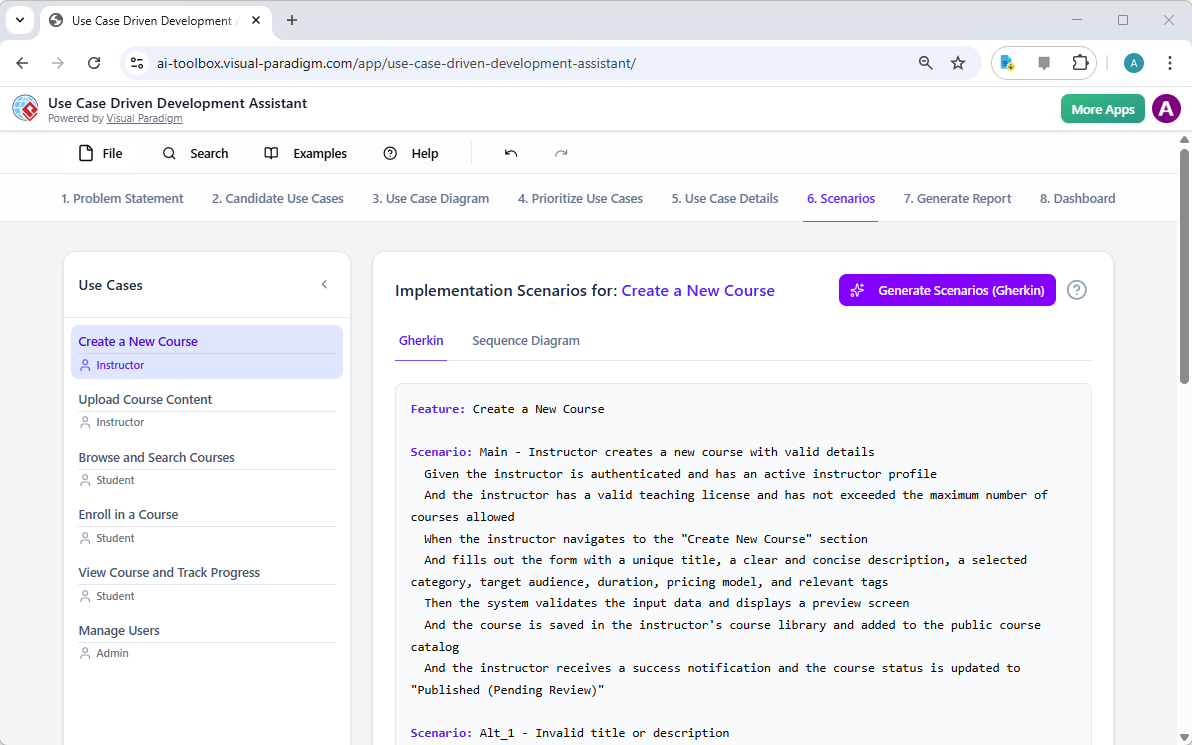
3. Visual Paradigm AI 如何提供專業級建模
Visual Paradigm 將繪圖轉化為一種對話式、標準導向且整合性流程。其 AI 理解 UML 2.5、ArchiMate 3、C4、BPMN、SysML 等多種標準,產出符合規範且可編輯的模型。
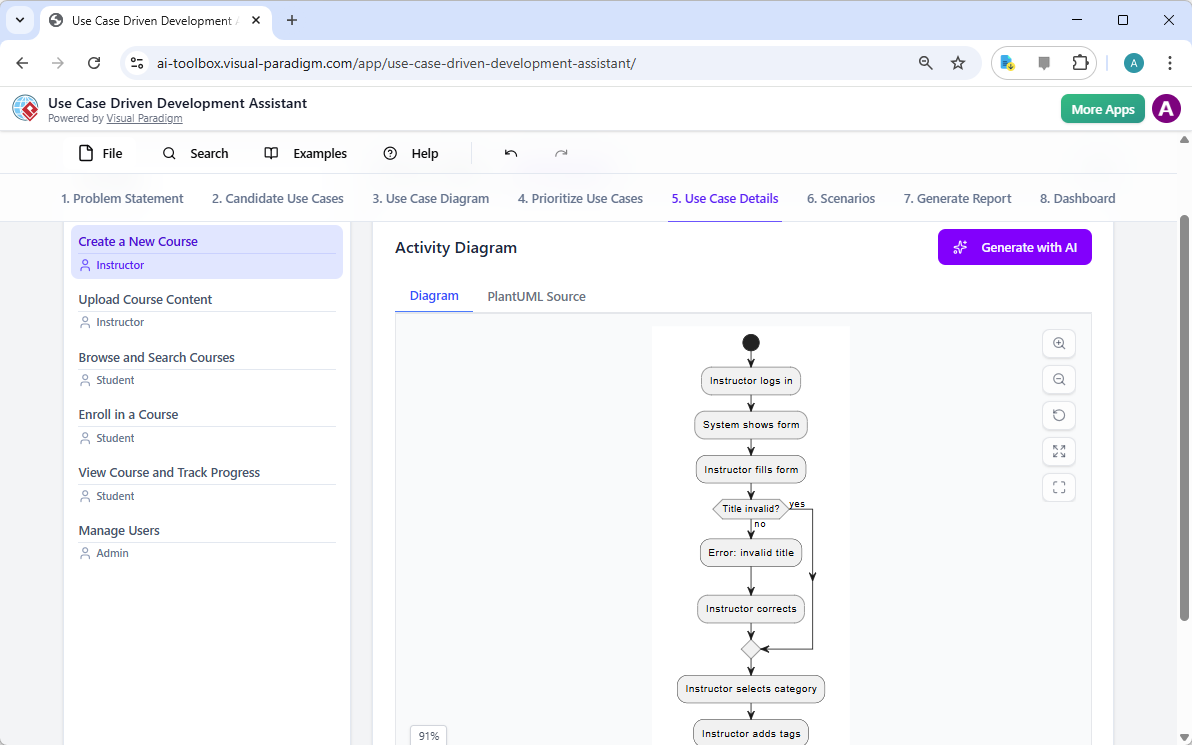
A. 具備「圖形微調」技術的持久化結構
VP 將圖形維持為活體物件。使用者以自然語言指令更新特定部分,無需重新生成。
- 對話式編輯:「登入後新增雙因素驗證步驟」或「將客戶參與者重命名為使用者」可立即調整版面、連接器與語意,同時保持完整性。
這可消除常見於一般工具中的連結損壞與版面混亂問題。
B. 符合標準的智慧
基於正式符號訓練,VP AI 強制執行規則:
- 關聯中的正確多重性
- 正確使用造型符號
- 有效的 ArchiMate 觀點(例如:能力地圖、技術使用)
圖形是技術上正確的「藍圖」,而非近似值。
C. 系統化步驟導向分析與引導
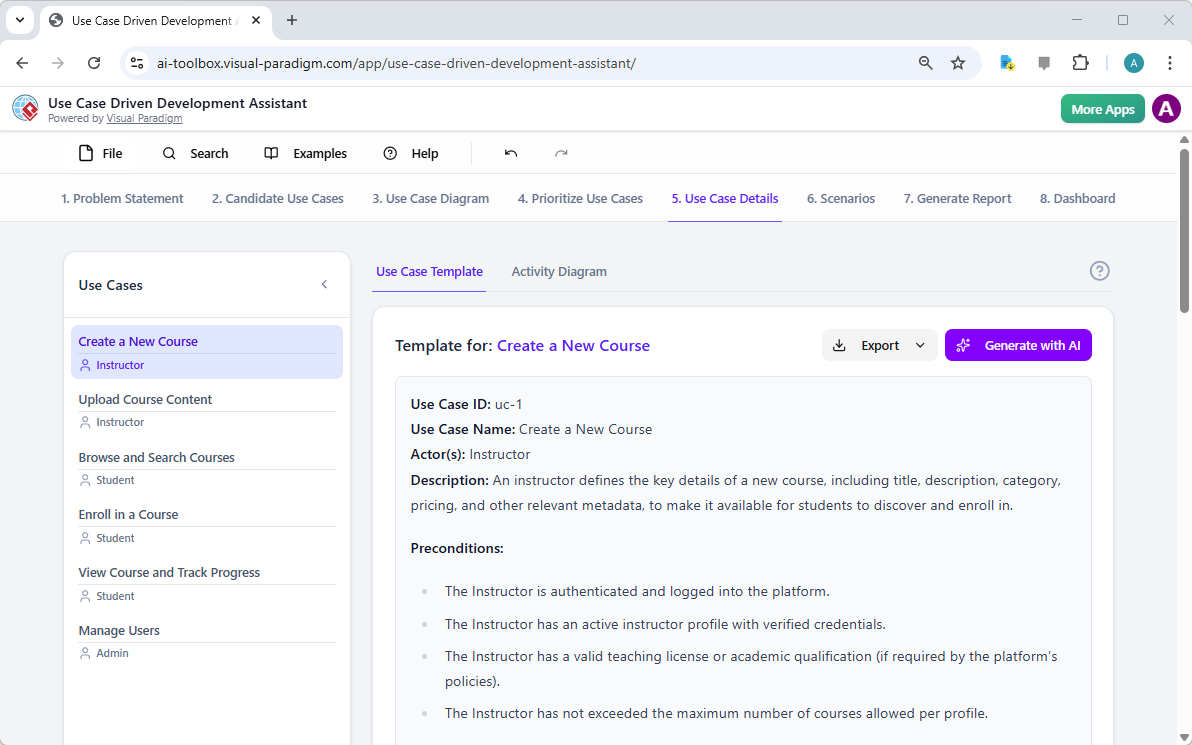
VP 提供結構化應用程式,以連結需求與設計:
-
AI 驅動的文字分析 — 分析非結構化文字(例如:需求文件、使用者故事),提取候選類別、屬性、操作與關係,並自動產生初始類別圖。
範例:輸入描述:「一個電子商務平台允許客戶瀏覽商品、加入購物車、透過支付網關結帳,並追蹤訂單。」AI 會識別類別(客戶、商品、購物車、訂單、支付網關)、屬性(例如:價格、數量),以及關聯(客戶下訂單)。
-
10 步驟 AI 導師(適用於 UML 類別圖及其他類型)—— 以邏輯步驟引導使用者:定義目的 → 範圍 → 類別 → 屬性 → 關係 → 操作 → 審查 → 產生。人機協同驗證可防止一次性錯誤。
D. AI 作為架構顧問
不僅僅是生成,VP AI 還會評估設計:
- 偵測單一故障點
- 識別邏輯漏洞
- 建議設計模式(例如:MVC、儲存庫、觀察者)
它扮演專家審查者的角色。
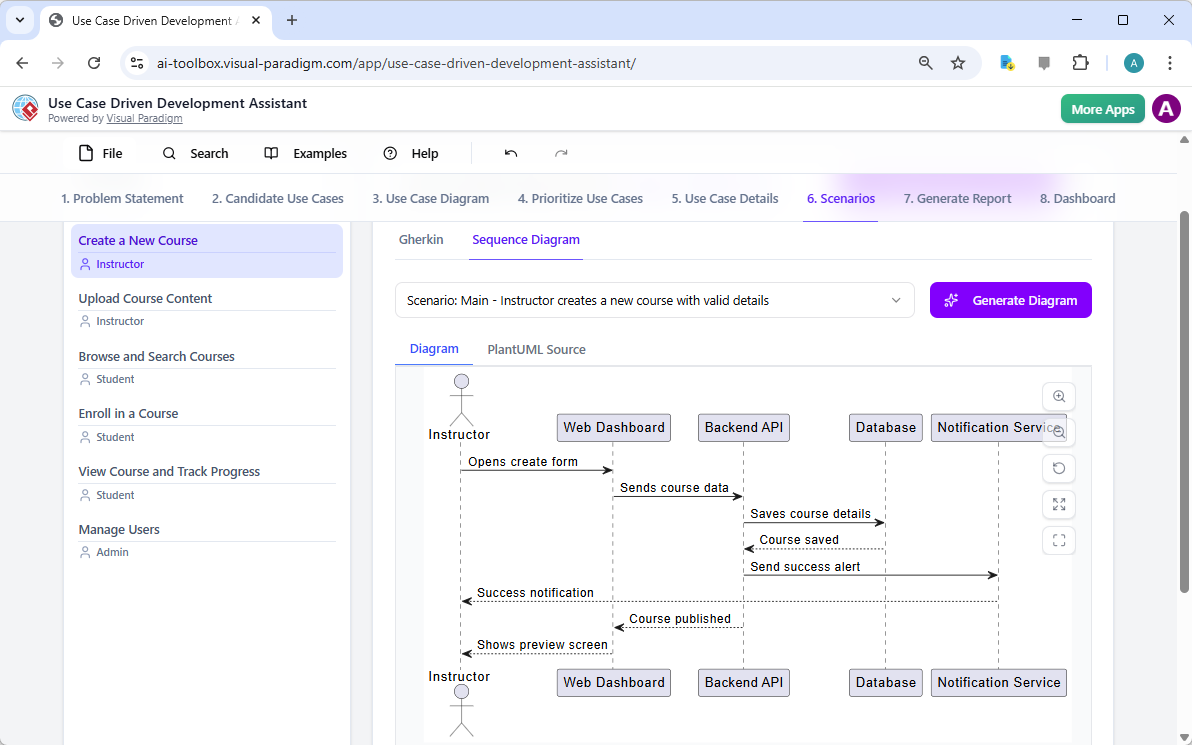
E. 無縫整合至專業工作流程
模型並非孤立的圖像:
- 可在 Visual Paradigm 桌面版/線上版中完全編輯
- 支援版本控制與協作
- 支援程式碼工程(例如:產生 Java/Hibernate ORM、資料庫結構)
- 跨工具匯出/匯入
這完成了從設計到程式碼的完整迴圈。
範例:透過提示產生「技術層」的 ArchiMate 觀點:「建立包含 AWS 元件的雲端微服務架構之 ArchiMate 圖表」。AI 產生符合規範的圖表。使用「圖表修飾」功能加入安全控制。匯出至桌面以供團隊審查與程式碼生成。
結論:從手動雕琢到 AI 驅動的 3D 列印
