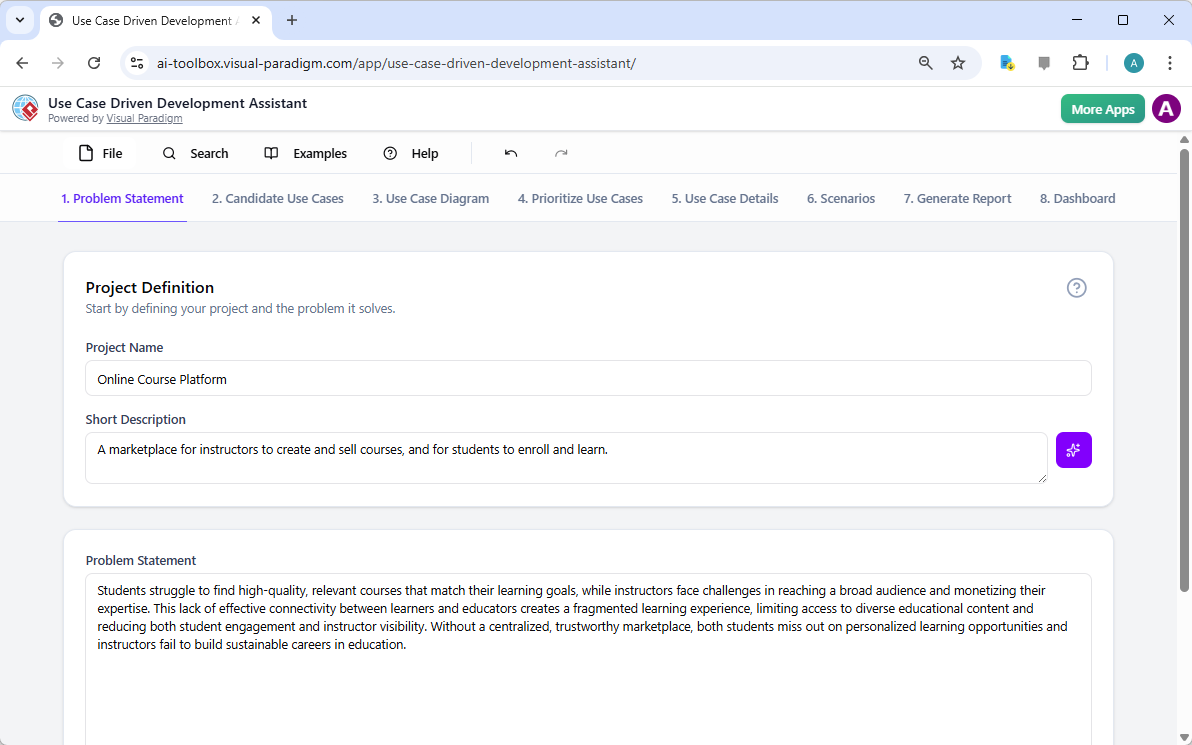
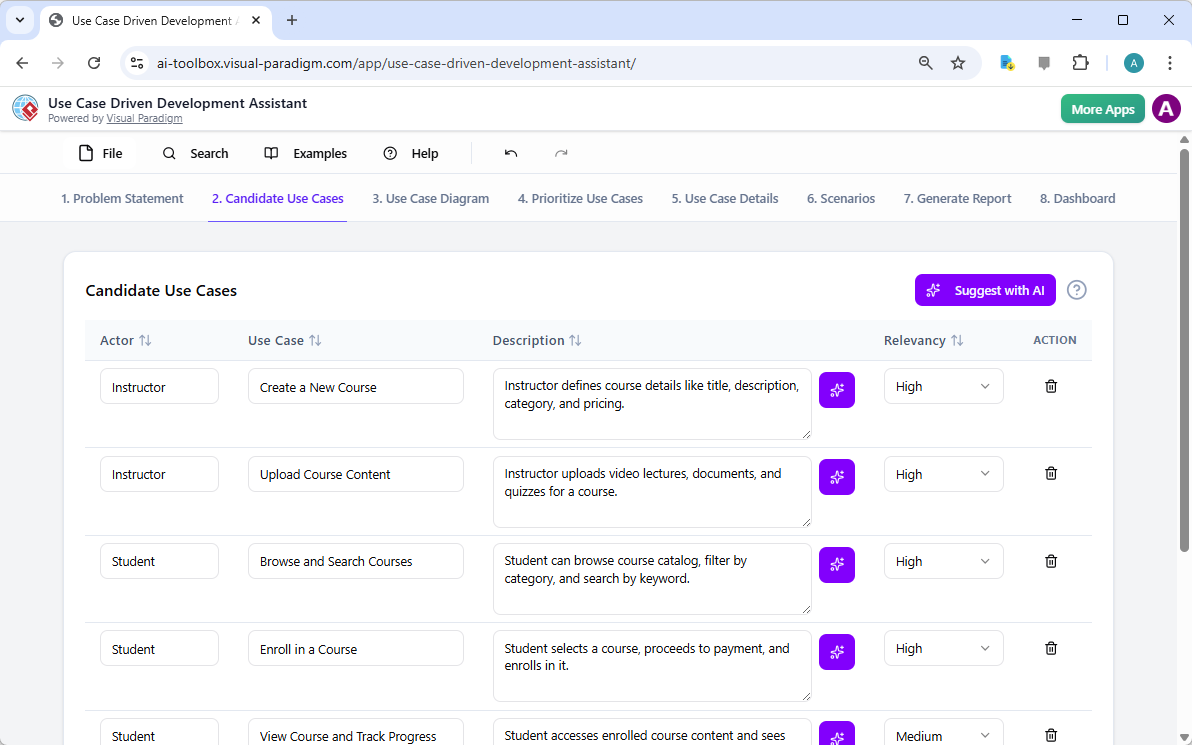
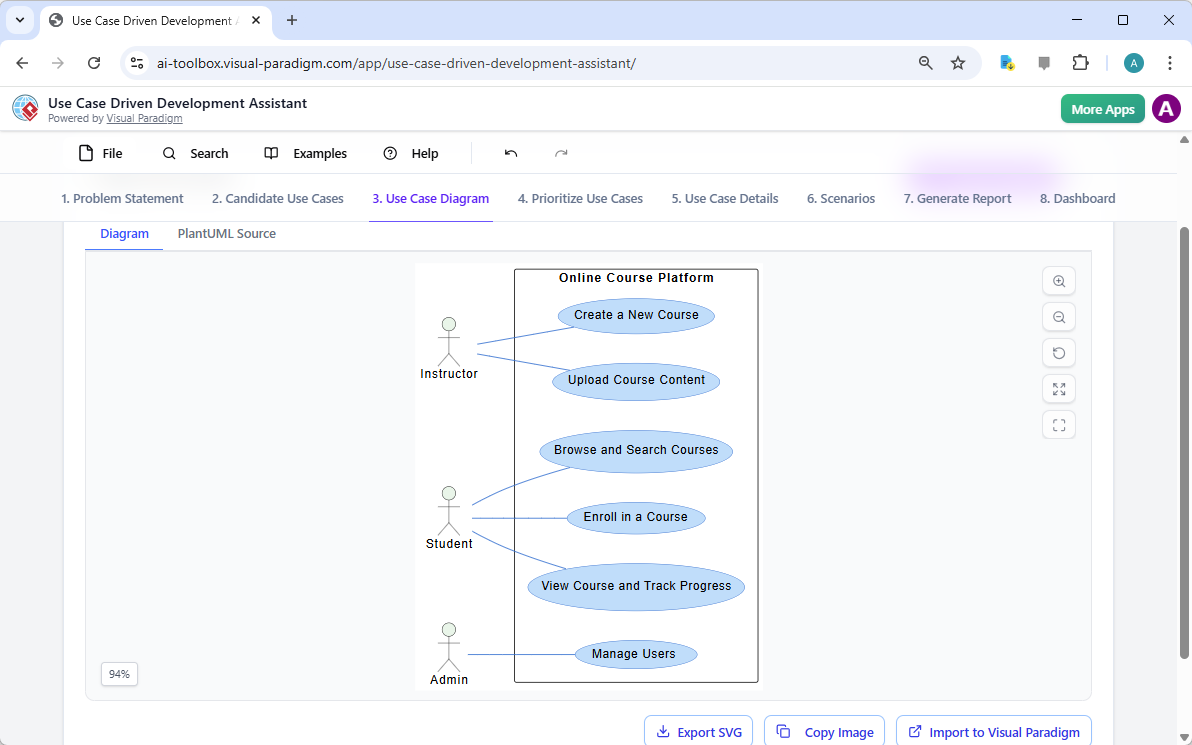
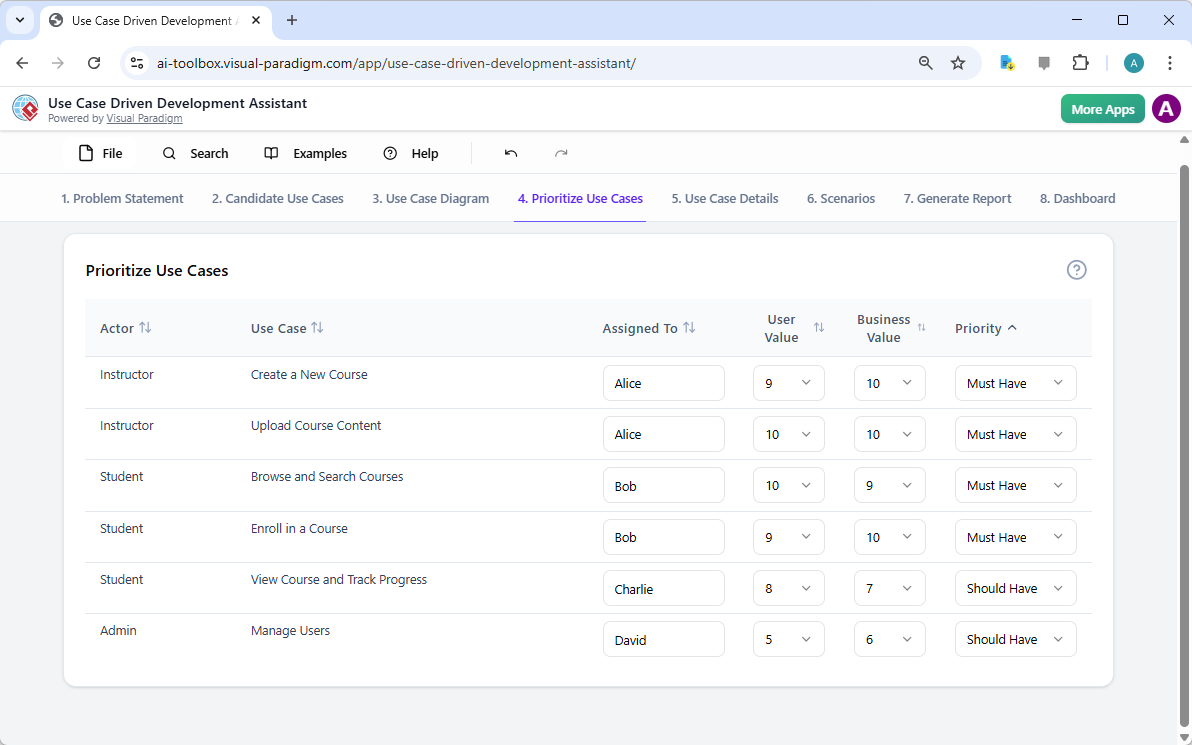
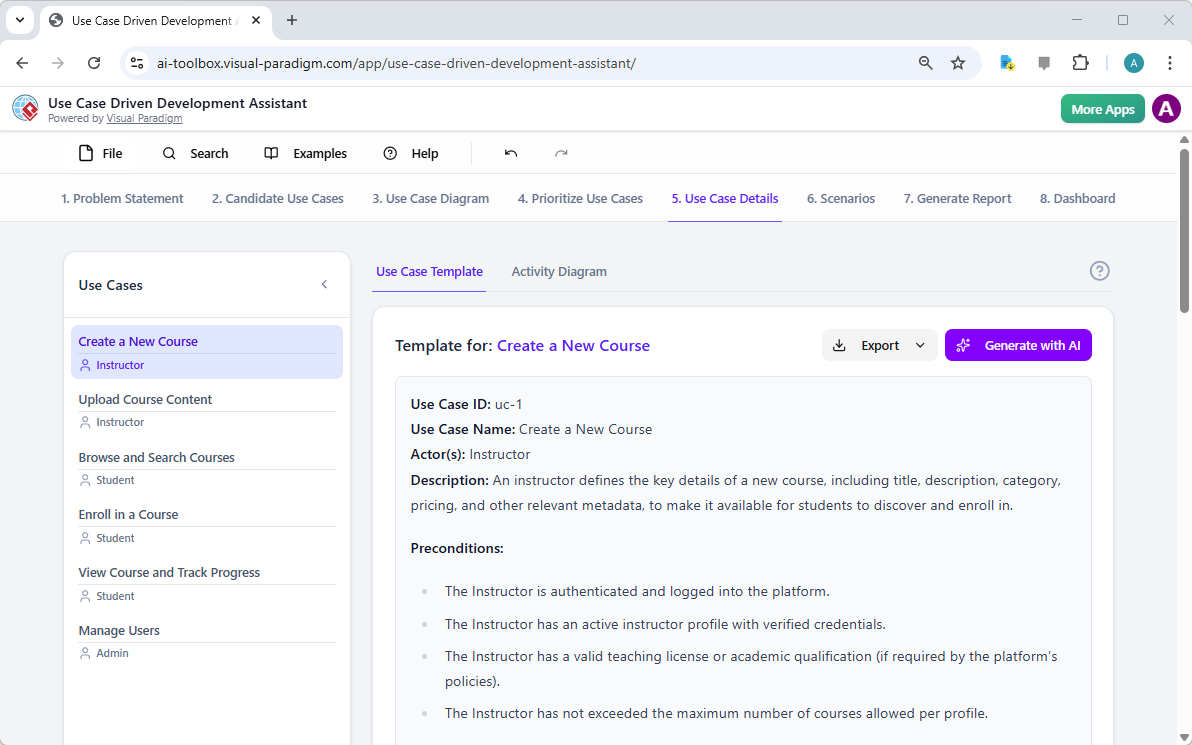
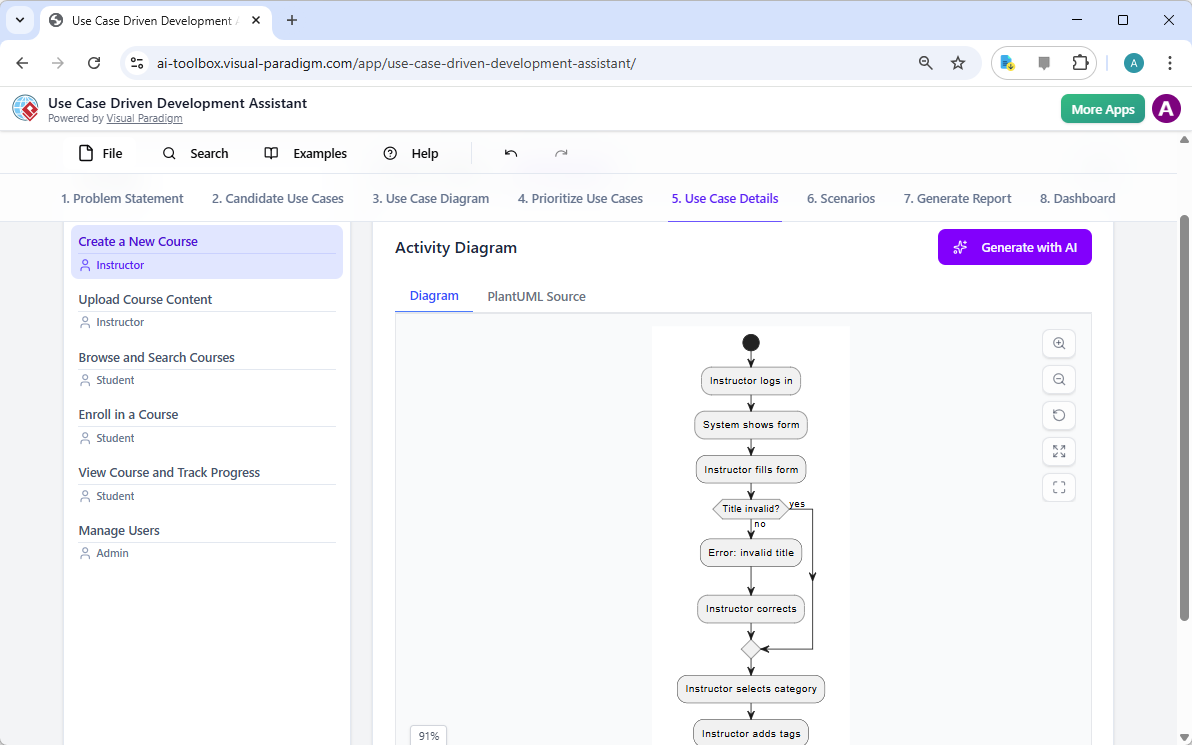
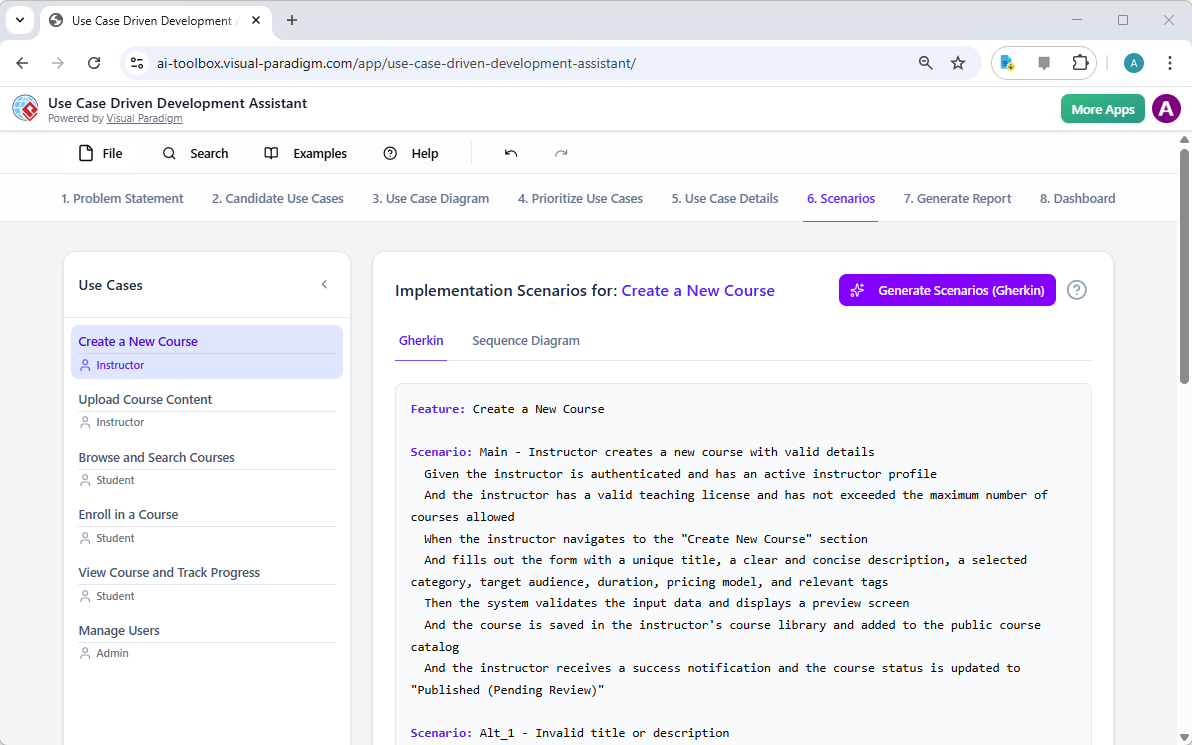
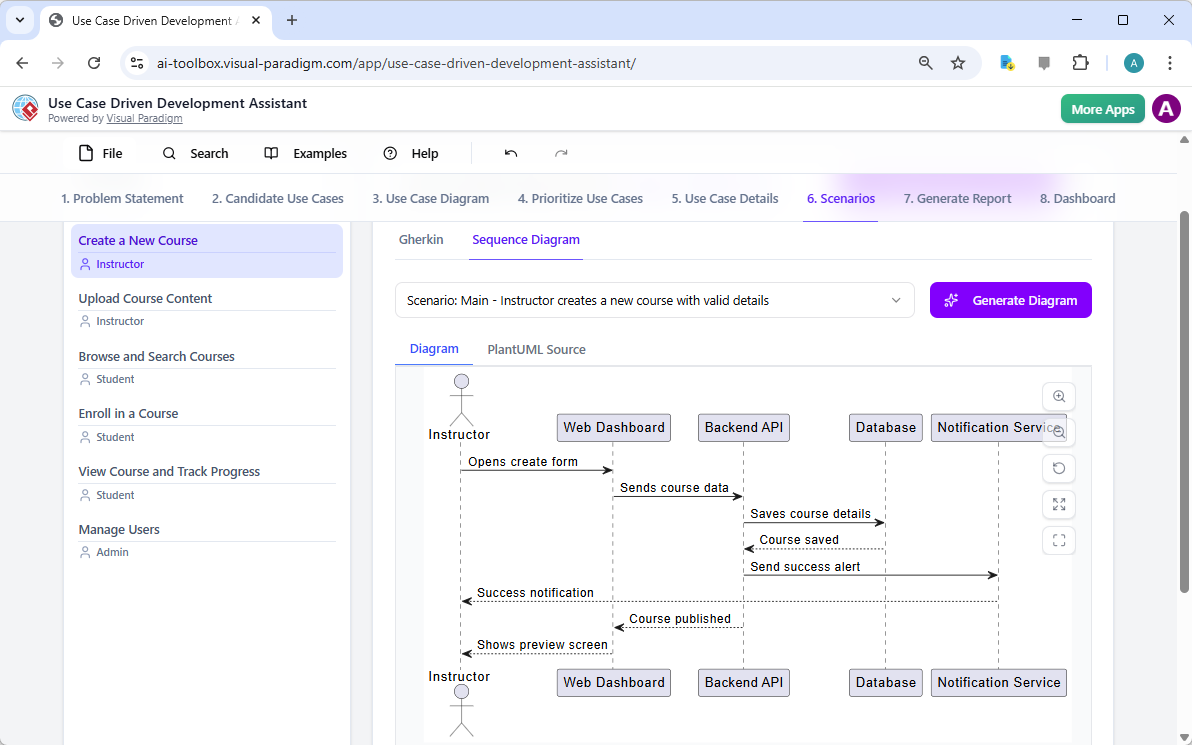
