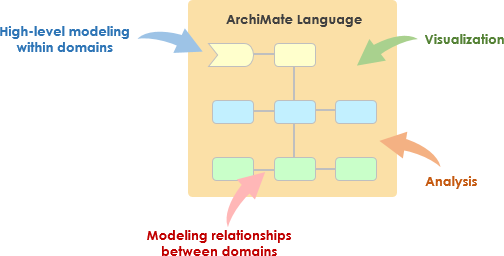
Introduction to ArchiMate
ArchiMate is an open and independent enterprise architecture modeling language that supports the description, analysis, and visualization of architecture within and across business domains. It is designed to provide a clear and unambiguous way to communicate complex architectures to stakeholders. ArchiMate is particularly useful when used in conjunction with the TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM), providing a standardized way to model and communicate enterprise architectures.
Key Concepts of ArchiMate
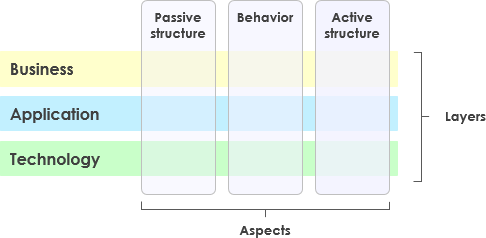
1. Layers of ArchiMate
ArchiMate divides the enterprise architecture into three main layers:
- Business Layer: Focuses on the business processes, services, and functions that support the organization’s goals.
- Application Layer: Deals with the application services, components, and their interactions that support the business layer.
- Technology Layer: Covers the technology infrastructure, including hardware, software, and network components that support the application layer.
2. Core Elements
ArchiMate defines several core elements that are used to model the architecture:
- Active Structure Elements: Represent the entities that perform behavior, such as business actors, application components, and devices.
- Behavior Elements: Represent the processes, functions, services, and interactions within the architecture.
- Passive Structure Elements: Represent the information or data used or produced by behavior elements, such as business objects and data objects.
3. Relationships
ArchiMate defines several types of relationships to connect the elements:
- Structural Relationships: Such as composition, aggregation, and specialization.
- Dependency Relationships: Such as association, realization, and used-by.
- Dynamic Relationships: Such as triggering and flow.
4. Viewpoints
ArchiMate provides several viewpoints to visualize the architecture from different perspectives:
- Business Process Viewpoint: Shows the business processes and their interactions.
- Application Cooperation Viewpoint: Shows how applications cooperate to support business processes.
- Technology Realization Viewpoint: Shows how technology components realize application components.
ArchiMate and TOGAF ADM
TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM)
TOGAF ADM is a comprehensive methodology for developing enterprise architectures. It consists of several phases, each focusing on a specific aspect of the architecture development process. ArchiMate supports TOGAF ADM by providing a standardized way to model and visualize the architecture at each phase.