傳統的圖表繪製感覺像是雕刻大理石——緩慢、容易出錯且不可逆。一般的 AI 大型語言模型雖提升了速度,但仍只是「草圖畫家」,產生不一致且無法保存的視覺內容。
Visual Paradigm AI 就像一台高精度 3D 列印機:輸入自然語言規格,即可獲得符合標準且可編輯的結構,透過對話式迭代,直接推動實作。透過在一個 AI 增強的平台上整合商業、企業與技術建模,它消除了白紙困境,確保所有利害關係人共享精確且可執行的基準。
對於厭倦反覆重建損壞的 Mermaid 程式碼片段的軟體架構師、企業團隊與開發人員而言,Visual Paradigm 代表了下一個進化:尊重標準、保留意圖並加速交付的智慧建模。
-
探索 Visual Paradigm AI 驅動的強大功能…… – Visualize AI:Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動影像翻譯工具,憑藉超越一般工具的先進功能,領先市場。
-
圖表繪製用 AI 聊天機器人:如何與 Visual Paradigm 搭配使用:AI 聊天機器人可將自然語言轉換為圖表,無需學習建模語法或標準。
-
AI 腦力激盪功能 – Visual Paradigm:Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動腦力激盪工具,提供智慧化想法產生與協作流程,提升創造力與生產力。
-
AI 腦力激盪工具 – Visual Paradigm AI:在 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 腦力激盪工具中,透過 AI 驅動的洞察與智慧模板,快速產生並整理想法。
-
AI 驅動的用例圖優化工具 – 智慧圖表增強:AI 驅動的優化可提升用例圖的清晰度、一致性與完整性。
-
將用例圖轉換為活動圖 – AI 驅動的轉換:自動將用例圖轉換為詳細的活動圖,以視覺化系統工作流程。
-
AI 協助的 UML 類別圖產生器 – Visual Paradigm: 使用AI驅動的建議、驗證、PlantUML匯出和設計分析功能生成UML類圖。
-
掌握AI驅動的UML活動圖 | Visual Paradigm部落格: 探討Visual Paradigm中的AI功能如何提升開發人員和分析師創建與優化UML活動圖的效率。
-
革新你的簡報:認識Visual Paradigm的AI Markdown簡報製作工具!: 使用AI驅動的Markdown輸入,將原始構思轉化為精緻且動畫化的簡報。
-
Lumina AI:立即生成AI驅動的影片簡報: 使用AI從文字生成動態影片簡報,適合敘事與快速內容創作。
-
Lumina AI簡報製作工具:使用AI創建令人驚豔的簡報: 使用人工智慧從簡單文字創建專業級簡報,節省時間並激發創意。
-