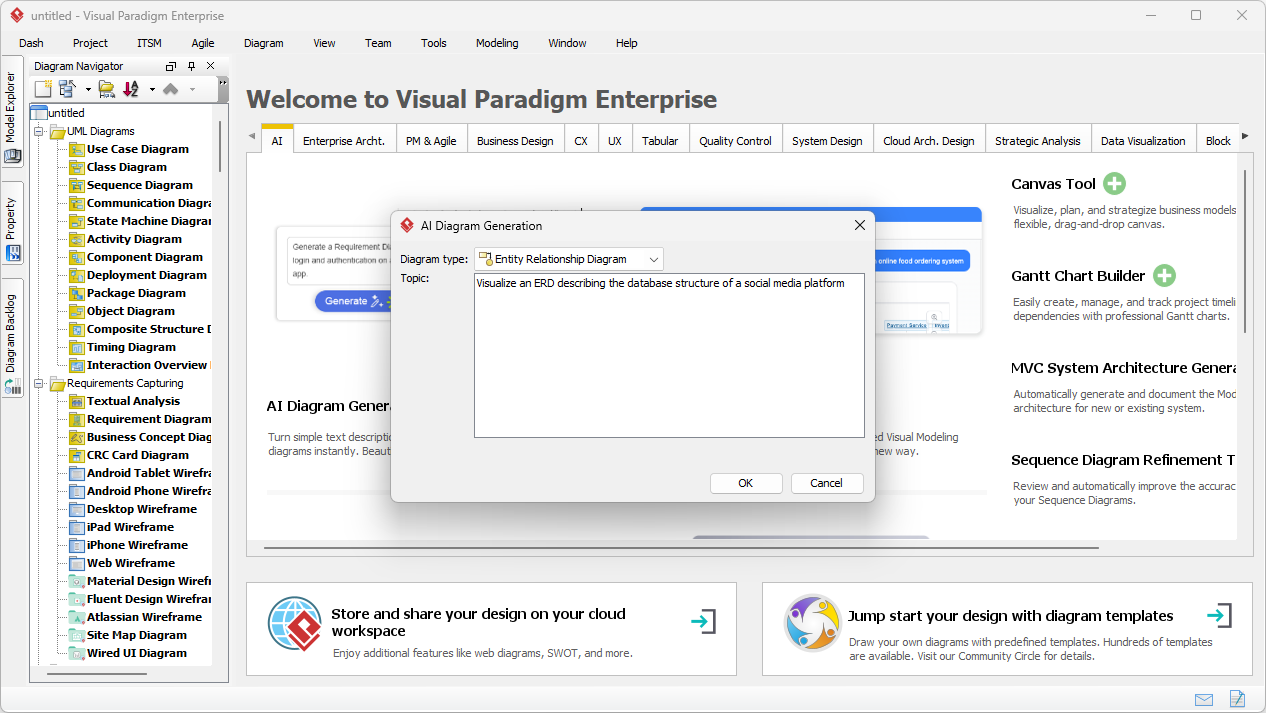
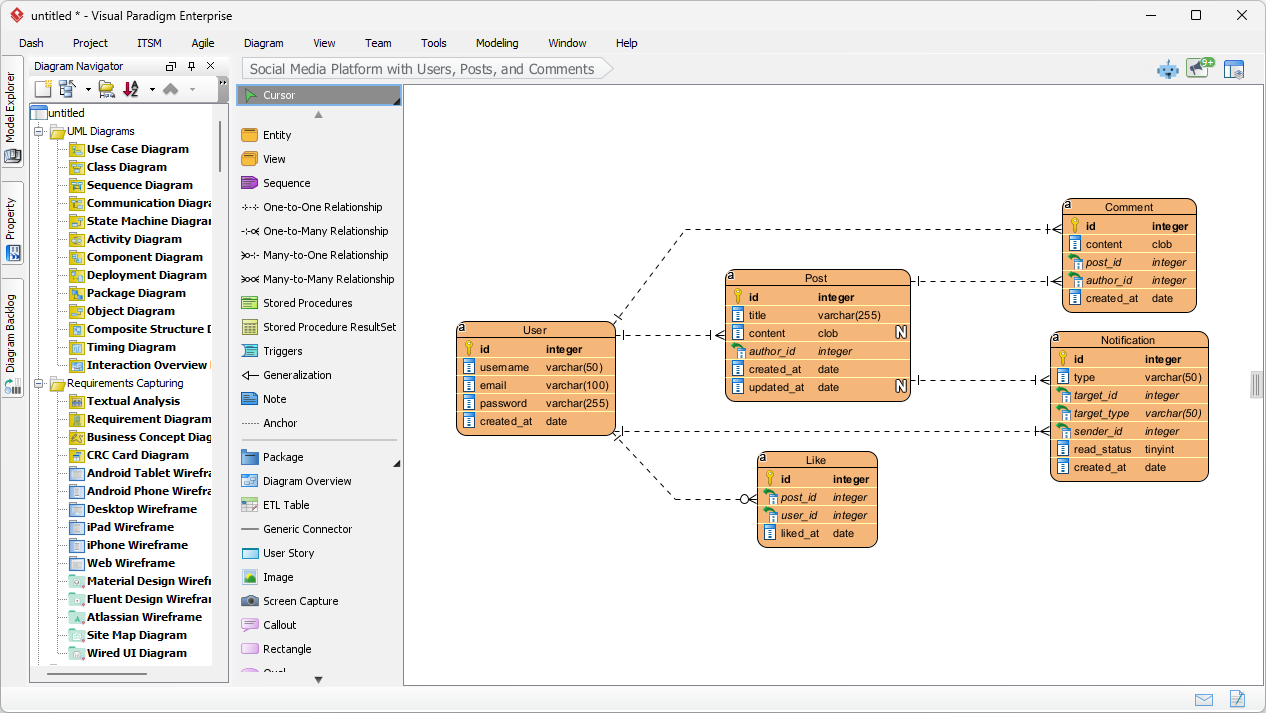
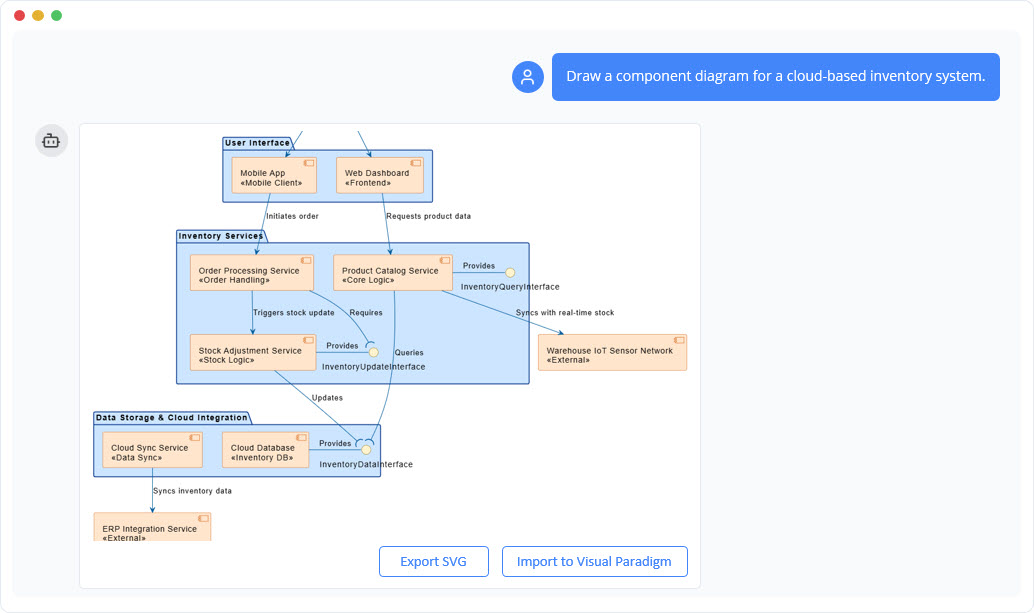
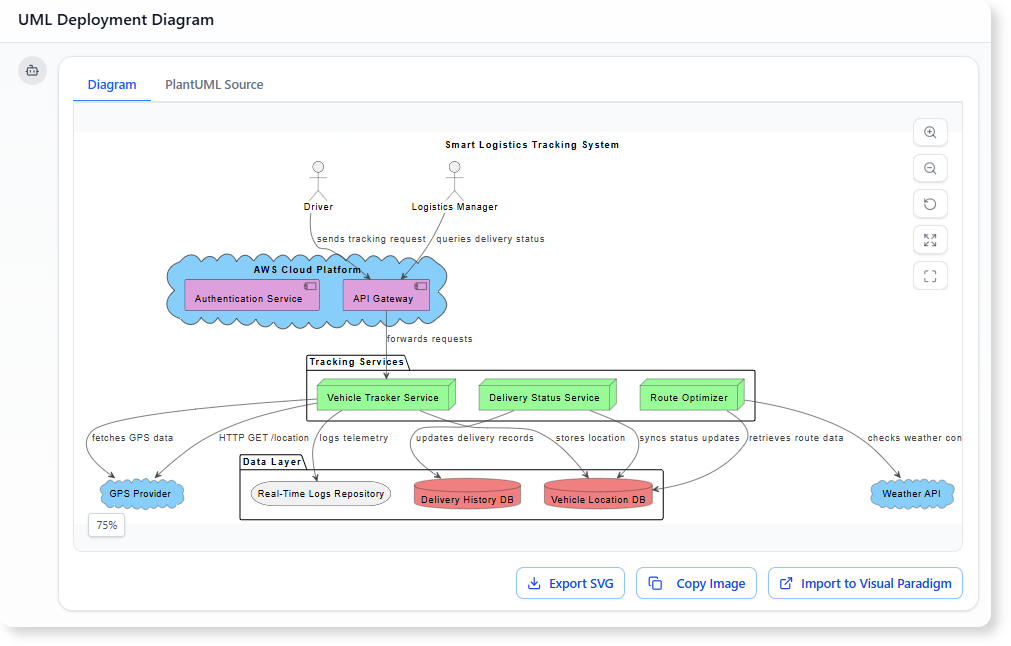
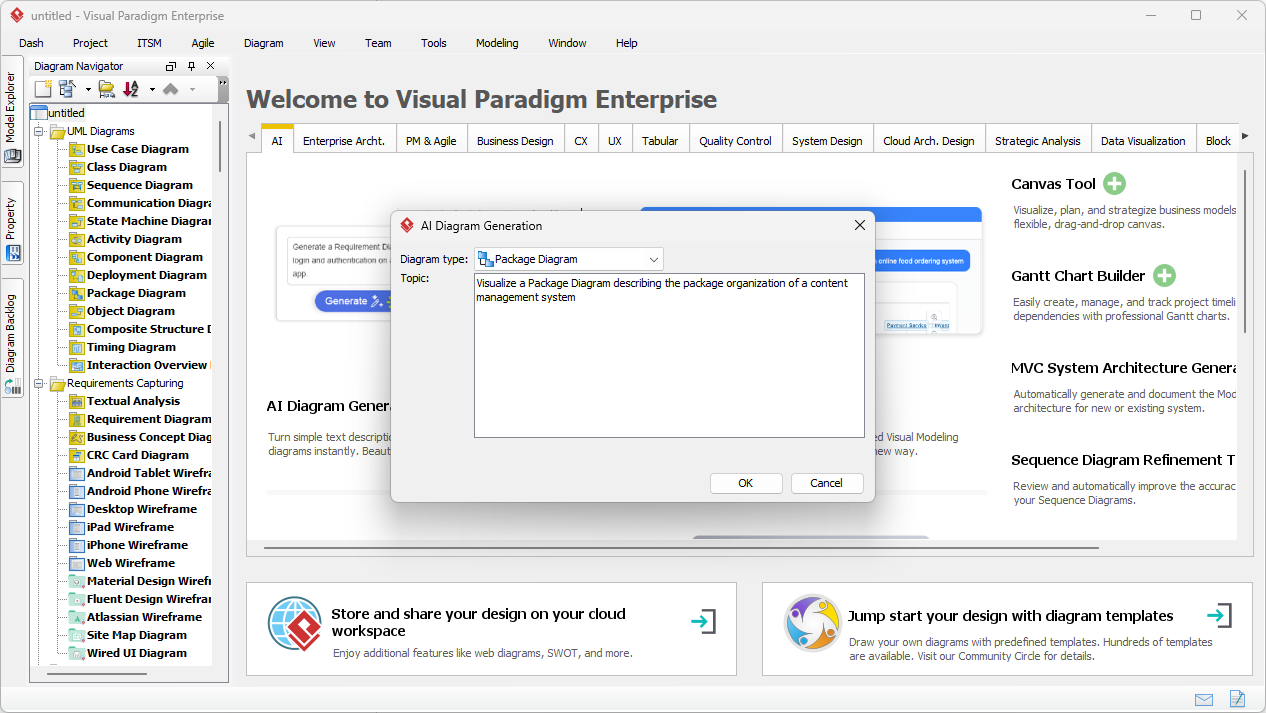
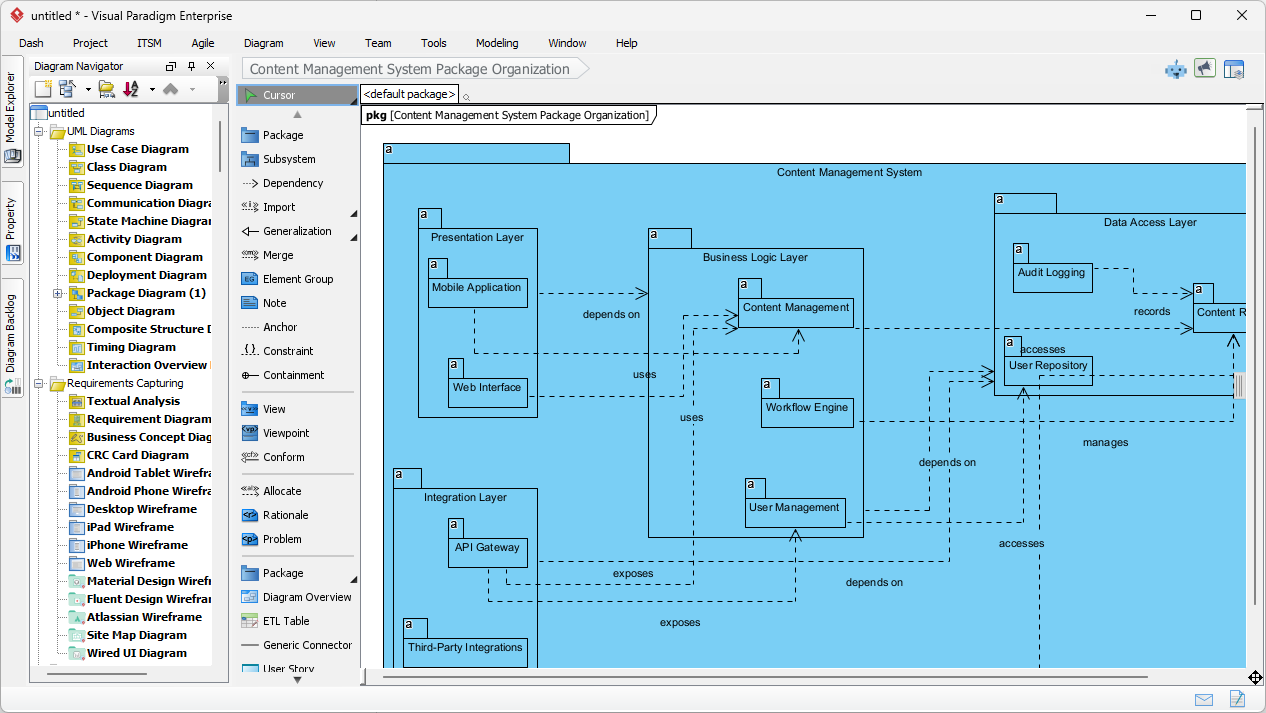
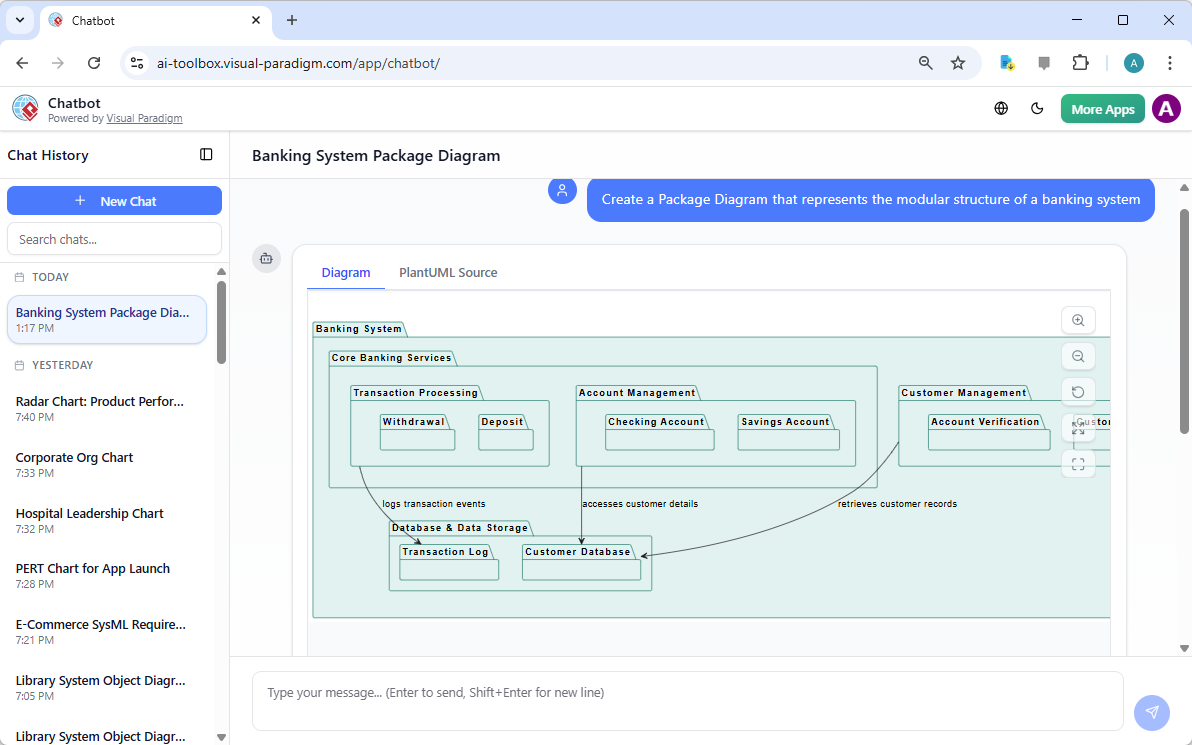
Trong thế giới kỹ thuật phần mềm và kiến trúc doanh nghiệp với nhịp độ nhanh ngày nay, chuyển đổi các yêu cầu trừu tượng thành các thiết kế chính xác và có thể hành động vẫn là một thách thức. Các mô hình ngôn ngữ quy mô lớn (LLMs) chuyên dụng thường xuất sắc trong việc phát ý tưởng và tạo văn bản, nhưng lại gặp khó khăn trong việc mô hình hóa trực quan chuyên nghiệp. Chúng tạo ra những bản phác thảo thay vì bản vẽ kỹ thuật chi tiết. Hệ sinh thái được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm thay đổi điều này bằng cách cung cấp các công cụ vẽ sơ đồ chuẩn mực, bền vững và lặp lại, giúp đẩy nhanh quá trình kiến trúc từ ý tưởng đến triển khai.
