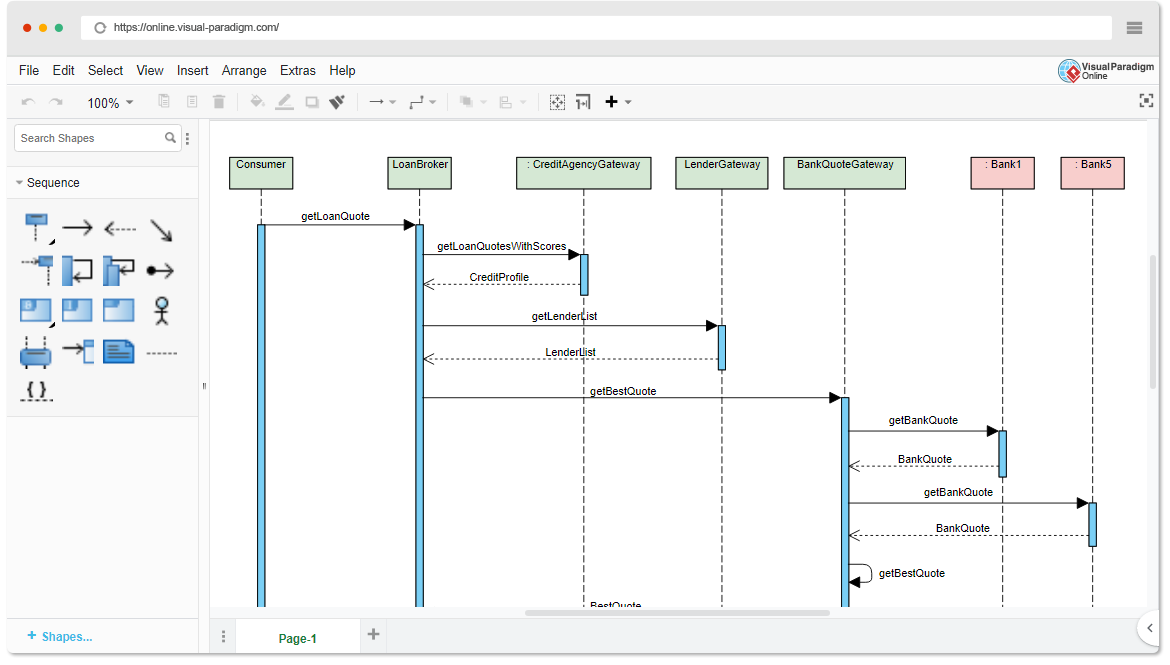
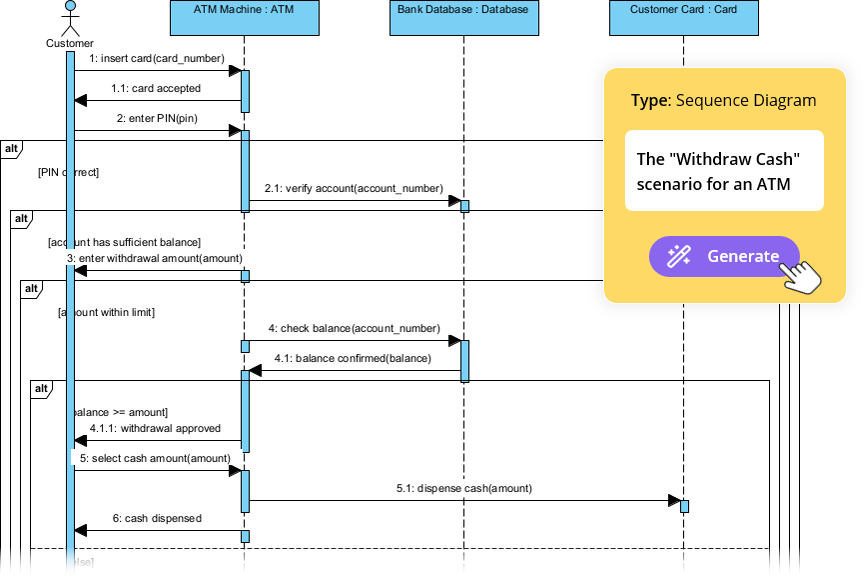
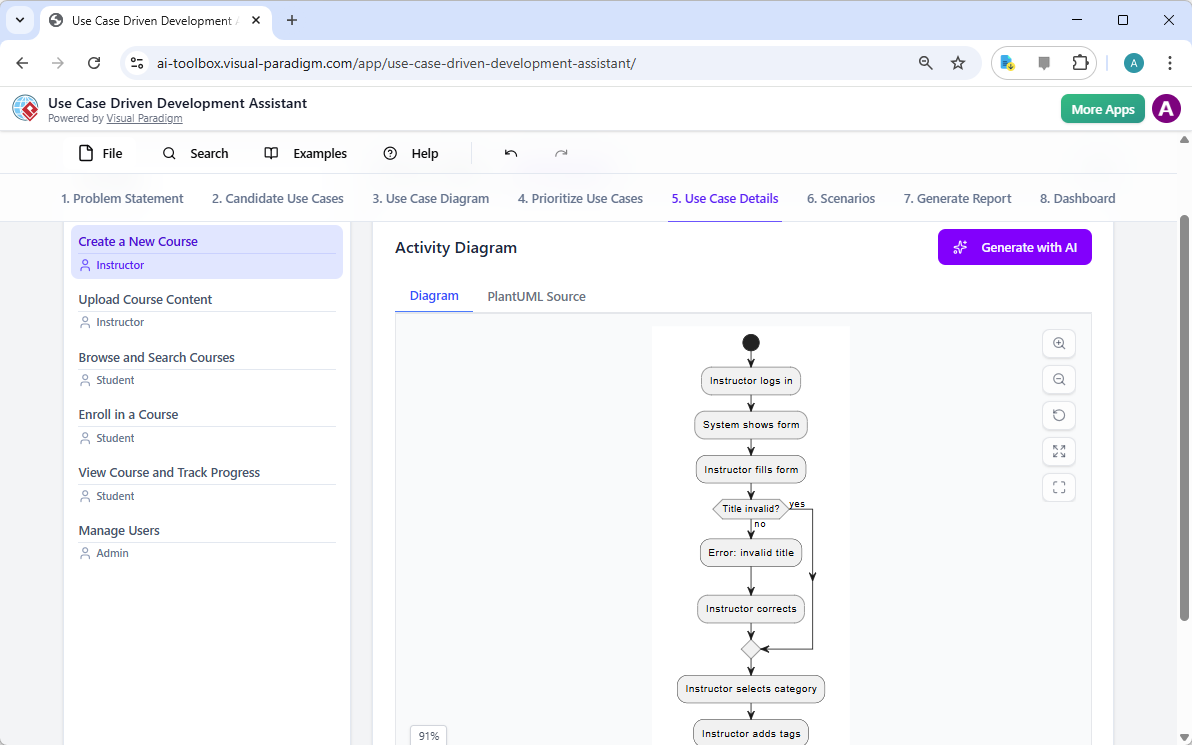
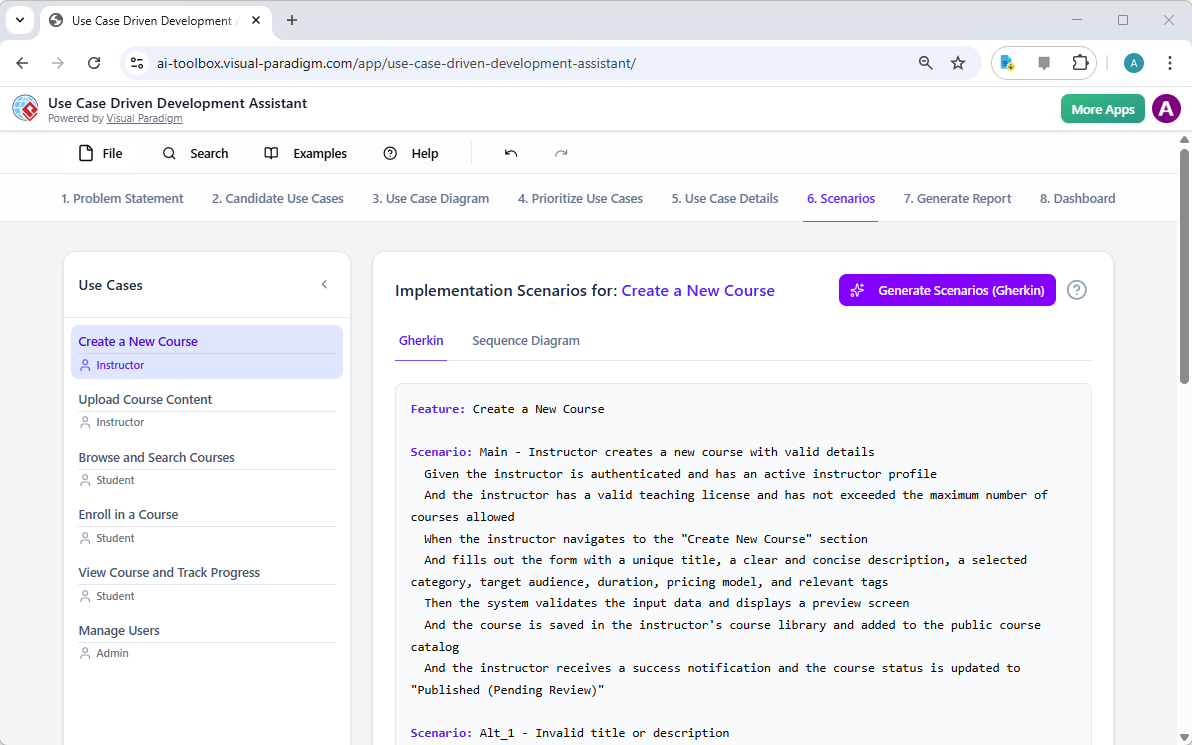
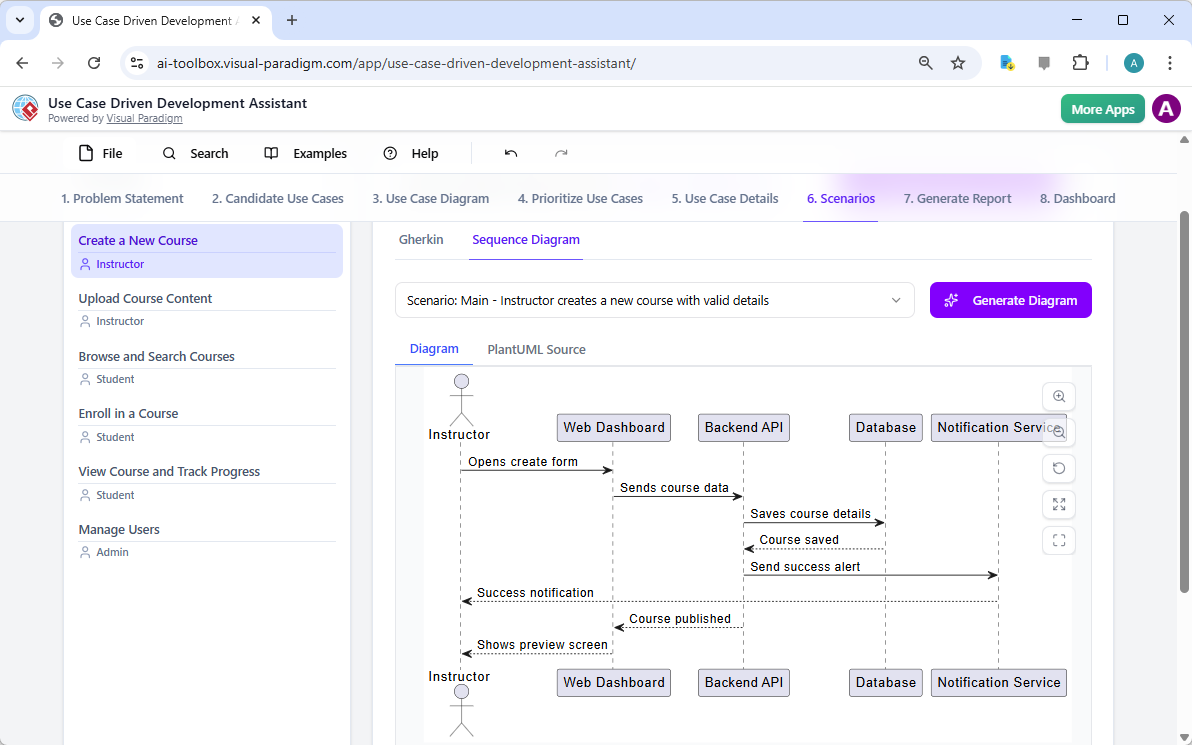