Illumy AI簡報製作工具:即時生成AI驅動的簡報: 使用AI在幾秒內創建專業且視覺豐富的簡報,專為行銷人員、教育工作者和企業專業人士量身打造。
-
AI動畫簡報工作室:輕鬆創建動態、動畫簡報: 使用AI驅動的敘事、動畫與視覺效果設計引人入勝的動畫簡報。
-
如何立即使用Agilien AI整理你的Jira待辦事項清單: 使用Agilien AI分析使用者故事,自動化整理Jira待辦事項清單,並生成有組織的迭代與大型功能。
-
Agilien AI驅動的Jira待辦事項規劃工具 – Visual Paradigm: 使用Agilien AI自動化並優化Jira待辦事項規劃,智能組織使用者故事與大型功能,以實現高效迭代。
-
如何使用Visual Paradigm的AI Markdown簡報製作工具創建令人驚豔的動畫簡報: 使用Visual Paradigm中的AI驅動Markdown工具,創建動態且視覺吸引人的簡報。
-
推出AI動畫簡報工作室 – 視覺敘事的新時代: 使用Visual Paradigm的AI動畫簡報工作室,輕鬆生成AI增強的動畫簡報。
-
Visual Paradigm Online – 為現代創作者打造的AI驅動簡報製作工具: Visual Paradigm Online的AI驅動簡報工具,為專業人士與教育工作者提供強大工具,輕鬆創建動態且專業的簡報。
-
完整教學:使用Visual Paradigm進行AI驅動的業務流程圖繪製: 學習如何使用Visual Paradigm的AI功能,以更快、更準確地進行業務流程圖繪製。
-
Visual Paradigm AI圖表生成指南: 使用Visual Paradigm AI工具快速且準確生成圖表的逐步指南。
-
Visual Paradigm中的AI圖表生成功能: Visual Paradigm的先進AI功能可根據自然語言描述生成圖表。
-
Visual Paradigm AI圖表生成器更新說明: Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖表生成功能最新更新與增強。
-
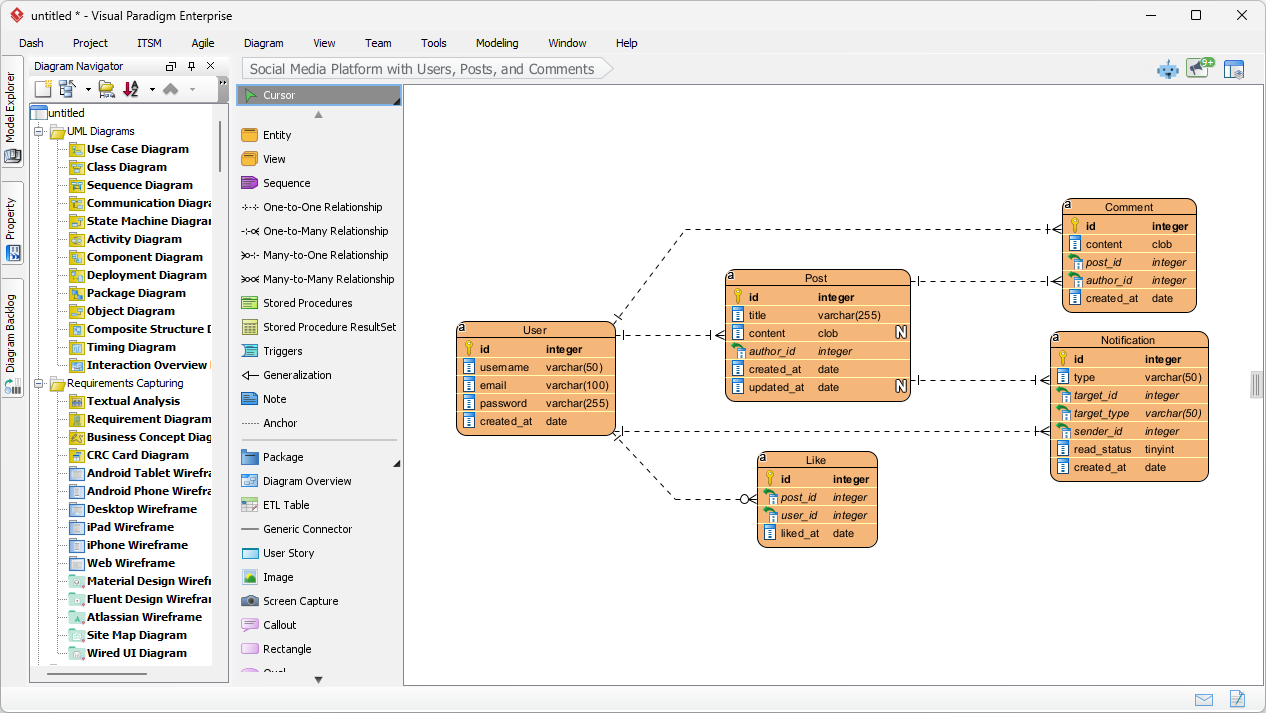
Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖表生成器擴展了即時創建功能: Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖表生成器現已支援即時建立資料流程圖 (DFD)、實體關係圖 (ERD)、思維導圖等。
-
新增圖表類型至 AI 圖表生成器:DFD 與 ERD: 對資料流程圖 (DFD) 與實體關係圖 (ERD) 的 AI 圖表生成支援已擴展。
-
AI 圖表生成器現已支援 Visual Paradigm 中的套件圖: 新版本可透過 AI 生成套件圖,以提升軟體架構的可視化效果。
