Database normalization is a critical process in system design, ensuring that data is organized efficiently to reduce redundancy and improve integrity. Traditionally, moving a schema from a raw concept to the Third Normal Form (3NF) required significant manual effort and deep theoretical knowledge. However, the Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler has revolutionized this approach by integrating normalization into an automated workflow. This guide explores how to leverage this tool to achieve an optimized database structure seamlessly.
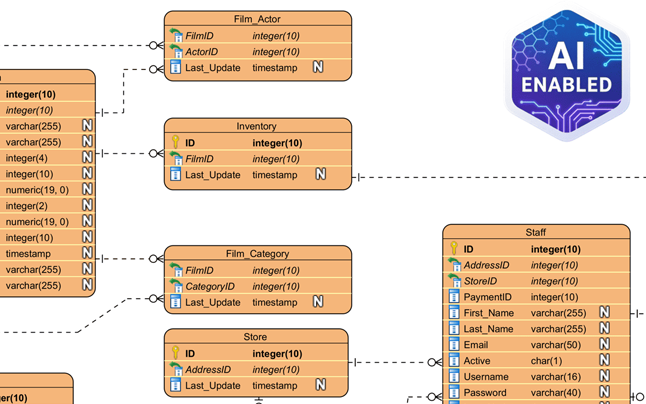
Key Concepts
To effectively use the AI DB Modeler, it is essential to understand the foundational definitions that drive the tool’s logic. The AI focuses on three primary stages of architectural maturity.
1. First Normal Form (1NF)
The foundational stage of normalization. 1NF ensures that the table structure is flat and atomic. In this state, each table cell contains a single value rather than a list or set of data. Furthermore, it mandates that every record within the table is unique, eliminating duplicate rows at the most basic level.
2. Second Normal Form (2NF)
Building upon the strict rules of 1NF, the Second Normal Form addresses the relationship between columns. It requires that all non-key attributes are fully functional and dependent on the primary key. This stage eliminates partial dependencies, which often occur in tables with composite primary keys where a column relies on only part of the key.
3. Third Normal Form (3NF)
This is the standard target for most production-grade relational databases. 3NF ensures that all attributes are only dependent on the primary key. It specifically targets and removes transitive dependencies (where Column A relies on Column B, and Column B relies on the Primary Key). Achieving 3NF results in a high degree of architectural maturity, minimizing data redundancy and preventing update anomalies.
Guidelines: The Automated Normalization Workflow
Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler incorporates normalization specifically within Step 5 of its automated 7-step workflow. Follow these guidelines to navigate the process and maximize the utility of the AI’s suggestions.
Step 1: Initiate the AI Workflow
Begin by inputting your initial project requirements or raw schema ideas into the AI DB Modeler. The tool will guide you through the initial phases of entity discovery and relationship mapping. Proceed through the early steps until you reach the optimization phase.
Step 2: Analyze the 1NF Transformation
When the workflow reaches Step 5, the AI effectively takes over the role of a database architect. It first analyzes your entities to ensure they meet 1NF standards. Watch for the AI to decompose complex fields into atomic values. For example, if you had a single field for “Address,” the AI might suggest breaking it down into Street, City, and Zip Code to ensure atomicity.
Step 3: Review 2NF and 3NF Refinements
The tool iteratively applies rules to progress from 1NF to 3NF. During this phase, you will observe the AI restructuring tables to handle dependencies correctly:
- It will identify non-key attributes that do not depend on the full primary key and move them to separate tables (2NF).
- It will detect attributes that depend on other non-key attributes and isolate them to eliminate transitive dependencies (3NF).
Step 4: Consult the Educational Rationales
One of the most powerful features of the Visual Paradigm AI DB Modeler is its transparency. As it modifies your schema, it provides educational rationales. Do not skip this text. The AI explains the reasoning behind every structural change, detailing how the specific optimization eliminates data redundancy or ensures data integrity. Reading these rationales is crucial for verifying that the AI understands the business context of your data.
Step 5: Validate in the SQL Playground
Once the AI claims the schema has reached 3NF, do not immediately export the SQL. Utilize the built-in interactive SQL playground. The tool seeds the new schema with realistic sample data.
Run test queries to verify performance and logic. This step allows you to confirm that the normalization process hasn’t made data retrieval overly complex for your specific use case before you commit to deployment.
Tips and Tricks
Maximize your efficiency with these best practices when using the AI DB Modeler.
- Verify Context Over Syntax: While the AI is excellent at applying normalization rules, it may not know your specific business domain quirks. Always cross-reference the “Educational Rationales” with your business logic. If the AI splits a table in a way that hurts your application’s read performance, you may need to denormalize slightly.
- Use the Sample Data: The sample data generated in the SQL playground is not just for show. Use it to check for edge cases, such as how null values are handled in your newly normalized foreign keys.
- Iterate on Prompts: If the initial schema generation in Steps 1-4 is too vague, the normalization in Step 5 will be less effective. Be descriptive in your initial prompts to ensure the AI starts with a robust conceptual model.
-
Comprehensive Review of DBModeler AI for Schema Design: A detailed analysis of how DBModeler AI transforms database schema design through automation and intelligence.
-
DBModeler AI: Intelligent Database Modeling Tool: Access the AI-driven tool for automated database modeling and schema generation in Visual Paradigm.
-
DBModeler AI: AI-powered database design tool with 7-step workflow . Generate domain models, ER diagrams, normalized schemas, and complete design reports. Launch live in-browser database playground to test queries instantly.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: Use AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML, BPMN, and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
-
Visual Paradigm ERD Tool – Create Entity-Relationship Diagrams Online: A powerful, web-based ERD tool that enables users to design and visualize database schemas with ease using intuitive drag-and-drop features.
-
Database Design with ERD Tools – Visual Paradigm Guide: Comprehensive guide on using ERD tools to design robust, scalable databases with best practices in data modeling and schema design.
-
What is an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)? – Visual Paradigm Guide: An in-depth explanation of ERDs, their components, and their importance in database design and data modeling.
-
Free ERD Tool – Design Databases Online with Visual Paradigm: Access a free, no-cost ERD tool online for creating professional entity-relationship diagrams without installation or subscription.
-
How to Draw Entities in Visual Paradigm ERD: Step-by-step user guide on creating and customizing entities in Visual Paradigm’s ERD tool for accurate database modeling.
-
How to Model a Relational Database with ERD – Visual Paradigm Tutorial: Practical tutorial showing how to use ERDs to model relational databases from concept to implementation.