1. Vấn đề ‘Nghệ sĩ phác thảo’: Những hạn chế của các mô hình LLM AI casual
Các công cụ AI casual (ví dụ: ChatGPT, Claude) coi việc vẽ sơ đồ như một phần mở rộng của việc tạo văn bản. Chúng xuất ra mã theo các định dạng nhưMermaid hoặc PlantUML, nhưng thiếu chiều sâu để sử dụng chuyên nghiệp.
Những hạn chế chính bao gồm:
- Không có bộ xử lý hiển thị hoặc trình chỉnh sửa tích hợpCác mô hình LLM tạo ra cú pháp dựa trên văn bản (ví dụ: mã sơ đồ luồng Mermaid), nhưng không cung cấp trình xem hoặc trình chỉnh sửa tích hợp cho các đồ họa vector chất lượng cao (SVG). Người dùng phải dán mã vào các công cụ hiển thị bên ngoài, làm mất tính tương tác. Mọi thay đổi đều yêu cầu tái tạo toàn bộ.
- Sai sót về ngữ nghĩa và vi phạm chuẩnCác mô hình chung hiểu sai các khái niệm UML/ArchiMate. Ví dụ, chúng nhầm lẫnsự tích hợp (sở hữu chung) vớisự kết hợp (sở hữu riêng), hoặc vẽ các mũi tên kế thừa không hợp lệ. Kết quả trông hấp dẫn nhưng không thể dùng như tài liệu kỹ thuật—ví dụ, một sơ đồ lớp có thể thể hiện các mối quan hệ hai chiều trong khi chỉ cần một chiều là đúng.
- Thiếu trạng thái bền vững và cập nhật từng bướcMỗi lời nhắc đều tái tạo sơ đồ từ đầu. Yêu cầu “thêm xử lý lỗi vào sơ đồ tuần tự này” thường làm hỏng bố cục, mất các kết nối hoặc quên các thành phần trước đó. Không có bộ nhớ về cấu trúc trực quan nào tồn tại.
Ví dụ: Yêu cầu ChatGPT tạo một “sơ đồ lớp UML của hệ thống ngân hàng trực tuyến với tài khoản, giao dịch và xác thực hai yếu tố” sẽ cho ra mã Mermaid. Khi thêm “bao gồm mô-đun phát hiện gian lận”, toàn bộ sơ đồ sẽ được tái tạo—có thể sắp xếp lại các lớp, bỏ mất các mối quan hệ hoặc tạo lỗi cú pháp.
Những vấn đề này tạo ra những bức tranh đẹp mắt thay vì các mô hình có thể duy trì.
2. Những vấn đề thực tế khi phụ thuộc vào việc vẽ sơ đồ bằng AI casual
Việc sử dụng các mô hình LLM chung sẽ tạo ra các rủi ro làm suy giảm chất lượng dự án:
- Khoảng cách giữa thiết kế và triển khaiCác hình ảnh mơ hồ hoặc sai lệch dẫn đến mã nguồn không đồng bộ. Các nhóm phải tốn thời gian trong các cuộc họp để làm rõ ý định vì sơ đồ thiếu độ chính xác.
- Phụ thuộc vào cú pháp và rào cản về chuyên mônViệc chỉnh sửa Mermaid/PlantUML đòi hỏi phải học cú pháp chuyên biệt—điều mỉa mai đối với các công cụ “hỗ trợ bởi AI”. Người không chuyên gặp khó khăn khi sửa chữa thủ công.
- Tách biệt quy trình làm việcCác sơ đồ là hình ảnh tĩnh hoặc đoạn mã, tách rời khỏi kiểm soát phiên bản, hợp tác hoặc các công việc tiếp theo (ví dụ: sinh mã, sơ đồ cơ sở dữ liệu).
- Thất bại với lời nhắc ‘một lần’Các hệ thống phức tạp cần phải lặp lại. Người dùng chỉ phát hiện các thiếu sót (ví dụ: thiếu cân bằng tải, lớp bộ nhớ đệm hoặc luồng xử lý ngoại lệ) sau khi nhận được đầu ra đầu tiên, nhưng việc tái tạo lại sẽ làm mất đi tiến độ đã đạt được.
Ví dụ: Trong các buổi phỏng vấn thiết kế hệ thống hoặc các buổi họp kiến trúc ban đầu, các nhà phát triển sử dụng ChatGPT để tạo sơ đồ mô hình C4 thông qua Mermaid. Các đầu ra ban đầu bỏ sót các ranh giới hoặc mối quan hệ quan trọng. Việc nhắc nhở lặp lại dẫn đến các phiên bản không nhất quán, gây thất vọng cho đội ngũ và làm chậm quyết định.
3. Visual Paradigm AI mang đến mô hình hóa chất lượng chuyên nghiệp như thế nào
Visual Paradigm biến việc vẽ sơ đồ thành mộtquá trình đối thoại, dựa trên tiêu chuẩn và tích hợpquá trình. Trí tuệ nhân tạo của nó hiểu được UML 2.5, ArchiMate 3, C4, BPMN, SysML và nhiều hơn nữa, tạo ra các mô hình tuân thủ và có thể chỉnh sửa.
A. Cấu trúc bền vững với công nghệ ‘Chỉnh sửa sơ đồ’
VP duy trì các sơ đồ nhưcác đối tượng sống động. Người dùng đưa ra lệnh bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên để cập nhật các phần cụ thể mà không cần tái tạo lại.
- Chỉnh sửa theo cách đối thoại: ‘Thêm bước xác thực hai yếu tố sau khi đăng nhập’ hoặc ‘Đổi tên tác nhân Khách hàng thành Người dùng’ sẽ ngay lập tức điều chỉnh bố cục, kết nối và ngữ nghĩa mà vẫn giữ nguyên tính toàn vẹn.
Điều này loại bỏ các liên kết bị hỏng và hỗn loạn về bố cục thường gặp trong các công cụ thông thường.
B. Trí tuệ tuân thủ tiêu chuẩn
Được huấn luyện trên các ký hiệu chính thức, AI của VP thực thi các quy tắc:
- Số lượng đúng trong các mối quan hệ
- Sử dụng đúng các kiểu đặc trưng
- Các quan điểm ArchiMate hợp lệ (ví dụ: Bản đồ năng lực, Sử dụng công nghệ)
Các sơ đồ là những ‘bản vẽ kỹ thuật’ vững chắc thay vì những bản phác sơ sài.
C. Phân tích và hướng dẫn theo từng bước hệ thống
VP cung cấp các ứng dụng có cấu trúc để nối kết yêu cầu với thiết kế:
-
Phân tích văn bản được hỗ trợ AI — Phân tích văn bản không cấu trúc (ví dụ: tài liệu yêu cầu, câu chuyện người dùng) để trích xuất các lớp, thuộc tính, thao tác và mối quan hệ tiềm năng. Nó tự động tạo sơ đồ lớp ban đầu.
