Understanding the Interactive SQL Playground
The Interactive SQL Playground (often called the Live SQL Playground) acts as a critical validation and testing environment within the modern database design lifecycle. It bridges the gap between a conceptual visual model and a fully functional, production-ready database. By allowing users to experiment with their schema in real-time, it ensures that design choices are robust before any code is deployed.
Think of the Interactive SQL Playground as a virtual flight simulator for pilots. Instead of taking a brand-new, untested airplane (your database schema) directly into the sky (production), you test it in a safe, simulated environment. You can add simulated passengers (AI-generated sample data) and try out various maneuvers (SQL queries) to see how the plane handles the weight and stress before you ever leave the ground.
Key Concepts
To fully utilize the playground, it is essential to understand the foundational concepts that drive its functionality:
- Schema Validation: The process of verifying the structural integrity and robustness of a database design. This involves ensuring that tables, columns, and relationships function as intended under realistic conditions.
- DDL (Data Definition Language): SQL commands used to define the database structure, such as
CREATE TABLEorALTER TABLE. The playground uses these to build your schema instantly. - DML (Data Manipulation Language): SQL commands used for managing data within the schema, such as
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE, andDELETE. These are used in the playground to test data retrieval and modification. - Architectural Debt: The implied cost of future reworking required when a database is designed poorly in the beginning. Identifying flaws in the playground significantly reduces this debt.
- Normalization Stages (1NF, 2NF, 3NF): The process of organizing data to reduce redundancy. The playground allows you to test different versions of your schema to observe performance implications.
Guidelines: Step-by-Step Validation Tutorial
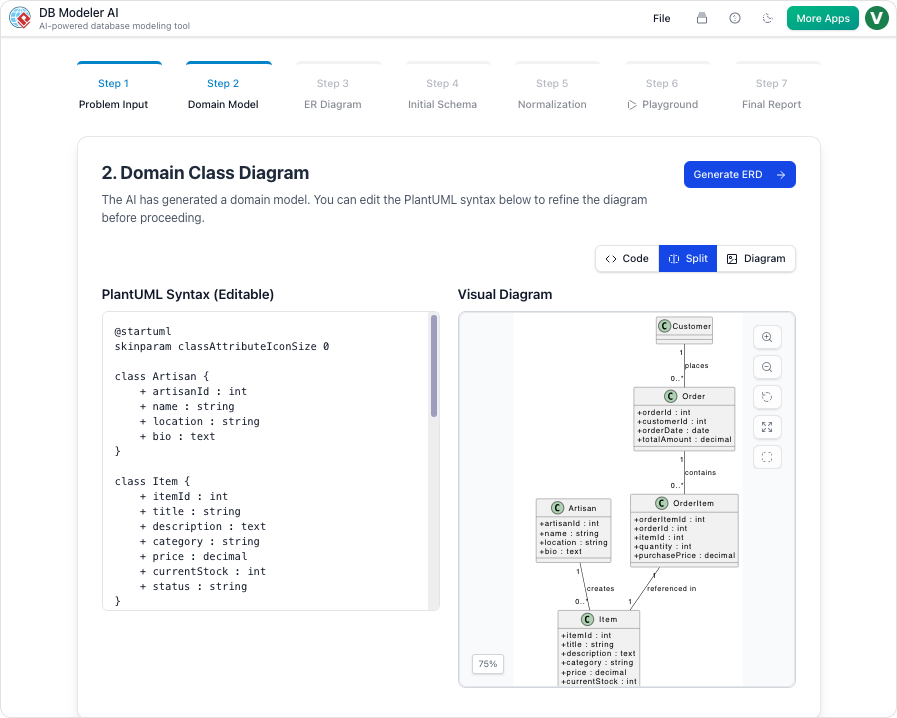
The Interactive SQL Playground is designed to be Step 6 of a comprehensive 7-step DB Modeler AI workflow, serving as the final quality check. Follow these steps to validate your database effectively.