-
AI 圖表生成器新增雷達圖支援: Visual Paradigm 引入 AI 驅動的雷達圖生成功能,用於視覺化複雜的效能與能力指標。
-
完整教學:使用 AI 生成 ArchiMate 圖表: 學習如何使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖表生成器,高效生成 ArchiMate 圖表與觀點。
-
從問題描述到類別圖:AI 驅動的文字分析: 使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動文字分析,將自然語言的問題描述轉換為精確的類別圖。
-
如何翻譯 UML、BPMN 與流程圖中的圖片文字: 使用 AI 工具提取並翻譯技術圖表中的文字,以促進全球合作與本地化。
-
Visual Paradigm 的 AI 文字分析工具: 將自然語言輸入轉換為結構化圖表,用於軟體設計、文件編寫與系統建模。
-
選擇生成式 AI 與 Visual Paradigm AI 進行圖表繪製的入門指南: 本文幫助使用者理解一般生成式 AI 與 Visual Paradigm AI 之間的關鍵差異,引導他們選擇適合的工具,以實現高效且精確的圖表製作。
-
Visual Paradigm AI 表格生成器完整指南:從自然語言到可執行程式碼: 使用 Visual Paradigm AI 的表格生成引擎,將自然語言轉換為功能性的資料庫表格與可執行程式碼。
-
案例研究:利用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動聊天機器人提升系統建模效率: 透過 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 聊天機器人進行對話式圖表創作,提升系統建模的效率與準確性。
-
如何使用 AI 為雲端應用程式建立 UML 部署圖: 使用 AI 工具高效生成雲端應用程式 UML 部署圖的逐步指南。
-
在 Azure 上利用深度學習與自然語言處理進行資訊探勘 – 模板: 使用此先進的 Azure 模板,結合深度學習與自然語言處理,建立能從非結構化資料中提取洞察的智慧系統。
-
精通使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動用例圖: 介紹如何使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 功能,為現代軟體系統建立智慧且動態的用例圖。
-
Visual Paradigm 桌面版中的 AI 驅動雷達圖製作: 學習如何使用 Visual Paradigm Desktop 中的 AI 功能生成智能、數據驅動的雷達圖,以增強分析可視化效果。
-