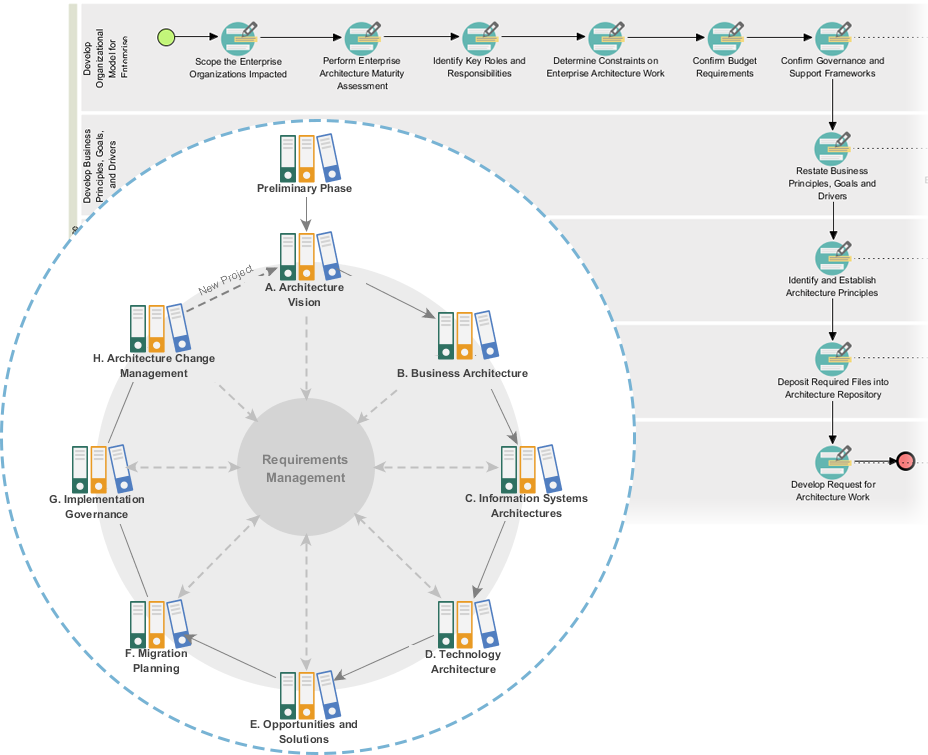
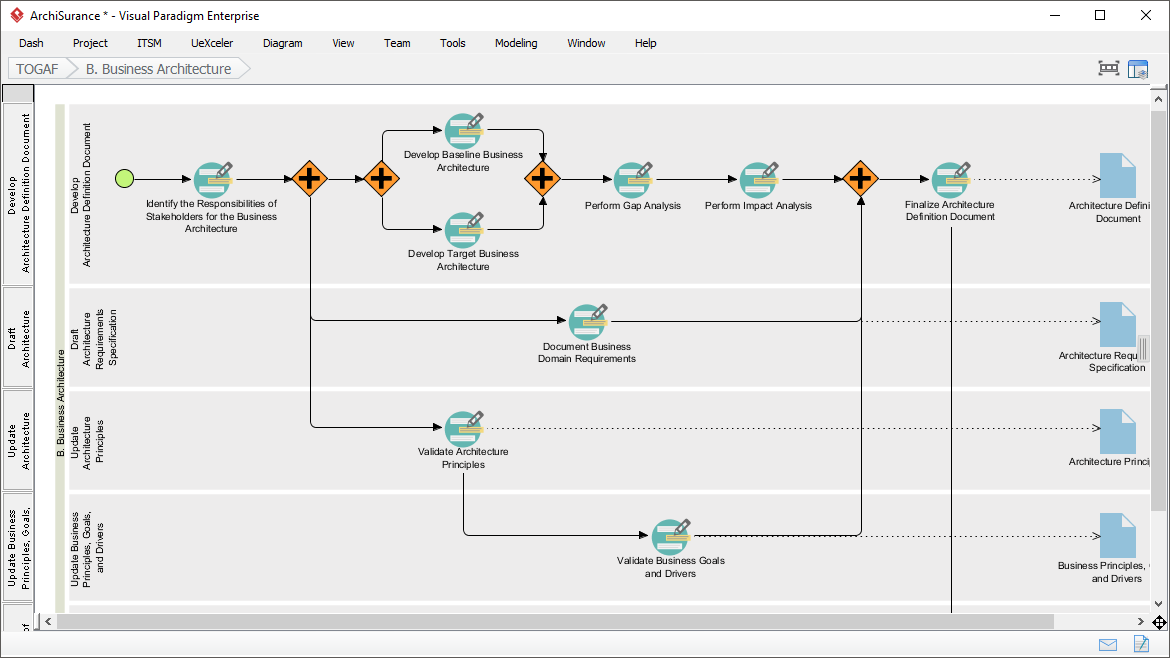
Phases of TOGAF ADM
- Preliminary Phase: Establishes the architecture principles, framework, and governance.
- Architecture Vision: Defines the scope, stakeholders, concerns, and business objectives.
- Business Architecture: Develops the business architecture, including business processes and services.
- Information Systems Architectures: Develops the data and application architectures.
- Technology Architecture: Develops the technology architecture.
- Opportunities and Solutions: Identifies and prioritizes architecture projects.
- Migration Planning: Develops the migration and implementation plan.
- Implementation Governance: Provides governance and support for the implementation of the architecture.
Examples of ArchiMate Models
This diagram illustrates a layered architecture for a healthcare management system, divided into two main layers: the Application Layer and the Technology Layer. Here’s a detailed explanation of each component and their interactions:
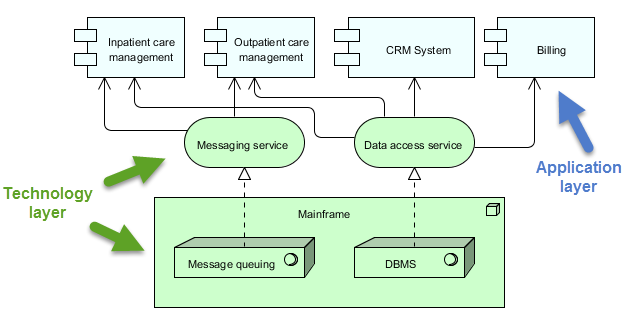
Application Layer (Blue)
This layer consists of the various applications and systems that directly interact with users or other systems to manage healthcare services. The key components in this layer are:
-
Inpatient Care Management:
- Manages services and processes related to patients who are admitted to the hospital.
-
Outpatient Care Management:
- Manages services and processes for patients who visit the hospital for treatment but are not admitted.
-
CRM System (Customer Relationship Management):
- Manages interactions with patients, including communication, follow-ups, and patient relationship management.
-
Billing:
- Handles the financial aspects, including generating bills, processing payments, and managing financial records.
Technology Layer (Green)
This layer provides the underlying infrastructure and services that support the applications in the Application Layer. The key components in this layer are:
-
Messaging Service:
- Facilitates communication between different applications and systems within the healthcare management system.
- Ensures that messages are delivered reliably and in the correct order.
-
Data Access Service:
- Provides a centralized way to access and manage data across the system.
- Ensures that data is retrieved and stored efficiently and securely.
-
Mainframe:
- The central computing system that hosts core services and data.
