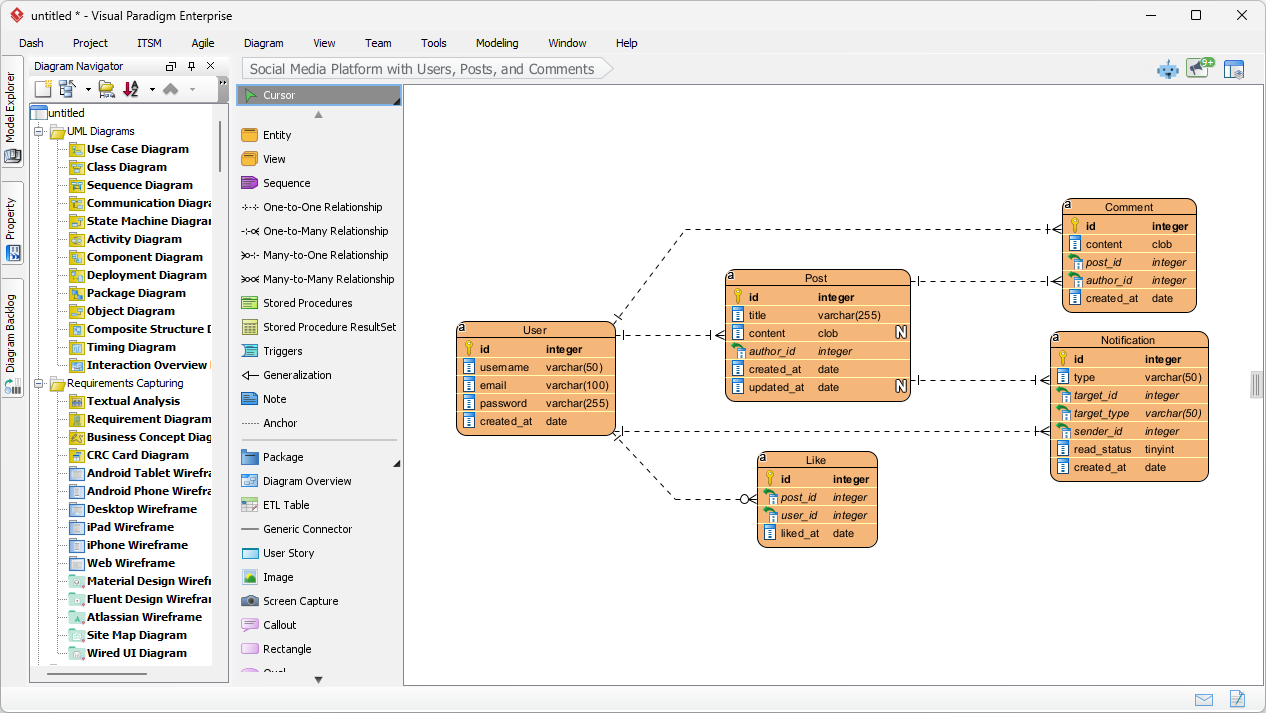
ERDs remain one of the most important tools for designing relational databases, communicating data requirements, and avoiding costly redesigns later.
1. What is an ERD and Why Do We Use It?
An Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) is a visual model that shows:
- The things we want to store (entities)
- The properties of those things (attributes)
- How those things are connected (relationships)
- How many of each thing can be connected (cardinality / multiplicity)
Main purposes in 2025–2026:
- Communicate structure between developers, analysts, product managers, and domain experts
- Serve as single source of truth before writing DDL (CREATE TABLE …)
- Catch logical mistakes early (redundancy, missing constraints, wrong cardinalities)
- Support microservices / domain-driven design boundary identification
- Generate documentation automatically in many modern tools
2. Core Notations Used Today
Three main families are still actively used:
| Notation |
Popularity (2025) |
Readability |
Best For |
Symbols for cardinality |
| Crow’s Foot |
Highest |
Very high |
Most teams, tools (Lucidchart, dbdiagram, Draw.io, QuickDBD, etc.) |
Crow’s feet, bars, circles, dashes |
| Chen |
Medium |
Medium |
Academia, some conceptual modeling |
Numbers (1, N), diamonds heavy |
| IDEF1X |
Low |
Medium |
Some government / legacy systems |
Specific box-in-box notation |
Crow’s Foot is the de-facto industrial standard in 2025–2026 → we will use it in this guide.