Ví dụ: Nhập mô tả: ‘Một nền tảng thương mại điện tử cho phép khách hàng duyệt sản phẩm, thêm vào giỏ hàng, thanh toán qua cổng thanh toán và theo dõi đơn hàng.’ AI xác định các lớp (Khách hàng, Sản phẩm, Giỏ hàng, Đơn hàng, Cổng thanh toán), thuộc tính (ví dụ: giá, số lượng) và các mối quan hệ (Khách hàng đặt Đơn hàng).
-
Bộ công cụ AI 10 bước (dành cho sơ đồ lớp UML và tương tự) — Hướng dẫn người dùng một cách logic: xác định mục đích → phạm vi → lớp → thuộc tính → mối quan hệ → thao tác → xem xét → tạo. Xác minh có sự tham gia của con người giúp ngăn ngừa lỗi do một lần nhắc nhở.
D. AI như một cố vấn kiến trúc
Không chỉ dừng lại ở việc tạo ra, AI của VP còn đánh giá các thiết kế:
- Phát hiện các điểm lỗi đơn lẻ
- Xác định các khoảng trống về logic
- Gợi ý các mẫu (ví dụ: MVC, Repository, Observer)
Nó hoạt động như một chuyên gia đánh giá.
E. Tích hợp liền mạch vào các quy trình làm việc chuyên nghiệp
Các mô hình không phải là những hình ảnh tách biệt:
- Có thể chỉnh sửa hoàn toàn trên Visual Paradigm Desktop/Online
- Hỗ trợ quản lý phiên bản và hợp tác
- Cho phép kỹ thuật mã hóa (ví dụ: tạo mã Java/Hibernate ORM, lược đồ cơ sở dữ liệu)
- Xuất/nhập giữa các công cụ
Điều này khép kín vòng từ thiết kế đến mã hóa.
Ví dụ: Tạo một góc nhìn ArchiMate cho “Lớp Công nghệ” thông qua lời nhắc: “Tạo sơ đồ ArchiMate cho kiến trúc microservices dựa trên đám mây với các thành phần AWS.” AI sẽ tạo ra một sơ đồ tuân thủ chuẩn. Sử dụng tính năng “Chỉnh sửa sơ đồ” để thêm các kiểm soát bảo mật. Xuất ra máy tính để bàn để nhóm xem xét và sinh mã.
Kết luận: Từ việc đục đẽo thủ công đến in 3D được hỗ trợ bởi AI
Việc vẽ sơ đồ truyền thống giống như đục đá cẩm thạch—chậm, dễ sai sót và không thể đảo ngược. Các mô hình AI LLM thông thường cải thiện tốc độ nhưng vẫn chỉ là “nghệ sĩ phác họa”, tạo ra hình ảnh không nhất quán và không bền vững.
Visual Paradigm AI giống như một máy in 3D độ chính xác cao: nhập các yêu cầu bằng tiếng Anh thuần túy, nhận được các cấu trúc tuân thủ chuẩn, có thể chỉnh sửa, tương tác theo cách trò chuyện, và trực tiếp thúc đẩy triển khai. Bằng cách tích hợp mô hình hóa kinh doanh, doanh nghiệp và kỹ thuật trong một nền tảng được hỗ trợ AI, nó loại bỏ trạng thái bế tắc khi bắt đầu từ trang trắng và đảm bảo các bên liên quan chia sẻ một cơ sở chuẩn xác và có thể hành động.
Đối với các kiến trúc sư phần mềm, các đội ngũ doanh nghiệp và nhà phát triển mệt mỏi vì phải tái tạo các đoạn mã Mermaid bị hỏng, Visual Paradigm đại diện cho bước tiến tiếp theo: mô hình hóa thông minh tuân thủ chuẩn, bảo tồn ý định và đẩy nhanh tiến độ.
-
Khám phá sức mạnh của Visual Paradigm với AI -Powered… – Visualize AI: Trình dịch hình ảnh được hỗ trợ AI của Visual Paradigm dẫn đầu thị trường nhờ các khả năng tiên tiến vượt xa các công cụ tiêu chuẩn.
-
Trợ lý ảo AI cho vẽ sơ đồ: Cách hoạt động với Visual Paradigm: Trợ lý ảo AI chuyển đổi ngôn ngữ tự nhiên thành sơ đồ, loại bỏ nhu cầu học ngữ pháp hoặc chuẩn mô hình hóa.
-
Tính năng Brainstorming bằng AI – Visual Paradigm: Các công cụ brainstorming được hỗ trợ AI của Visual Paradigm mang đến quá trình sinh ý tưởng thông minh và quy trình làm việc hợp tác để nâng cao sự sáng tạo và năng suất.
-
Công cụ Brainstorming bằng AI – Visual Paradigm AI: Tạo và sắp xếp ý tưởng nhanh chóng với các thông tin được hỗ trợ AI và mẫu thông minh trong công cụ Brainstorming bằng AI của Visual Paradigm.
-
Công cụ tinh chỉnh sơ đồ trường hợp sử dụng được hỗ trợ AI – Nâng cấp sơ đồ thông minh: Tinh chỉnh được hỗ trợ AI giúp cải thiện độ rõ ràng, tính nhất quán và tính đầy đủ của sơ đồ trường hợp sử dụng.
-
Chuyển đổi sơ đồ trường hợp sử dụng thành sơ đồ hoạt động – Chuyển đổi được hỗ trợ AI: Tự động chuyển đổi sơ đồ trường hợp sử dụng thành sơ đồ hoạt động chi tiết để trực quan hóa luồng công việc hệ thống.
-
Trình tạo sơ đồ lớp UML được hỗ trợ AI – Visual Paradigm: Tạo sơ đồ lớp UML với các gợi ý được hỗ trợ bởi AI, kiểm tra tính hợp lệ, xuất sang PlantUML và phân tích thiết kế.
-
Thành thạo sơ đồ hoạt động UML với AI | Blog Visual Paradigm: Khám phá cách các tính năng AI trong Visual Paradigm nâng cao quá trình tạo và tối ưu hóa sơ đồ hoạt động UML dành cho nhà phát triển và chuyên gia phân tích.
-
: Cách mạng hóa bài thuyết trình của bạn: Gặp gỡ Công cụ tạo bài thuyết trình Markdown AI của Visual Paradigm!: Chuyển đổi ý tưởng thô thành các bài thuyết trình được hoàn thiện, có hoạt hình bằng cách sử dụng đầu vào Markdown được hỗ trợ bởi AI.
-
Lumina AI: Tạo ngay các slideshow video được hỗ trợ bởi AI: Tạo các bài thuyết trình video động từ văn bản bằng AI, lý tưởng cho kể chuyện và tạo nội dung nhanh chóng.
-
Công cụ tạo slideshow Lumina AI: Tạo các bài thuyết trình ấn tượng với AI: Tạo các slide chất lượng chuyên nghiệp từ văn bản đơn giản bằng trí tuệ nhân tạo để tiết kiệm thời gian và khơi gợi sự sáng tạo.
-
Công cụ tạo slideshow Illumy AI: Tạo bài thuyết trình ngay lập tức với AI: Tạo các slide chuyên nghiệp, phong phú về hình ảnh trong vài giây bằng AI, được thiết kế riêng cho các chuyên gia tiếp thị, giáo viên và chuyên gia kinh doanh.
-
Studio thuyết trình AI có hoạt hình: Tạo các slide động, có hoạt hình một cách dễ dàng: Thiết kế các bài thuyết trình hấp dẫn, có hoạt hình với kể chuyện được hỗ trợ bởi AI, chuyển động và hiệu ứng hình ảnh.
-
Làm thế nào để cấu trúc danh sách công việc Jira ngay lập tức với Agilien AI: Tự động hóa việc cấu trúc danh sách công việc Jira bằng cách phân tích các câu chuyện người dùng và tạo các đợt phát hành và các dự án lớn được tổ chức nhờ Agilien AI.
-
Kế hoạch viên danh sách công việc Jira được hỗ trợ bởi AI – Visual Paradigm: Tự động hóa và cải thiện việc lập kế hoạch danh sách công việc Jira với Agilien AI, giúp tổ chức thông minh các câu chuyện người dùng và các dự án lớn cho các đợt phát hành hiệu quả.
-
Làm thế nào để tạo các bài thuyết trình có hoạt hình ấn tượng với Công cụ tạo bài thuyết trình Markdown AI của Visual Paradigm: Tạo các bài thuyết trình động, thu hút về mặt hình ảnh bằng cách sử dụng công cụ Markdown được hỗ trợ bởi AI trong Visual Paradigm.
-
Giới thiệu Studio thuyết trình AI có hoạt hình – Một kỷ nguyên mới trong kể chuyện hình ảnh: Tạo các bài thuyết trình có hoạt hình được nâng cao bởi AI một cách dễ dàng với Studio thuyết trình có hoạt hình AI của Visual Paradigm.
-
Visual Paradigm Online – Công cụ tạo bài thuyết trình được hỗ trợ bởi AI dành cho người sáng tạo hiện đại: Công cụ tạo bài thuyết trình được điều khiển bởi AI của Visual Paradigm Online cung cấp một công cụ mạnh mẽ cho các chuyên gia và giáo viên để tạo các bài thuyết trình động, chuyên nghiệp một cách dễ dàng.
-
Hướng dẫn hoàn chỉnh: Bản đồ quy trình kinh doanh được hỗ trợ bởi AI với Visual Paradigm: Học cách sử dụng các tính năng được hỗ trợ bởi AI trong Visual Paradigm để bản đồ hóa quy trình kinh doanh nhanh hơn và chính xác hơn.
-
Hướng dẫn tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm: Hướng dẫn từng bước sử dụng các công cụ được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm để tạo sơ đồ nhanh chóng và chính xác.
-
Tính năng tạo sơ đồ AI trong Visual Paradigm: Các khả năng AI nâng cao trong Visual Paradigm cho phép tạo sơ đồ từ mô tả bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên.
-
Ghi chú phát hành Công cụ tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm: Cập nhật mới nhất và cải tiến cho tính năng tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm.
-
Tính năng tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm mở rộng khả năng tạo tức thì: Bộ tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm hiện hỗ trợ tạo tức thì các sơ đồ luồng dữ liệu (DFD), sơ đồ quan hệ thực thể (ERD), sơ đồ tư duy và nhiều loại khác.