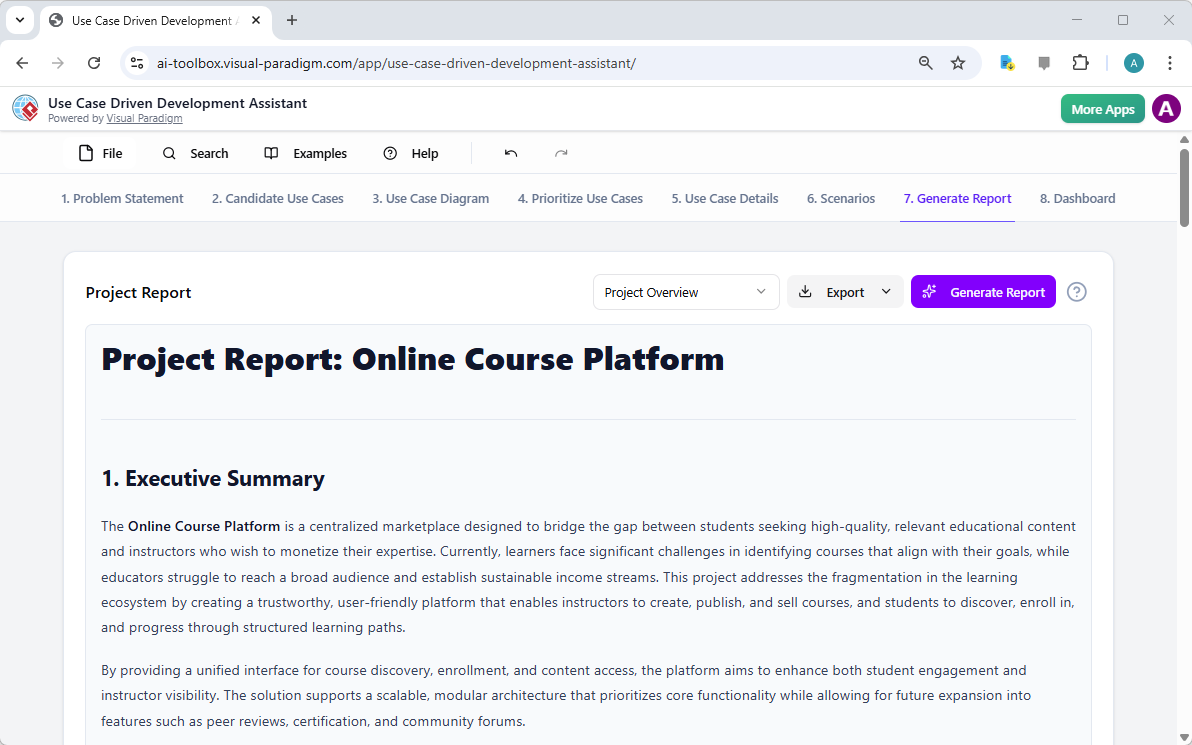
Are you ready to revolutionize your database design workflow? Creating a professional Entity Relationship Diagram used to involve hours of manual shape dragging and meticulous connection drawing. Not anymore! With the AI-powered ERD maker integrated directly into Visual Paradigm, you can generate Entity Relationship Diagram models from simple text descriptions in mere seconds. Whether you are building a complex library system or a high-traffic retail inventory, this easy-to-use diagramming tool uses advanced intelligence to handle the heavy lifting, allowing you to focus on high-level architecture rather than manual formatting!