完整教程:使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 開發計畫生成器: 使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動工具,為軟體與 AI 項目創建詳細且具戰略性的開發計畫。
-
使用 Visual Paradigm AI 工具進行 C4 模型可視化的最終指南: 借助 Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 工具,自動化並提升 C4 模型可視化,以實現更智慧的架構設計。
-
使用 AI 翻譯技術圖表中文本的完整指南: 展示 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖像翻譯器如何自動化 UML、BPMN 和流程圖中文字的精確翻譯。
-
Visual Paradigm AI 圖表生成功能的全面評估: 評估 Visual Paradigm AI 從自然語言生成圖表的高準確性與快速能力。
-
AI 驅動的使用者故事 3Cs 編輯器:提升清晰度與完整性: 由 AI 驅動的工具,協助敏捷團隊使用 3Cs 框架(卡片、對話、確認)撰寫有效的使用者故事。
-
AI 驅動的甘特圖建構工具 – 即時專案規劃工具: 由 AI 驅動的工具,可從簡單的任務輸入生成甘特圖,實現智慧排程與視覺化規劃。
-
使用 AI 驅動的樹狀圖可視化複雜概念: 由 AI 驅動的樹狀圖工具協助使用者將複雜概念分解為清晰的視覺結構,以提升理解。
-
AI 驅動的魚骨圖生成器 – 數秒內揭露根本原因: 由 AI 驅動的工具自動化魚骨圖的建立,以加速根本原因分析與決策過程。
-
AI 驅動的圖表生成:UML 時序圖的新功能: Visual Paradigm 的 AI 功能可自動生成 UML 時序圖,實現更快、更準確的建模。
-
介紹 Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 驅動 ArchiMate 觀點生成器: 由 AI 驅動的 ArchiMate 觀點生成,自動化企業架構建模,提升準確性與效率。
-
Visual Paradigm AI 聊天機器人:全球首個專為視覺化建模設計的 AI 助手: Visual Paradigm 的 AI 聊天機器人支援自然語言互動,引導使用者完成視覺化建模任務。
-
AI 如何提升 Visual Paradigm 中類圖的建立: AI 透過自動化設計並以最少的使用者輸入提升準確性,增強類圖的建立。
-
Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 驅動序列圖優化: 使用 AI 驅動的優化,將用例描述轉換為精確且專業的序列圖。
-