-
Các loại sơ đồ mới được thêm vào bộ tạo sơ đồ AI: DFD và ERD: Hỗ trợ tạo sơ đồ AI mở rộng cho Sơ đồ luồng dữ liệu (DFD) và Sơ đồ quan hệ thực thể (ERD).
-
Bộ tạo sơ đồ AI hiện hỗ trợ sơ đồ gói trong Visual Paradigm: Phiên bản mới cho phép tạo sơ đồ gói bằng AI nhằm cải thiện khả năng trực quan hóa kiến trúc phần mềm.
-
Bộ tạo sơ đồ AI bổ sung hỗ trợ biểu đồ radar: Visual Paradigm giới thiệu tính năng tạo biểu đồ radar được hỗ trợ bởi AI để trực quan hóa các chỉ số hiệu suất và năng lực phức tạp.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện: Tạo sơ đồ ArchiMate bằng AI: Học cách tạo sơ đồ ArchiMate và các góc nhìn một cách hiệu quả bằng bộ tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm.
-
Từ mô tả vấn đề đến sơ đồ lớp: Phân tích văn bản được hỗ trợ bởi AI: Chuyển đổi mô tả vấn đề bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên thành sơ đồ lớp chính xác bằng cách sử dụng phân tích văn bản được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm.
-
Làm thế nào để dịch văn bản trong hình ảnh cho UML, BPMN và sơ đồ luồng: Sử dụng công cụ AI để trích xuất và dịch văn bản trong các sơ đồ kỹ thuật nhằm hỗ trợ hợp tác toàn cầu và địa phương hóa.
-
Công cụ phân tích văn bản AI của Visual Paradigm: Chuyển đổi đầu vào bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên thành các sơ đồ có cấu trúc cho thiết kế phần mềm, tài liệu và mô hình hóa hệ thống.
-
Giới thiệu về việc lựa chọn giữa AI tạo nội dung và AI của Visual Paradigm cho việc tạo sơ đồ: Bài viết này giúp người dùng hiểu được những điểm khác biệt chính giữa AI tạo nội dung thông thường và AI của Visual Paradigm, hướng dẫn họ lựa chọn công cụ phù hợp để tạo sơ đồ một cách hiệu quả và chính xác.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện về bộ tạo bảng AI của Visual Paradigm: Từ ngôn ngữ tự nhiên đến mã thực thi: Chuyển đổi ngôn ngữ tự nhiên thành các bảng cơ sở dữ liệu chức năng và mã thực thi bằng bộ động cơ tạo bảng AI của Visual Paradigm.
-
Nghiên cứu trường hợp: Nâng cao hiệu quả mô hình hóa hệ thống với chatbot được hỗ trợ AI của Visual Paradigm: Nâng cao hiệu quả và độ chính xác trong mô hình hóa hệ thống với chatbot AI của Visual Paradigm cho việc tạo sơ đồ theo cách trò chuyện.
-
Làm thế nào để tạo sơ đồ triển khai UML cho ứng dụng đám mây bằng AI: Hướng dẫn từng bước sử dụng các công cụ được hỗ trợ AI để tạo sơ đồ triển khai UML hiệu quả cho các ứng dụng đám mây.
-
Phát hiện thông tin với học sâu và xử lý ngôn ngữ tự nhiên trên Azure – Mẫu: Xây dựng các hệ thống thông minh có khả năng trích xuất thông tin từ dữ liệu không cấu trúc bằng học sâu và xử lý ngôn ngữ tự nhiên với mẫu Azure nâng cao này.
-
Chinh phục các sơ đồ trường hợp sử dụng được dẫn dắt bởi AI với Visual Paradigm: Một hướng dẫn về việc sử dụng các tính năng AI trong Visual Paradigm để tạo các sơ đồ trường hợp sử dụng thông minh, động cho các hệ thống phần mềm hiện đại.
-
Tạo biểu đồ radar được hỗ trợ AI trên Desktop của Visual Paradigm: Học cách tạo biểu đồ radar thông minh, dựa trên dữ liệu bằng các tính năng AI trong Visual Paradigm Desktop để tăng cường trực quan hóa phân tích.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện: Sử dụng Công cụ tạo kế hoạch phát triển AI của Visual Paradigm: Sử dụng công cụ được hỗ trợ AI của Visual Paradigm để tạo các kế hoạch phát triển chi tiết và chiến lược cho các dự án phần mềm và AI.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện về trực quan hóa Mô hình C4 bằng các công cụ AI của Visual Paradigm: Tận dụng các công cụ được hỗ trợ AI trong Visual Paradigm để tự động hóa và nâng cao trực quan hóa mô hình C4 nhằm thiết kế kiến trúc thông minh hơn.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện về dịch văn bản trong sơ đồ kỹ thuật bằng AI: Chỉ ra cách công cụ Dịch ảnh AI của Visual Paradigm tự động hóa việc dịch chính xác văn bản trong UML, BPMN và sơ đồ luồng.
-
Bài đánh giá toàn diện về các tính năng tạo sơ đồ bằng AI của Visual Paradigm: Đánh giá khả năng tạo sơ đồ từ ngôn ngữ tự nhiên với độ chính xác và tốc độ cao của AI Visual Paradigm.
-
Trình chỉnh sửa User Story 3Cs được hỗ trợ AI: Nâng cao độ rõ ràng và tính đầy đủ: Công cụ được hỗ trợ AI giúp các đội Agile viết các câu chuyện người dùng hiệu quả bằng khung 3Cs: Thẻ, Cuộc trò chuyện và Xác nhận.
-
Trình tạo biểu đồ Gantt được hỗ trợ AI – Công cụ lập kế hoạch dự án tức thì: Công cụ được hỗ trợ AI tạo biểu đồ Gantt từ đầu vào nhiệm vụ đơn giản, giúp lập lịch thông minh và lập kế hoạch trực quan.
-
Trực quan hóa các ý tưởng phức tạp bằng sơ đồ cây được hỗ trợ AI: Các công cụ sơ đồ cây được điều khiển bởi AI giúp người dùng phân tích ý tưởng phức tạp thành các cấu trúc trực quan rõ ràng để hiểu tốt hơn.
-
Trình tạo sơ đồ xương cá được hỗ trợ AI – Phát hiện nguyên nhân gốc rễ trong vài giây: Công cụ được hỗ trợ AI tự động hóa việc tạo sơ đồ xương cá để tăng tốc phân tích nguyên nhân gốc rễ và ra quyết định.
-
Tạo sơ đồ được hỗ trợ AI: Các tính năng mới cho sơ đồ thời gian UML: Tính năng được hỗ trợ AI của Visual Paradigm cho phép tạo tự động sơ đồ thời gian UML để mô hình hóa nhanh hơn và chính xác hơn.
-
Giới thiệu Trình tạo quan điểm ArchiMate được hỗ trợ AI trong Visual Paradigm: Tự động hóa mô hình hóa kiến trúc doanh nghiệp bằng cách tạo quan điểm ArchiMate dựa trên AI nhằm nâng cao độ chính xác và hiệu quả.
-
Trợ lý AI Visual Paradigm: Trợ lý AI chuyên dụng đầu tiên trên thế giới cho mô hình hóa trực quan: Trợ lý AI của Visual Paradigm cho phép tương tác bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên để hướng dẫn người dùng thực hiện các nhiệm vụ mô hình hóa trực quan.
-
AI nâng cao việc tạo sơ đồ lớp trong Visual Paradigm như thế nào: AI nâng cao việc tạo sơ đồ lớp bằng cách tự động hóa thiết kế và cải thiện độ chính xác với đầu vào người dùng tối thiểu.
-
Tinh chỉnh sơ đồ tuần tự được hỗ trợ AI trong Visual Paradigm: Chuyển đổi mô tả trường hợp sử dụng thành các sơ đồ tuần tự chính xác, chuyên nghiệp bằng cách tinh chỉnh nhờ AI.
-
Làm đơn giản hóa sơ đồ lớp với AI của Visual Paradigm: Các công cụ AI trong Visual Paradigm giảm thời gian và độ phức tạp khi tạo sơ đồ lớp chính xác cho các dự án phần mềm.
-
Trình tạo kiến trúc hệ thống MVC được hỗ trợ AI bởi Visual Paradigm: Tự động tạo ra các kiến trúc hệ thống MVC mở rộng và sạch sẽ bằng cách sử dụng mô hình hóa dựa trên AI trong Visual Paradigm.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện: Tạo sơ đồ ArchiMate được hỗ trợ bởi AI trong Visual Paradigm Desktop: Tạo các sơ đồ ArchiMate chuyên nghiệp một cách hiệu quả bằng cách sử dụng công nghệ tạo hình dựa trên AI trong Visual Paradigm Desktop.
-
Giới thiệu trợ lý chatbot AI của Visual Paradigm: Hỗ trợ thiết kế thông minh: Trợ lý chatbot AI của Visual Paradigm nâng cao quy trình thiết kế nhờ các gợi ý thời gian thực và tự động hóa các nhiệm vụ lặp lại.
-
Tận dụng Visual Paradigm AI C4 Studio để chuẩn hóa tài liệu kiến trúc hệ thống: Sử dụng C4 Studio được nâng cấp bởi AI để tạo tài liệu kiến trúc phần mềm sạch sẽ, dễ mở rộng và dễ bảo trì.
-
Mô hình kinh doanh là gì? Tại sao nên sử dụng các mô hình trực quan và công cụ AI?: Hướng dẫn này giải thích Mô hình Kinh doanh và cách các mô hình trực quan cùng công cụ AI nâng cao quá trình lập kế hoạch chiến lược và đổi mới.
-
Hướng dẫn phân tích văn bản được hỗ trợ bởi AI cho thiết kế phần mềm với Visual Paradigm: Học cách sử dụng phân tích văn bản được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm để trích xuất các yếu tố thiết kế phần mềm từ các yêu cầu bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên.