Key Takeaways for AI-Powered Modeling
-
Instant Model Transformation: Turn natural language requirements into precise database schemas.
-
Standards-Compliant Notation: Automatically use the correct Crow’s Foot or IDEF1X notation for entities and relationships.
-
Rapid Exploration: Test different architectural scenarios by simply adjusting your text prompt.
-
Full Editability: Every generated element is a native Visual Paradigm object, ready for manual refinement.
The Core Workflow: How to Generate Entity Relationship Diagrams with AI
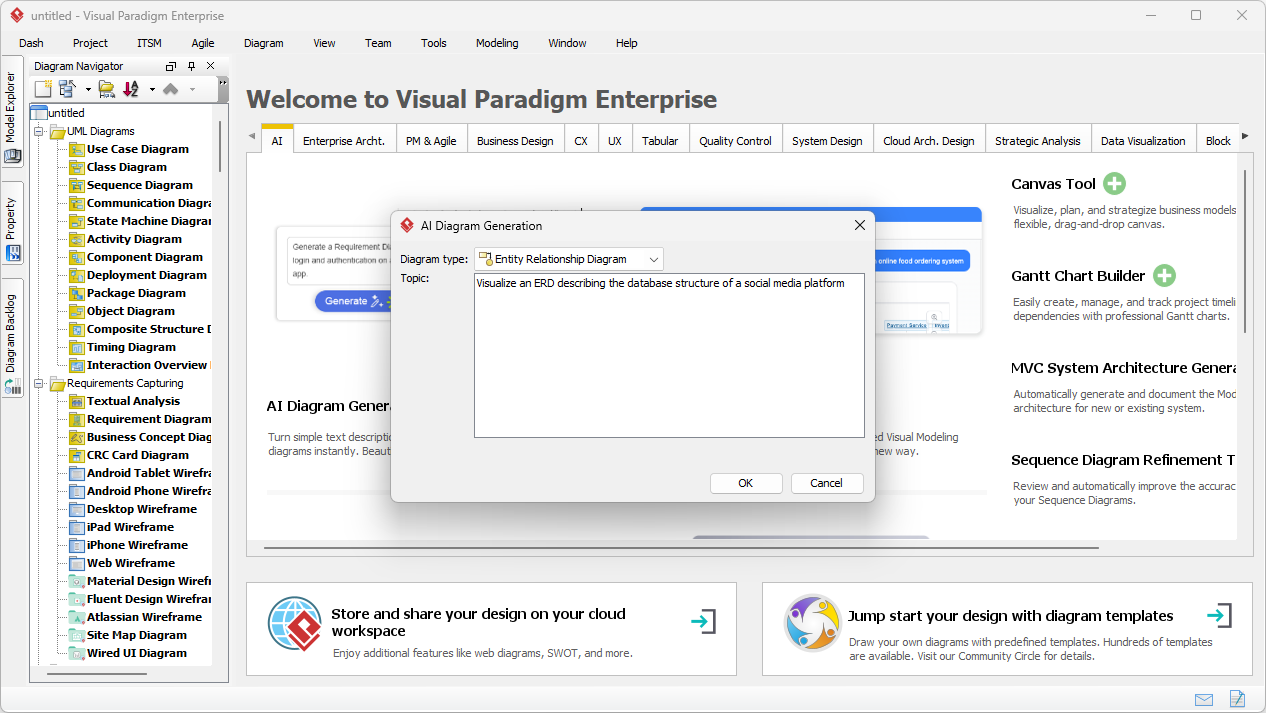
The journey to a perfect database model begins within the robust environment of Visual Paradigm Desktop. To initiate the magic, simply navigate to the main menu and select Tools > AI Diagram Generation. This opens a dedicated portal where your verbal descriptions are translated into structural blueprints. It is the ultimate starting point for any software engineer or data architect who values efficiency!