3. Basic Building Blocks (Crow’s Foot)
| Concept |
Symbol |
Description |
Example |
| Strong Entity |
Rectangle |
Exists independently, has its own primary key |
Customer, Order, Product |
| Weak Entity |
Double rectangle |
Existence depends on owner entity; partial key + owner’s key = full key |
OrderLine (depends on Order) |
| Attribute |
Oval (connected to entity) |
Property of an entity |
name, price, email |
| Primary Key |
Underlined attribute |
Uniquely identifies entity instance |
customer_id, isbn |
| Multivalued Attr |
Double oval |
Can have multiple values (usually becomes separate table) |
phone_numbers, tags |
| Derived Attr |
Dashed oval |
Can be calculated from other attributes |
age (from birth_date) |
| Composite Attr |
Oval containing other ovals |
Attribute made of several sub-attributes |
full_address → street, city, zip |
4. Relationships & Cardinality (The Heart of ERD)
Relationship = diamond (sometimes just a line in modern minimalist style)
Cardinality answers two questions for each side of the relationship:
- Minimum number of related instances? (0 or 1)
- Maximum number of related instances? (1 or many = N)
| Symbol (Crow’s Foot) |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Meaning (from this side) |
Common name |
Example sentence |
| Circle (○) |
0 |
— |
Optional |
Zero |
A customer may have placed zero orders |
| Short bar ( |
) |
1 |
— |
Mandatory |
One (exactly) |
| Crow’s foot (> ) |
0 |
N |
Zero or many |
Optional many |
A customer can place many orders |
| Bar + crow’s foot (> |
) |
1 |
N |
One or many |
Mandatory many |
| Double bar ( |
|
) |
1 |
1 |
Exactly one |
Common patterns (written left → right):
- 1:1 || — || Person ↔ Passport (current)
- 1:0..1 || — ○| Department ↔ Manager (some depts have no manager)
- 1:N || — >| Author → Book
- 1:0..N || — ○> Customer → Order
- M:N >| — >| Student ↔ Course (many-to-many)
5. Participation Constraints
- Total participation = double line from entity to relationship (every instance must participate)
- Partial participation = single line (some instances may not participate)
Examples:
- Every Order must have at least one OrderLine → total participation (double line) + 1..N
- Not every Customer has placed an Order → partial + 0..N
6. Weak Entities & Identifying Relationships
Weak entity:
- Cannot exist without its owner (strong entity)
- Its primary key = owner’s PK + partial key (discriminator)
Symbol:
- Double rectangle
- Identifying relationship = double diamond or bold line
- Usually 1:N identifying relationship (owner → many weak entities)
Classic example:
Order contains OrderLine
(double rect + bold line)
PK: order_id PK: (order_id, line_number)
7. Step-by-Step ERD Modeling Process (Practical 2025–2026 Workflow)
-
Understand the domain deeply Talk to stakeholders → collect nouns & verbs
-
List candidate entities (nouns) → Filter real-world objects that need to be stored independently
-
List attributes for each entity → Mark primary keys (underlined) → Identify candidate keys / natural keys → Spot multivalued, composite, derived attributes
-
Find relationships (verbs) → Ask: “Which entities are directly associated?” → Avoid transitive relationships (they usually hide missing entities)
-
Determine cardinality & participation for each direction → Write 4–6 sentences using the template: “Each A can/must be associated with zero/one/many B.” “Each B can/must be associated with zero/one/many A.”
-
Handle M:N relationships Almost always resolve them into junction table (weak or strong entity) Add attributes if the relationship itself has properties (e.g. enrollment_date, grade)
-
Identify weak entities Ask: “Can this entity exist without the other?”
-
Add supertype/subtype (if needed — inheritance) Use circle with d (disjoint) / o (overlapping)
-
Review for common smells
- Fan trap / chasm trap
- Too many M:N without attributes → missing entity?