-
Xác định các lớp miền sử dụng phân tích văn bản AI trong Visual Paradigm: Tự động xác định các lớp miền từ văn bản bằng công cụ AI của Visual Paradigm để tối ưu hóa quy trình mô hình hóa phần mềm.
-
Hộp công cụ AI của Visual Paradigm: Công cụ phân tích văn bản cho mô hình hóa phần mềm: Chuyển đổi văn bản không cấu trúc thành các mô hình phần mềm có cấu trúc bằng cách xác định các thực thể, mối quan hệ và các khái niệm chính nhờ AI.
-
Phần mềm bảng điểm cân bằng được hỗ trợ bởi AI cho lập kế hoạch chiến lược: Tận dụng thông tin được hỗ trợ bởi AI để xây dựng và quản lý bảng điểm cân bằng nhằm thực hiện chiến lược hiệu quả.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện về công cụ xây dựng sơ đồ hiệu suất KPI được hỗ trợ bởi AI: Một hướng dẫn về việc sử dụng công cụ được hỗ trợ bởi AI để tạo các sơ đồ hiệu suất KPI động, thời gian thực nhằm hỗ trợ ra quyết định dựa trên dữ liệu.
-
Hiểu rõ sơ đồ hiệu suất KPI được hỗ trợ bởi AI dành cho một quán cà phê: Một ví dụ thực tế về cách các doanh nghiệp nhỏ, như quán cà phê, có thể sử dụng sơ đồ KPI được hỗ trợ bởi AI để theo dõi doanh số, hành vi khách hàng và hoạt động kinh doanh.
-
Trình tạo cấu trúc phân tích rủi ro được hỗ trợ bởi AI: Đơn giản hóa quản lý rủi ro chủ động: Một công cụ được hỗ trợ bởi AI trong Visual Paradigm giúp tự động hóa việc tạo cấu trúc phân tích rủi ro nhằm nhận diện và quản lý rủi ro một cách chủ động.
-
Các ví dụ thực tế về cấu trúc phân tích rủi ro được tạo bởi AI: Khám phá các ứng dụng thực tế của cấu trúc phân tích rủi ro được hỗ trợ bởi AI trong lĩnh vực CNTT, xây dựng và tài chính nhằm nâng cao độ chính xác và hiệu quả đánh giá rủi ro.
-
Giảm thiểu rủi ro: Xây dựng các chiến lược W.T. hiệu quả với AI: Sử dụng thông tin được hỗ trợ bởi AI để xây dựng các chiến lược phản ứng với tình huống xấu nhất và mối đe dọa mạnh mẽ, nhằm tăng tính bền vững cho lập kế hoạch và thực hiện dự án.
-
Sử dụng AI để đánh giá rủi ro trong Ma trận Ansoff cho tăng trưởng chiến lược: Áp dụng AI để đánh giá rủi ro trong Ma trận Ansoff, giúp ra quyết định dựa trên dữ liệu cho mở rộng thị trường và chiến lược sản phẩm.
-
Phân tích tình huống được hỗ trợ bởi AI cho lập kế hoạch kinh doanh chiến lược: Sử dụng phân tích kịch bản dựa trên AI để mô hình hóa các kết quả tương lai, đánh giá rủi ro và hỗ trợ ra quyết định chiến lược trong kinh doanh.
-
Công cụ trực quan được hỗ trợ bởi AI để tạo biểu đồ thông tin, biểu đồ và đồ họa: Tạo nhanh chóng các biểu đồ thông tin, biểu đồ và đồ họa chuyên nghiệp bằng các công cụ được hỗ trợ bởi AI, cung cấp gợi ý thiết kế thông minh và tự động hóa.
-
Visual Paradigm giới thiệu công cụ biểu đồ thông tin AI-3 chiều nhằm nâng cao hiệu quả thiết kế: Khám phá công cụ biểu đồ thông tin AI-3 chiều, với ba chiều thiết kế thông minh nhằm tăng cường sự sáng tạo và tối ưu hóa quá trình tạo nội dung.
-
Visual Paradigm ra mắt nhà thiết kế biểu đồ thông tin AI-8 chiều cho sáng tạo hình ảnh nâng cao: Tận dụng nhà thiết kế biểu đồ thông tin AI-8 chiều với tám tính năng thiết kế thông minh giúp tăng tốc và nâng cao chất lượng nội dung hình ảnh.
-
Thành thạo sơ đồ tuần tự với Visual Paradigm: Hướng dẫn chatbot AI: Hướng dẫn dành cho người mới bắt đầu về việc tạo sơ đồ tuần tự trong Visual Paradigm bằng ví dụ về chatbot thương mại điện tử.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện: Sử dụng công cụ tạo sơ đồ AI của Visual Paradigm: Hướng dẫn từng bước sử dụng công cụ tạo sơ đồ được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm để tạo sơ đồ một cách hiệu quả.
-
Visual Paradigm AI: Tối ưu hóa việc tạo sơ đồ nhờ AI: Hướng dẫn này minh họa cách các tính năng AI của Visual Paradigm cho phép tạo và hoàn thiện sơ đồ phần mềm theo thời gian thực.
-
Sonix – Dịch vụ chuyển văn bản từ giọng nói bằng AI: Sonix sử dụng AI để cung cấp dịch vụ chuyển văn bản nhanh chóng và chính xác từ âm thanh và video cho các cuộc họp, phỏng vấn và sản xuất nội dung.
-
Thành thạo việc chuyển đổi sơ đồ với công cụ chuyển ảnh AI của Visual Paradigm: Hướng dẫn sử dụng công cụ chuyển ảnh thành sơ đồ được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm Online để chuyển đổi các sơ đồ vẽ tay hoặc dựa trên hình ảnh thành các mô hình có thể chỉnh sửa.
-
Click-Start AI: Tích hợp AI nhanh chóng cho người dùng Visual Paradigm: Hướng dẫn từng bước để kích hoạt và sử dụng các tính năng AI trong Visual Paradigm nhằm tăng tốc quá trình tạo sơ đồ nhờ tự động hóa thông minh.
-
Hướng dẫn chuyển ảnh được hỗ trợ bởi AI cho Visual Paradigm Online: Hướng dẫn sử dụng công cụ chuyển ảnh được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm Online để tự động chuyển nội dung hình ảnh thành các sơ đồ và mô hình có cấu trúc.
-
LinkVP – Nền tảng quản lý liên kết và phân tích được hỗ trợ bởi AI: LinkVP cung cấp nền tảng được điều khiển bởi AI để tạo, theo dõi và tối ưu hóa các liên kết tùy chỉnh với phân tích thời gian thực và tùy chỉnh nâng cao.
-
Top công cụ tạo sơ đồ năm 2024: Hướng dẫn toàn diện từ WritingMate AI: Tổng quan về các công cụ tạo sơ đồ được hỗ trợ bởi AI hàng đầu, làm nổi bật các tính năng chính, tính dễ sử dụng và ứng dụng lý tưởng dành cho chuyên gia và người sáng tạo.
-
MyMap AI – Công cụ tạo sơ đồ thông minh với đầu vào bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên: MyMap AI tạo ngay các sơ đồ chuyên nghiệp từ các yêu cầu văn bản, kết hợp trí tuệ nhân tạo với thiết kế trực quan để lập kế hoạch dễ dàng.
-
DiagrammingAI – Tạo sơ đồ bằng AI thế hệ tiếp theo dành cho đội nhóm và cá nhân: DiagrammingAI sử dụng trí tuệ nhân tạo để nhanh chóng biến ý tưởng thành các sơ đồ hoàn chỉnh với sự hợp tác theo thời gian thực và gợi ý bố cục thông minh.
-
Tại sao công cụ chuyển ảnh được hỗ trợ bởi AI của Visual Paradigm… – Visualize AI: Trình dịch hình ảnh được tích hợp AI của Visual Paradigm cung cấp dịch hình ảnh chuyên nghiệp, nâng cao cho các quy trình kỹ thuật và thiết kế.
-
Trình tạo sơ đồ cây AI | Trực quan hóa dữ liệu phân cấp ngay lập tức: Tạo các sơ đồ phân cấp chuyên nghiệp như sơ đồ tư duy, sơ đồ tổ chức và sơ đồ phân tích công việc ngay lập tức bằng AI thông qua việc mô tả chủ đề của bạn.
-
Tích hợp sơ đồ hoạt động AI vào Visual Paradigm của bạn …: Tạo và hoàn thiện các sơ đồ hoạt động UML bằng đầu vào ngôn ngữ tự nhiên thông qua mô hình hóa được hỗ trợ AI trong Visual Paradigm.
-
AI sơ đồ hoạt động – Visual Paradigm Online: Khám phá bộ sưu tập toàn cầu các sơ đồ hoạt động do người dùng tạo ra để lấy cảm hứng và ý tưởng thiết kế chuyên nghiệp.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện về các công cụ vẽ sơ đồ được hỗ trợ AI (2025): Khám phá cách các công cụ vẽ sơ đồ được hỗ trợ AI đang cách mạng hóa giao tiếp trực quan nhờ vào tự động hóa thông minh và tính dễ sử dụng.
-
Trình tạo sơ đồ lớp UML được hỗ trợ AI bởi Visual Paradigm: Tạo các sơ đồ lớp UML chính xác từ mô tả bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên bằng cách sử dụng tự động hóa hỗ trợ AI.
-
Nghiên cứu trường hợp thực tế: Tạo sơ đồ lớp UML bằng AI của Visual Paradigm: Một dự án thực tế minh họa cách trợ lý AI của Visual Paradigm chuyển đổi các yêu cầu văn bản thành các sơ đồ lớp UML chính xác.
-
Hướng dẫn toàn diện: Tạo sơ đồ lớp UML bằng trợ lý AI của Visual Paradigm: Học cách tạo các sơ đồ lớp UML chính xác từ văn bản thuần túy bằng trợ lý AI của Visual Paradigm Online thông qua hướng dẫn từng bước.