Step 1: Access the Zero-Setup Environment
Unlike traditional database management systems that require complex local installations, the playground is accessible entirely in-browser. Simply navigate to the playground interface immediately after generating your schema. Because there is no software installation required, you can begin testing instantly.
Step 2: Select Your Schema Version
Before running queries, decide which version of your database schema you wish to test. The playground allows you to launch instances based on different normalization stages:
- Initial Design: Test your raw, unoptimized concepts.
- Optimized Versions: Select between 1NF, 2NF, or 3NF versions to compare how strict normalization affects query complexity and performance.
Step 3: Seed with AI-Powered Data
A comprehensive test requires data. Use the built-in AI-Powered Data Simulation to populate your empty tables.
- Locate the “Add Records” or “Generate Data” feature within the playground interface.
- Specify a batch size (e.g., “Add 10 records”).
- Execute the command. The AI will automatically generate realistic, AI-generated sample data relevant to your specific tables (e.g., creating customer names for a “Customers” table rather than random strings).
Step 4: Execute DDL and DML Queries
With a populated database, you can now verify the schema’s behavior.
- Run Structural Tests: Check if your data types are correct and if the table structures accommodate the data as expected.
- Run Logic Tests: Execute complex
SELECTstatements withJOINclauses to ensure relationships between tables are correctly established. - Verify Constraints: Attempt to insert data that violates Primary Key or Foreign Key constraints. The system should reject these entries, confirming that your data integrity rules are active.
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Testing
Maximize the value of your testing sessions with these practical tips:
- Iterate Rapidly: Take advantage of the “Instant Feedback” loop. If a query feels clunky or a relationship is missing, return to the visual diagram, adjust the model, and reload the playground. This typically takes only minutes and prevents hard-to-fix errors later.
- Stress Test with Volume: Don’t just add one or two rows. Use the batch generation feature to add significant amounts of data. This helps reveal performance bottlenecks that aren’t visible with a small dataset.
- Compare Normalization Performance: Run the exact same query against the 2NF and 3NF versions of your schema. This comparison can highlight the trade-off between data redundancy (storage) and query complexity (speed), helping you make an informed architectural decision.
- Validate Business Logic: Use the playground to simulate specific business scenarios. For example, if your application requires finding all orders placed by a specific user in the last month, write that specific SQL query in the playground to ensure the schema supports it efficiently.
-
Comprehensive Review of DBModeler AI for Schema Design: A detailed analysis of how DBModeler AI transforms database schema design through automation and intelligence.
-
DBModeler AI: Intelligent Database Modeling Tool: Access the AI-driven tool for automated database modeling and schema generation in Visual Paradigm.
-
DBModeler AI: AI-powered database design tool with 7-step workflow . Generate domain models, ER diagrams, normalized schemas, and complete design reports. Launch live in-browser database playground to test queries instantly.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: Use AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML, BPMN, and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
-
Visual Paradigm ERD Tool – Create Entity-Relationship Diagrams Online: A powerful, web-based ERD tool that enables users to design and visualize database schemas with ease using intuitive drag-and-drop features.
-
Database Design with ERD Tools – Visual Paradigm Guide: Comprehensive guide on using ERD tools to design robust, scalable databases with best practices in data modeling and schema design.
-
What is an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)? – Visual Paradigm Guide: An in-depth explanation of ERDs, their components, and their importance in database design and data modeling.
-
Free ERD Tool – Design Databases Online with Visual Paradigm: Access a free, no-cost ERD tool online for creating professional entity-relationship diagrams without installation or subscription.
-
How to Draw Entities in Visual Paradigm ERD: Step-by-step user guide on creating and customizing entities in Visual Paradigm’s ERD tool for accurate database modeling.
-
How to Model a Relational Database with ERD – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: Practical tutorial showing how to use ERDs to model relational databases from concept to implementation.