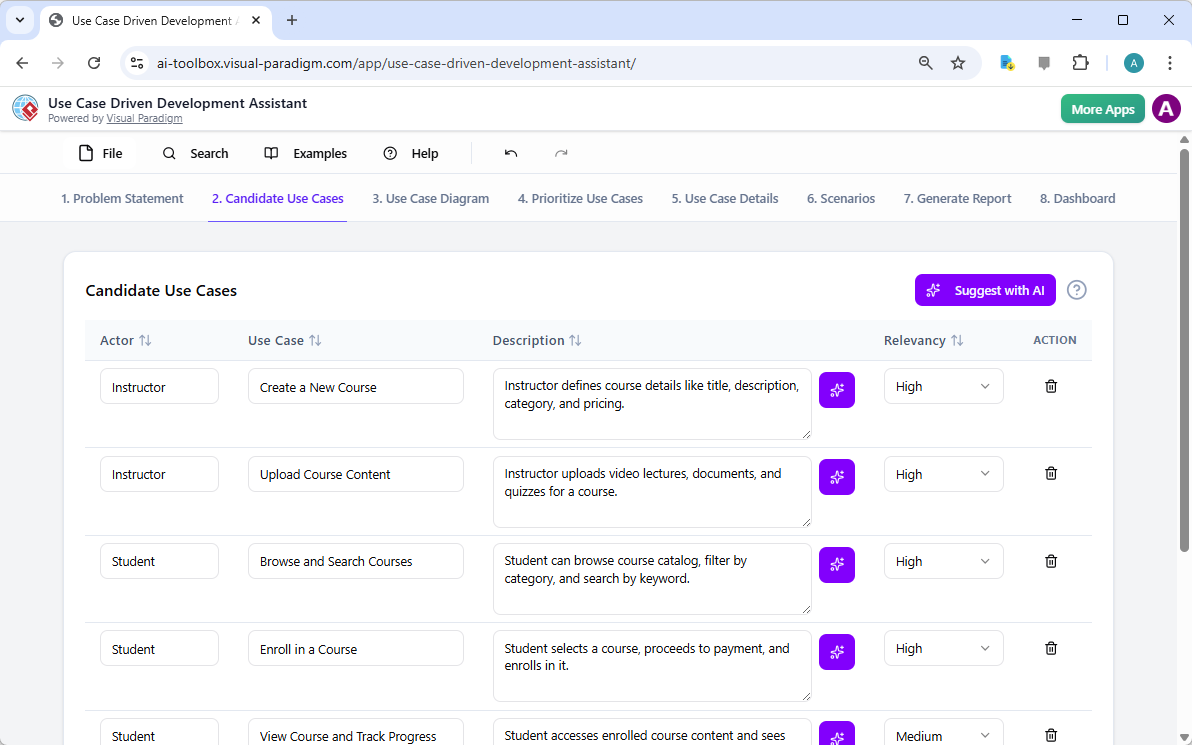
Once the generation window appears, you are presented with a streamlined interface designed for maximum productivity. First, ensure you have selected Entity Relationship Diagram from the Diagram Type dropdown menu. Next, enter your descriptive prompt into the Topic field. For our example, we provided a highly specific requirement: “A library management ERD that defines relationships between books, members, and loans.” This clarity allows the professional AI diagramming software to infer necessary entities like ISBNs, due dates, and membership types without further instruction!