- Redundant relationships
- Missing mandatory participation
- Entities with only foreign keys → probably weak entity
-
Validate with stakeholders using concrete examples
8. Modern Best Practices & Tips (2025–2026)
- Prefer minimalist style (no diamonds — just labeled lines)
- Use verb phrases on relationship lines (places, contains, taught_by)
- Color-code domains / bounded contexts in large models
- Keep logical ERD separate from physical (data types, indexes come later)
- Version control the .drawio / .dbml / .erd file
- Use tools that can generate SQL / Prisma / TypeORM schema (dbdiagram.io, erdgo, QuickDBD, Diagrams.net + plugins)
- For very large systems → modular ERDs per bounded context
Quick Reference – Most Common Patterns
- Customer 1 —— 0..* Order
- Order 1 —— 1..* OrderLine
- Product * —— * Category → resolve to junction + attributes
- Employee 1 —— 0..1 Department (manager)
- Department 1 —— 0..* Employee (members)
- Person 1 —— 0..1 Car (current_car)
Recommended AI ERD Tool
Visual Paradigm offers a comprehensive ecosystem for ERD visual modeling, combining desktop-grade engineering power with cloud-based agility, AI acceleration, and team collaboration features. This makes it suitable for individual modelers, agile teams, enterprise architects, and database professionals working on everything from quick prototypes to complex legacy system re-engineering.
The ecosystem primarily consists of two main platforms that complement each other:
- Visual Paradigm Desktop (downloadable application for Windows, macOS, Linux) — focused on deep, professional database engineering.
- Visual Paradigm Online (browser-based, no installation required) — optimized for fast, collaborative, AI-assisted diagramming.
Both support core ERD notations (including Crow’s Foot and Chen), conceptual/logical/physical levels, and full traceability between model layers.
Key Ways the Ecosystem Helps in the ERD Visual Modeling Process
- Intuitive & Fast Diagram Creation
- Drag-and-drop interface with resource-centric modeling (no constant toolbar switching).
- Automatic foreign key column generation when creating relationships.
- Support for all standard ERD elements: strong/weak entities, identifying/non-identifying relationships, multivalued/derived/composite attributes, stored procedures, triggers, views, unique constraints, etc.
- Sub-diagrams help break large enterprise schemas into logical views.
- Full Lifecycle Support: Conceptual → Logical → Physical
- One-click derivation: generate logical ERD from conceptual, physical from logical (with automatic traceability and navigation via Model Transitor).
- Maintain consistency across abstraction levels — changes in one level can propagate intelligently.
- AI-Powered Acceleration (especially strong in VP Online)
- DB Modeler AI and AI Diagram Generator — describe your data requirements in plain English (e.g., “We have customers who place orders containing products from multiple categories”), and the AI instantly generates a normalized, professional ERD complete with entities, relationships, and keys.
- Supports Chen notation for ERD in the AI generator.
- Ideal for rapid prototyping or when starting from vague business requirements.
- Database Engineering & Synchronization
- Forward engineering — generate complete, error-free DDL scripts (or directly create/update databases) for major DBMS: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, SQLite, Amazon Redshift, etc.
- Reverse engineering — import existing databases and instantly reconstruct visual ERDs (extremely helpful for legacy systems or documentation recovery).
- Patch / diff tool — compare model vs. live database, generate delta scripts to apply changes safely without data loss.
- Enter sample data directly in ERD entities → export to database for quick seeding.
- Team Collaboration & Versioning
- Real-time concurrent editing (multiple users on the same ERD simultaneously).
- Built-in conflict detection and smart resolution.
- Full revision history, commit/update, revert changes.
- Commenting directly on diagram elements for feedback.
- Publish & share — generate web links, embed diagrams, export to PDF/image/HTML for stakeholders who don’t have licenses.
- Centralized cloud repository (VPository) keeps everyone aligned across dev/test/prod environments.
- Integration Across the Broader Modeling Ecosystem
- Link ERD entities to other diagrams: reference a data entity in DFDs, UML class diagrams, wireframes, BPMN processes, etc.
- Generate ORM code (Hibernate, etc.) from ERD → bridge visual model to application layer.
- Visual Diff — compare different versions or model vs. database schema.
- Export professional data dictionary / specifications for documentation & handover.
Quick Comparison: When to Use Which Part of the Ecosystem
| Need / Scenario |
Recommended Platform |
Key Strengths in ERD Context |
| Deep reverse engineering, patching prod DB, ORM generation |
Desktop |
Full engineering suite, offline work, advanced synchronization |
| Quick sketches, AI-assisted design from text, zero setup |
Online |
AI generation, browser access, lightweight |
| Real-time team modeling sessions |
Online (or Desktop + Teamwork Server) |
Simultaneous editing, commenting, conflict resolution |
| Enterprise-scale schemas with sub-models |
Desktop |
Better performance for very large models |
| Stakeholder reviews & sharing |
Both (publish feature) |
Web links, embeds, PDF exports |
| Free / non-commercial use |
Community Edition (Desktop) or Free VP Online account |
Full ERD editing, limited advanced engineering |
In summary, Visual Paradigm’s ecosystem removes friction at every stage of ERD modeling — from initial brainstorming (AI + quick drag-drop), through collaborative refinement and validation, to final implementation and maintenance (round-trip engineering). It is particularly strong when your workflow involves both visual communication and actual database delivery.