利用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 簡化類圖建立: Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 工具可減少建立軟體專案精確類圖所需時間與複雜度。
-
由 Visual Paradigm 提供的 AI 驅動 MVC 系統架構生成器:利用 Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 驅動建模,自動產生可擴展且乾淨的 MVC 系統架構。
-
完整教程:在 Visual Paradigm 桌面版中使用 AI 驅動的 ArchiMate 圖表生成:在 Visual Paradigm 桌面版中使用 AI 驅動的生成功能,高效創建專業的 ArchiMate 圖表。
-
介紹 Visual Paradigm AI 聊天機器人:智慧設計協助:Visual Paradigm 的 AI 聊天機器人透過即時建議與重複性任務的自動化,提升設計工作流程。
-
利用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI C4 Studio,簡化架構文件編制:使用 AI 增強的 C4 Studio,建立乾淨、可擴展且易於維護的軟體架構文件。
-
什麼是商業模式畫布?為何要使用視覺範式與 AI 工具:本指南說明商業模式畫布,以及視覺範式與 AI 工具如何提升戰略規劃與創新。
-
使用 Visual Paradigm 進行軟體設計的 AI 驅動文字分析教程:學習如何使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動文字分析,從自然語言需求中提取軟體設計元素。
-
使用 Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 文字分析識別領域類別:利用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 工具,自動從文字中識別領域類別,以簡化軟體建模。
-
Visual Paradigm AI 工具箱:用於軟體建模的文字分析工具:利用 AI 識別實體、關係與關鍵概念,將非結構化文字轉換為結構化軟體模型。
-
AI 驅動的平衡計分卡軟體,用於戰略規劃:利用 AI 驅動的洞察,建立並管理平衡計分卡,以實現有效的戰略執行。
-
AI 驅動 KPI 績效圖表建構器的完整指南:使用 AI 驅動工具建立動態、即時的 KPI 績效圖表,以支援資料驅動決策。
-
理解咖啡店的 AI 驅動 KPI 績效圖表:一個實際範例,說明小型企業(如咖啡店)如何利用 AI 驅動的 KPI 圖表追蹤銷售、客戶行為與營運。
-