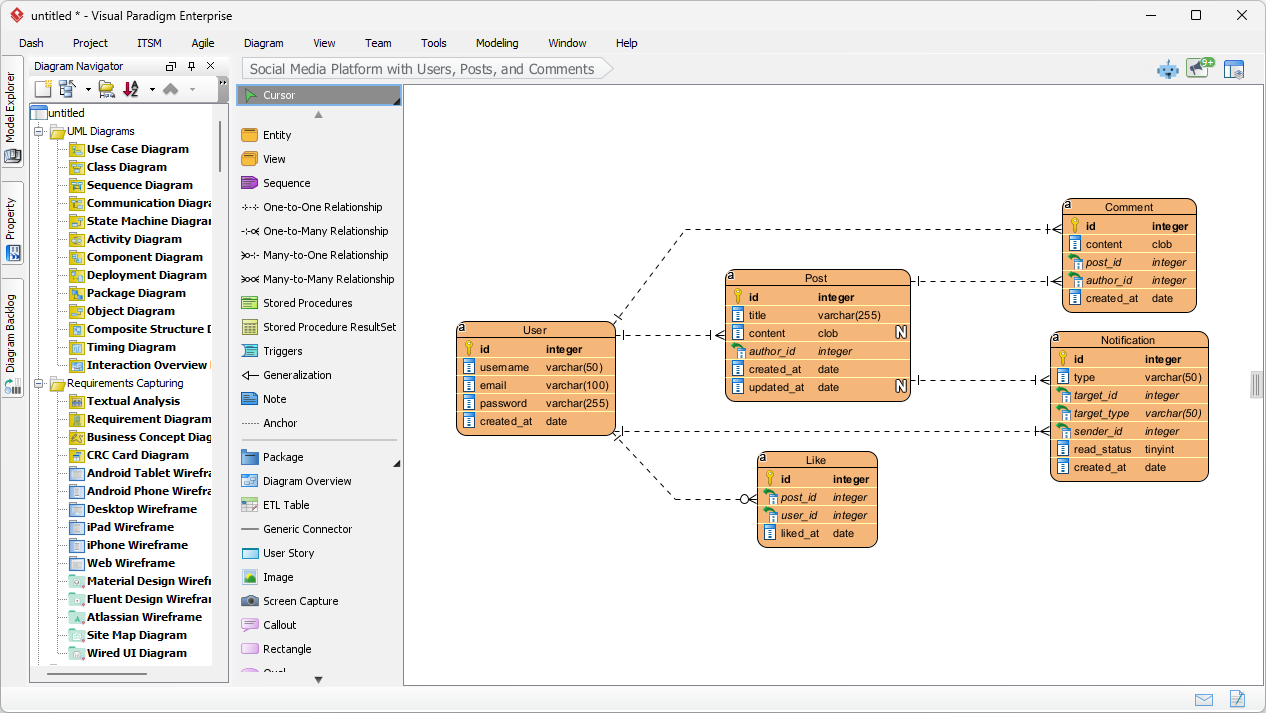
Analyzing the Intelligent Output
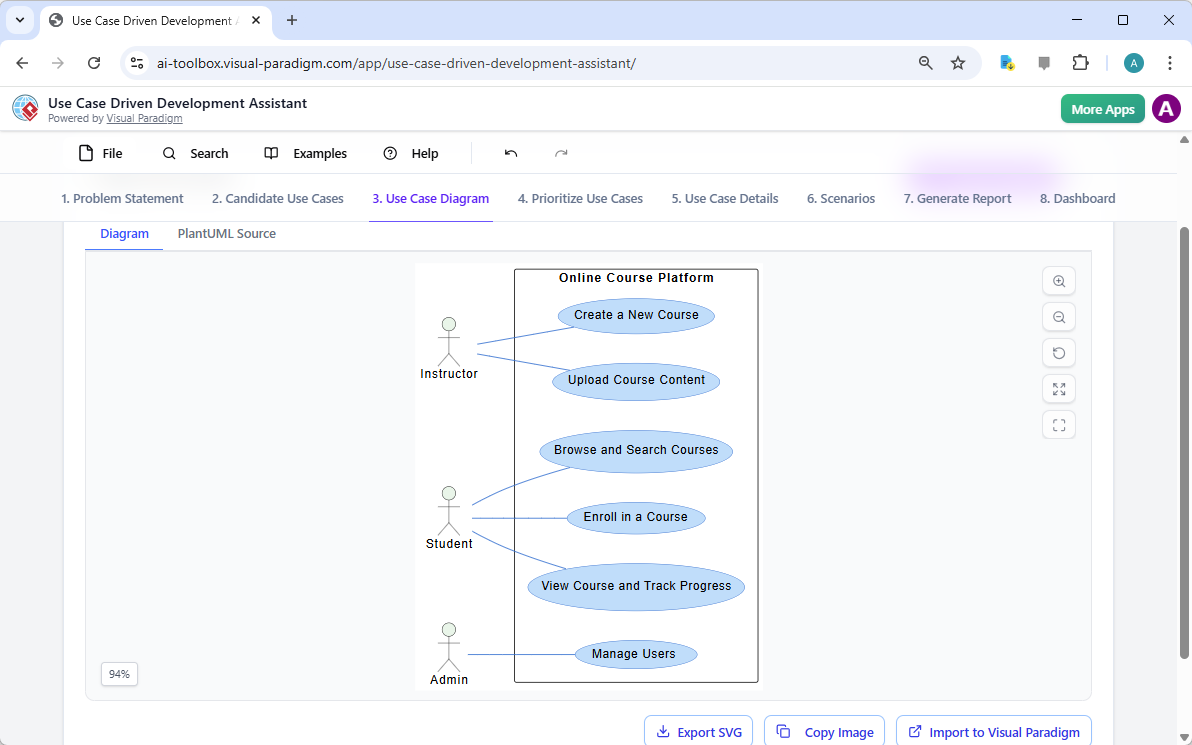
After clicking “OK,” the AI-powered design tool performs a deep analysis of your text and constructs a comprehensive model. In our library management scenario, the AI successfully identified and created entities such as CatalogEntry, Book, BookCopy, Member, and Loan. It even intelligently suggested supporting tables like Fine, Payment, Staff, and OverdueRecord to ensure a complete system logic. Every primary key, foreign key, and cardinality connection is placed with precision, providing a rock-solid foundation for your database documentation.
One of the most powerful aspects of this feature is that the result is not a static image, but a fully integrated and editable model. You can perform immediate “touch-ups” to tailor the diagram to your specific project needs. Whether you need to rename an attribute, add a new entity, or modify a relationship type—such as changing a connection to a One-to-One Relationship—the intuitive interface allows for seamless manual adjustments using the resource catalog and editor tools.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Design Strategy
By choosing to generate Entity Relationship Diagram models with Visual Paradigm’s cutting-edge AI, you are not just saving time; you are ensuring that your documentation follows industry best practices from the very first click. This professional AI-powered ERD tool bridges the gap between conceptual requirements and technical execution, making it the best easy-to-use software for modern development teams. Experience the future of visual modeling today and let your creativity lead the way!
Ready to transform your workflow?
Unlock the full potential of your design process by downloading the latest version of Visual Paradigm. Follow the link below to get started with the world’s most advanced AI diagramming application.