ERD Articles
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: Use AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML, BPMN, and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
-
Visual Paradigm ERD Tool – Create Entity-Relationship Diagrams Online: A powerful, web-based ERD tool that enables users to design and visualize database schemas with ease using intuitive drag-and-drop features.
-
Database Design with ERD Tools – Visual Paradigm Guide: Comprehensive guide on using ERD tools to design robust, scalable databases with best practices in data modeling and schema design.
-
What is an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)? – Visual Paradigm Guide: An in-depth explanation of ERDs, their components, and their importance in database design and data modeling.
-
Free ERD Tool – Design Databases Online with Visual Paradigm: Access a free, no-cost ERD tool online for creating professional entity-relationship diagrams without installation or subscription.
-
How to Draw Entities in Visual Paradigm ERD: Step-by-step user guide on creating and customizing entities in Visual Paradigm’s ERD tool for accurate database modeling.
-
How to Model a Relational Database with ERD – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: Practical tutorial showing how to use ERDs to model relational databases from concept to implementation.
-
Generating Database from ERD in Visual Paradigm: Detailed guide on automatically generating a database schema from an ERD using Visual Paradigm’s reverse engineering capabilities.
-
Generate Class Diagram from ERD – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: Learn how to convert an ERD into a class diagram to support object-oriented design and development workflows.
-
Visual Paradigm ERD Tool for Database Design – Complete Solution: A full-featured ERD tool designed for database architects and developers to model, visualize, and generate databases efficiently.
-
Free UML Design Tool – Visual Paradigm: Free UML modeler designed for software design and database design with UML (Unified Modeling Language), ERD. Run on Windows, Linux, Mac OS X.
-
Visual Paradigm – Advanced Database Design and Modeling Tool: A comprehensive database modeling tool offering ERD creation, schema generation, and integration with development workflows.
-
Visual Paradigm Online – Access Diagrams and Tools: Direct access to Visual Paradigm’s full suite of diagramming tools, including UML, ERD, flowcharts, and more, all in the cloud.
-
MODAF OV-5: Operational Activity Model in Visual Paradigm: Learn how to create the OV-5 Operational Activity Model using Visual Paradigm to map out operational processes, activities, and their interdependencies.
-
How to Create Database Specifications in Visual Paradigm: A step-by-step tutorial on creating database specifications using Visual Paradigm, a powerful modeling tool for database design and development.
-
Visual Paradigm’s AI Diagram Generator Expands Instant Creation Capabilities: Coverage of how Visual Paradigm’s AI diagram generator now supports instant creation of DFDs, ERDs, mind maps, and more.
-
New Diagram Types Added to AI Diagram Generator: DFD & ERD: Announcement of expanded AI diagram generation support for Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) and Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD).
-
Why Visual Paradigm Online is Ideal for ERD Design in Development Teams: A case study and recommendation on using Visual Paradigm Online for designing Entity-Relationship Diagrams, emphasizing collaboration and real-time editing in agile teams.
-
Reverse Engineering Database to ERD in Visual Paradigm: Learn how to reverse engineer a database into an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) using Visual Paradigm’s intuitive interface and powerful modeling tools.
-
Step-by-Step Guide to Reverse Engineering Databases in Visual Paradigm: Follow a detailed tutorial to reverse engineer existing databases into visual ERDs, enabling efficient data modeling and documentation.
-
Reverse Engineering Oracle Databases with Visual Paradigm: A hands-on tutorial demonstrating how to reverse engineer Oracle databases into ERDs using Visual Paradigm’s dedicated database modeling features.
-
Reverse Engineering from DDL to ERD Using Visual Paradigm: Download a step-by-step PDF guide to reverse engineer database schemas from DDL scripts into fully visual Entity-Relationship Diagrams.
-
Introduction to Data Modeling with Visual Paradigm: ERD, Code Generation & Reverse Engineering: An introductory guide to data modeling using Visual Paradigm, covering ERD creation, code generation, and reverse engineering from databases.