AI 驅動風險分解結構產生器:簡化主動式風險管理:Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 驅動工具,可自動化建立風險分解結構,以主動識別與管理風險。
-
AI 生成風險分解結構的實際案例:探索 AI 驅動風險分解結構在資訊科技、建築與金融領域的實際應用,以提升風險評估的準確性與效率。
-
降低風險:利用 AI 建立有效的最壞情境與威脅應對策略:利用 AI 驅動的洞察,建立強大的最壞情境與威脅應對策略,以提升專案規劃與執行的韌性。
-
利用 AI 評估安索夫矩陣中的風險,以促進戰略成長:應用 AI 評估安索夫矩陣中的風險,以支援市場擴張與產品策略的資料驅動決策。
-
AI 驅動的情境分析,用於戰略商業規劃: 利用人工智能驅動的情境分析來模擬未來結果、評估風險,並支援戰略性商業決策。
-
AI 驅動的視覺工具,用於創建資訊圖表、圖表與圖形: 使用 AI 驅動的工具快速創建專業的資訊圖表、圖表與圖形,這些工具提供智慧設計建議與自動化功能。
-
Visual Paradigm 推出 AI-3 面資訊圖表工具,以提升設計效率: 探索 AI-3 面資訊圖表工具,具備三大智慧設計維度,以提升創意並簡化內容創作流程。
-
Visual Paradigm 發布 AI-8 面資訊圖表設計師,用於進階視覺創作: 借助 AI-8 面資訊圖表設計師的八項智慧設計功能,加速並提升視覺內容品質。
-
精通 Visual Paradigm 中的序列圖:AI 聊天機器人教學: 針對初學者,透過電商聊天機器人案例研究,介紹如何在 Visual Paradigm 中建立序列圖。
-
完整教學:使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖表生成器: 使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動圖表生成器進行高效圖表創建的逐步指南。
-
Visual Paradigm AI:透過 AI 簡化圖表創建: 本教學示範 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 功能如何實現軟體圖表的即時生成與優化。
-
Sonix – AI 驅動的語音轉文字轉錄服務: Sonix 利用 AI 快速且準確地轉錄會議、面談與內容創作中的音訊與視訊。
-
精通使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 圖像翻譯工具進行圖表轉譯: 使用 Visual Paradigm Online 的 AI 驅動圖像轉圖表翻譯工具,將手繪或圖像型圖表轉換為可編輯模型的指南。
-
Click-Start AI:Visual Paradigm 用戶的快速 AI 整合: 逐步說明如何啟用並使用 Visual Paradigm 中的 AI 功能,透過智慧自動化加速圖表製作。