- Includes two main components:
- Message Queuing: Manages the queuing and processing of messages to ensure reliable communication.
- DBMS (Database Management System): Stores and manages the data used by the various applications.
Interactions
- Inpatient Care Management, Outpatient Care Management, CRM System, and Billing interact with the Messaging Service and Data Access Service to perform their respective functions.
- The Messaging Service and Data Access Service rely on the Mainframe for core services like message queuing and database management.
- The Mainframe ensures that messages are processed correctly and data is managed efficiently, supporting the entire system’s operations.
The diagram depicts a structured approach to managing healthcare services by separating the application-level functions from the underlying technology infrastructure. This separation allows for more modular and maintainable system design, where changes in one layer have minimal impact on the other. The Messaging Service and Data Access Service act as intermediaries, facilitating communication and data management between the application components and the mainframe.
Recommended ArchiMate EA Tool
Visual Paradigm is widely recognized as one of the best tools for ArchiMate modeling in Enterprise Architecture (EA) projects. Here are some reasons why it is highly recommended:
1. Comprehensive ArchiMate Support
- Full ArchiMate Standard: Visual Paradigm supports the latest ArchiMate standards, including ArchiMate 3.1, ensuring that you can model using all the official ArchiMate elements and relationships.
- Rich Library of Elements: It provides a extensive library of ArchiMate symbols, making it easy to create detailed and accurate models.
2. User-Friendly Interface
- Intuitive Design: The tool offers a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate, even for users who are new to ArchiMate modeling.
- Drag-and-Drop: The drag-and-drop functionality allows for quick and efficient model creation.
3. Advanced Modeling Features
- Layered Views: Supports the creation of layered views (e.g., Business, Application, Technology) to provide a holistic view of the enterprise architecture.
- Cross-Layer Relationships: Easily define and visualize relationships across different layers of the architecture.
4. Collaboration and Sharing
- Team Collaboration: Visual Paradigm supports collaborative work, allowing multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously.
- Version Control: Integrated version control helps manage changes and track the evolution of your models.
5. Integration Capabilities
- Tool Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other tools and platforms, such as JIRA, Confluence, and various databases, enhancing the overall EA practice.
- Import/Export: Supports importing and exporting models in various formats, including ArchiMate Exchange File Format, ensuring compatibility with other tools.
6. Documentation and Reporting
- Automated Documentation: Generates comprehensive documentation from your ArchiMate models, saving time and ensuring consistency.
- Custom Reports: Allows for the creation of custom reports tailored to specific stakeholder needs.
7. Training and Support
- Extensive Resources: Offers a wealth of tutorials, guides, and examples to help users get started and master ArchiMate modeling.
- Customer Support: Provides robust customer support to assist with any issues or questions that may arise.
8. Scalability
- Scalable Solutions: Suitable for both small and large-scale EA projects, making it a versatile tool for organizations of all sizes.
9. Compliance and Standards
- Industry Standards: Aligns with industry standards and best practices, ensuring that your EA models are compliant and up-to-date.
Conclusion
ArchiMate provides a powerful and standardized way to model enterprise architectures, supporting the TOGAF ADM methodology. By understanding the key concepts, layers, elements, and relationships in ArchiMate, you can effectively model and communicate complex architectures to stakeholders. The examples provided illustrate how ArchiMate can be used to model business processes, application cooperation, and technology realization, supporting the various phases of the TOGAF ADM.
ArchiMate Tool Resource
-
Free Online ArchiMate Diagram Tool
- Description: Create ArchiMate diagrams online with a free tool that supports ArchiMate 3 visual modeling language. Includes examples and templates to help you get started.
- URL: Free Online ArchiMate Diagram Tool 1
-
Main Page – ArchiMate Resources for FREE
- Description: Offers a visual language to model and capture enterprise architecture, providing a means to visualize relationships within and between different domains.
- URL: Main Page – ArchiMate Resources for FREE 2
-
Visual Paradigm – UML, Agile, PMBOK, TOGAF, BPMN and More!
-
Chapter 7. ArchiMate – Visual Paradigm Community Circle
-
What is ArchiMate?
- Description: Step-by-step learning guide for ArchiMate, including how to use it for enterprise architecture modeling.
- URL: What is ArchiMate? 5
-
ArchiMate tools
- Description: Learn how to use Visual Paradigm, a design and management tool designed for agile software teams.
- URL: ArchiMate tools 6
-
Best ArchiMate Software
- Description: Certified ArchiMate tool for effective EA design and modeling. Quickly draw ArchiMate diagrams that conform to The Open Group official specification.
- URL: Best ArchiMate Software 7
-
How to Format ArchiMate Elements?
-
ArchiMate Viewpoint Guide – Resource Map Viewpoint
-
ArchiMate Diagram Tutorial
- Description: Tutorial that helps you learn about ArchiMate diagrams, how to create them, and when to use them. Includes examples and tips.
- URL: ArchiMate Diagram Tutorial 10
These resources should provide a comprehensive starting point for using Visual Paradigm’s ArchiMate tool for enterprise architecture modeling.