In the evolving landscape of software engineering, bridging the gap between abstract business requirements and executable code is a critical challenge.
The DB Modeler AI workflow addresses this by implementing a guided 7-step journey. This structured process transforms an initial concept into a fully optimized, production-ready database schema, ensuring that technical execution aligns perfectly with business intent.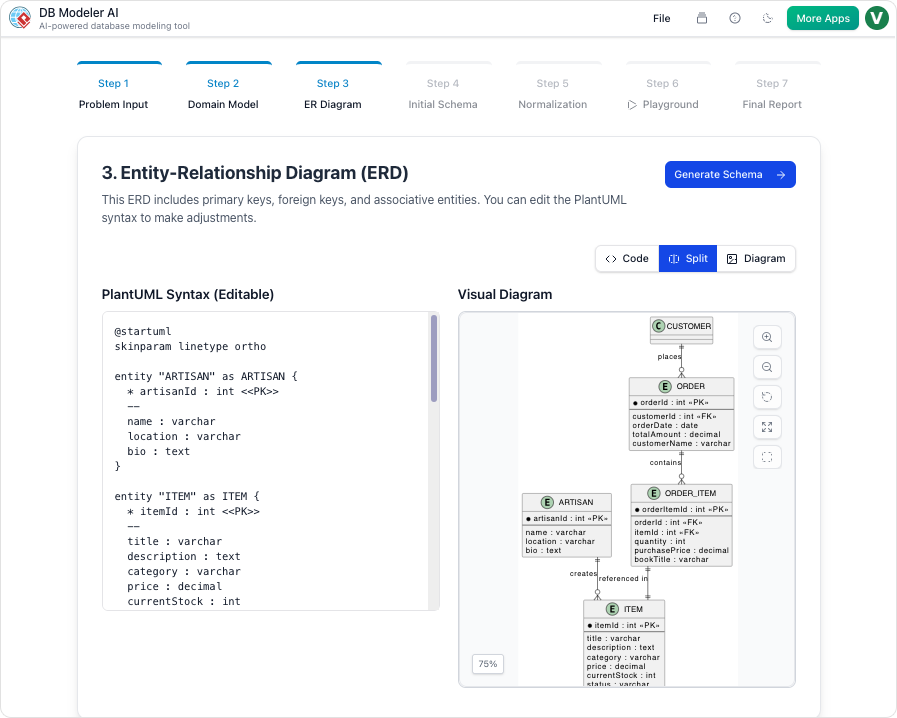
The Conceptual Phase: From Text to Visuals
The first stage of the workflow focuses on interpreting user intent and establishing a high-level visual representation of the data structure.
Step 1: Problem Input (Conceptual Input)
The journey begins with the user describing their application or project in plain English. Unlike traditional tools that require immediate technical syntax, DB Modeler AI allows for natural language input. The AI interprets this intent and expands it into comprehensive technical requirements. This step provides the necessary context for identifying core entities and business rules, ensuring that no critical data point is overlooked during the initial scoping.
Step 2: Domain Class Diagram (Conceptual Modeling)
Once the requirements are established, the AI translates the textual data into a high-level visual blueprint known as a Domain Model Diagram. This diagram is rendered using editable PlantUML syntax, offering a flexible environment where users can visualize high-level objects and their attributes. This step is crucial for refining the scope of the database before committing to specific relationships or keys.
The Logical and Physical Design Phase
Moving beyond concepts, the workflow transitions into strict database logic and executable code generation.
Step 3: ER Diagram (Logical Modeling)
In this pivotal step, the tool converts the conceptual domain model into a database-specific Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD). The AI automatically handles the complexity of defining essential database components. This includes the assignment of Primary Keys (PKs) and Foreign Keys (FKs), as well as the determination of cardinalities such as 1:1, 1:N, or M:N relationships. This transforms the abstract model into a logically sound database structure.
Step 4: Initial Schema Generation (Physical Code Generation)
With the logical model validated, the workflow proceeds to the physical layer. The refined ERD is translated into executable PostgreSQL-compatible SQL DDL statements. This automated process generates the code for all necessary tables, columns, and constraints directly derived from the visual model, eliminating the manual effort typically associated with writing Data Definition Language scripts.
Optimization, Validation, and Documentation
The final phases of the workflow ensure the database is efficient, tested, and well-documented for handover.
Step 5: Intelligent Normalization (Schema Optimization)
A standout feature of the DB Modeler AI workflow is its focus on efficiency. The AI progressively optimizes the schema by advancing it through the First (1NF), Second (2NF), and Third Normal Forms (3NF). Crucially, the tool provides educational rationales for every modification. This helps users understand how data redundancy is eliminated and how data integrity is ensured, turning the optimization process into a learning opportunity.
Step 6: Interactive Playground (Validation & Testing)
Before deployment, verification is essential. Users can experiment with their finalized schema in a live, in-browser SQL client. To facilitate immediate testing, the environment is automatically seeded with realistic, AI-generated sample data. This allows users to run custom queries and verify performance metrics in a sandbox environment effectively simulating real-world usage.
Step 7: Final Report and Export (Documentation)
The conclusion of the workflow is the generation of a professional Final Design Report. Typically formatted in Markdown, this report summarizes the entire design lifecycle. Users can export all diagrams, documentation, and SQL scripts as a polished PDF or JSON package, ready for project hand-off, team review, or long-term archiving.
More ERD Examples Generated by Visual Paradigm AI
Understanding the Process: The Car Factory Analogy
To better understand the distinct value of each step, it is helpful to visualize the workflow as building a custom car in an automated factory. The following table maps the database engineering steps to this manufacturing analogy:
| Workflow Step | Database Action | Car Factory Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Problem Input | Your initial description of the car you want. |
| Step 2 | Domain Class Diagram | The artist’s sketch of the car’s look. |
| Step 3 | ER Diagram | The mechanical blueprint of how parts connect. |
| Step 4 | Initial Schema Generation | The actual manufacturing code for the machines. |
| Step 5 | Intelligent Normalization | Fine-tuning the engine for maximum efficiency. |
| Step 6 | Interactive Playground | A test drive on a virtual track with simulated passengers. |
| Step 7 | Final Report and Export | The final owner’s manual and the keys to the vehicle. |
-
Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm AI Table Generator: From Natural Language to Executable Code: This guide walks users through transforming natural language descriptions into fully functional database tables and executable code using Visual Paradigm AI’s advanced table generation engine.
-
Kata AI Marketing Platform ERD – Sample Database Design: A real-world example of an ERD for an AI-powered marketing platform, demonstrating how to model users, campaigns, analytics, and content relationships.
-
The Comprehensive Guide to DBModeler AI… – Cybermedian: Visual Paradigm ’s DBModeler AI represents a significant leap forward in database design. By combining expert guidance, visual diagramming, and live SQL testing , it allows users to…
-
AI-Powered Database Modeling with DBModeler AI: Discover how DBModeler AI enables intelligent database schema design and automated modeling in Visual Paradigm.