-
Visual Paradigm Online 的 AI 驅動圖像翻譯教學: 教學說明如何使用 Visual Paradigm Online 的 AI 驅動圖像翻譯工具,自動將視覺內容轉換為結構化圖表與模型。
-
LinkVP – AI 驅動的連結管理與分析平台: LinkVP 提供 AI 驅動的平台,用於建立、追蹤與優化自訂連結,具備即時分析與進階自訂功能。
-
2024 年頂尖圖表生成工具:WritingMate AI 的完整指南: 精選頂尖 AI 驅動圖表生成工具的概覽,強調其核心功能、易用性及專業人士與創作者的理想應用場景。
-
MyMap AI – 具備自然語言輸入的智慧圖表生成器: MyMap AI 可根據文字提示立即生成專業圖表,結合 AI 智慧與直覺式設計,實現無痛規劃。
-
DiagrammingAI – 面向團隊與個人的下一代 AI 圖表創作: DiagrammingAI 利用人工智慧,快速將構想轉化為精緻圖表,並支援即時協作與智慧版面建議。
-
為何 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動圖像翻譯工具…… – Visualize AI: Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動影像翻譯工具,為技術與設計工作流程提供先進且專業級的影像翻譯。
-
AI 樹狀圖製作工具 | 即時可視化層級資料: 透過描述您的主題,利用 AI 即時建立專業的層級圖表,例如思維導圖、組織圖和工作分解結構。
-
將 AI 活動圖整合至您的 Visual Paradigm …: 透過 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 驅動建模,使用自然語言輸入來生成並優化 UML 活動圖。
-
活動圖 AI – Visual Paradigm 在線: 探索全球使用者創建的活動圖集合,獲取靈感與專業設計想法。
-
AI 驅動圖表工具完全指南(2025): 探索 AI 驅動的圖表工具如何透過智慧自動化與易用性,改變視覺溝通方式。
-
由 Visual Paradigm 提供的 AI 驅動 UML 類別圖生成器: 使用 AI 輔助自動化,從自然語言描述生成精確的 UML 類別圖。
-
真實案例研究:使用 Visual Paradigm AI 生成 UML 類別圖: 一個真實專案示範了 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 助手如何將文字需求轉換為精確的 UML 類別圖。
-
完整教學:使用 Visual Paradigm 的 AI 助手生成 UML 類別圖: 透過逐步指南,學習如何使用 Visual Paradigm 在線的 AI 助手,從純文字創建精確的 UML 類別圖。