Download Visual Paradigm Desktop: https://www.visual-paradigm.com/download/
Related Links
Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERD) are foundational tools for database design and data modeling, used to visualize the static structure of information systems by defining entities, attributes, and their interactions. Visual Paradigm provides an extensive suite of ERD tools—available both on desktop and in the cloud—that support various standards, including Chen notation, to facilitate precise schema development. Modern advancements in the platform now include AI-powered features that can instantly generate editable ERDs from natural language descriptions or through reverse engineering existing databases, significantly streamlining the implementation workflow.
-
What is an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)? – Visual Paradigm Guide: A comprehensive resource covering the components, notation, and significance of ERDs in modern database modeling.
-
Visual Paradigm ERD Tool – Create Entity-Relationship Diagrams Online: Details on a powerful web-based editor designed for intuitive drag-and-drop design of complex database schemas.
-
How to Model a Relational Database with ERD – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: A practical, step-by-step tutorial guiding users from conceptual data modeling to final implementation.
-
Database Design with ERD Tools – Visual Paradigm Guide: Explores best practices for building scalable, robust databases and synchronizing models across different development stages.
-
New Diagram Types Added to AI Diagram Generator: DFD & ERD: Information on the latest AI capabilities that enable users to create structured ERDs automatically from simple text prompts.
-
Streamlining Entity-Relationship Modeling with Visual Paradigm: A detailed look at how to effectively move from initial data concepts to implementation using visual modeling tools.