Imagine you’re a project manager tasked with launching a new online course platform. The first challenge is to articulate the problem clearly and then translate it into a functional system. This is where the Use Case Driven Development Assistant, an AI-powered tool from Visual Paradigm, steps in. It doesn’t just help you write documents; it guides you through a complete, structured workflow to transform a vague idea into a detailed, actionable project plan. The process is so intuitive, it feels like having a seasoned business analyst and a technical architect working side-by-side with you. This deep dive explores the core features of this powerful tool, using a real-world example of an online course platform to show how it streamlines the entire use case lifecycle.
Quick Summary: Key Takeaways from the Use Case Driven Development Assistant
-
Start with a clear problem statement to define the project’s core objective.
-
Use AI to automatically generate a list of candidate use cases and actors.
-
Visualize system functionality with AI-generated Use Case and Activity Diagrams.
-
Prioritize features using a structured MoSCoW method to focus on high-value work.
-
Generate detailed use case descriptions and executable Gherkin test scenarios.
-
Create comprehensive reports to communicate project scope and plans.
-
Track progress and maintain a single source of truth with a central dashboard.
Step 1: Defining the Problem with AI
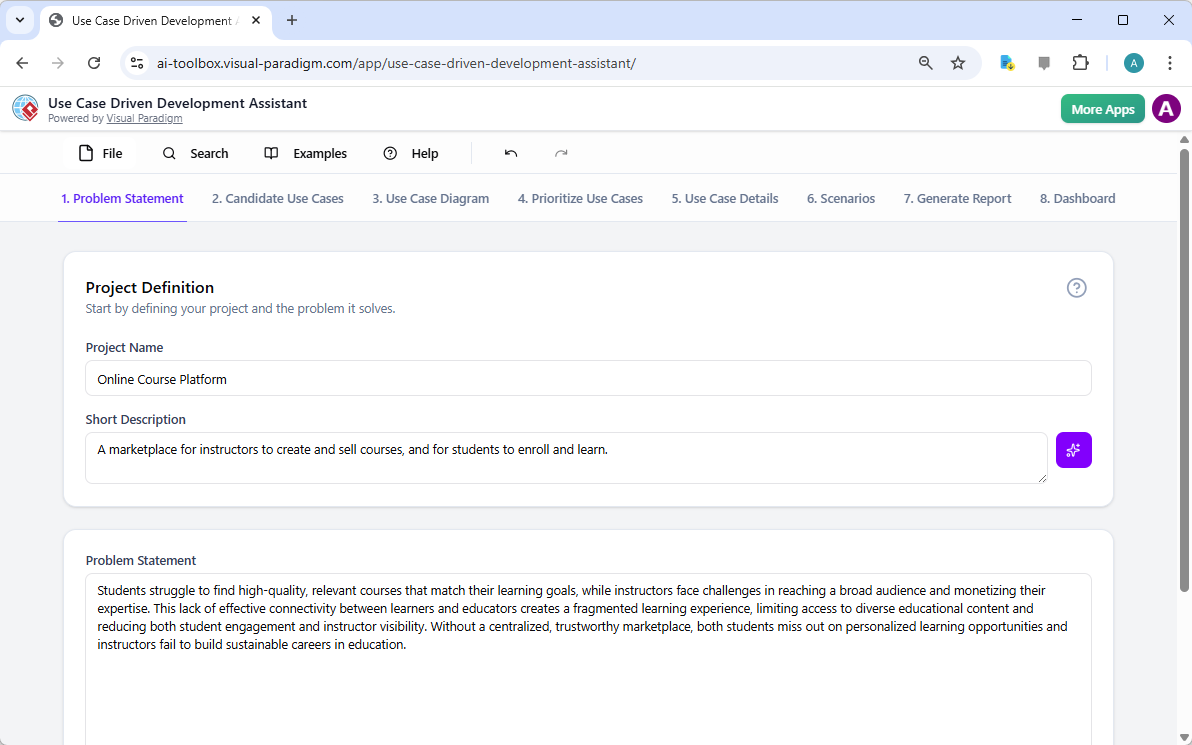
Every successful project begins with a clear understanding of the problem it aims to solve. The journey with the Use Case Driven Development Assistant starts in the “Problem Statement” tab. Here, you input a project name and a short description. The AI then leverages this information to generate a comprehensive problem statement. As seen in Image 1, the tool has taken the project name “Online Course Platform” and the short description “A marketplace for instructors to create and sell courses, and for students to enroll and learn” to produce a detailed narrative. This narrative identifies the core pain points: students struggle to find relevant courses, while instructors face challenges in reaching a broad audience and monetizing their expertise. This AI-generated problem statement serves as the project’s foundation, ensuring everyone on the team shares a unified understanding from the very beginning.
Step 2: Identifying Use Cases with AI Assistance
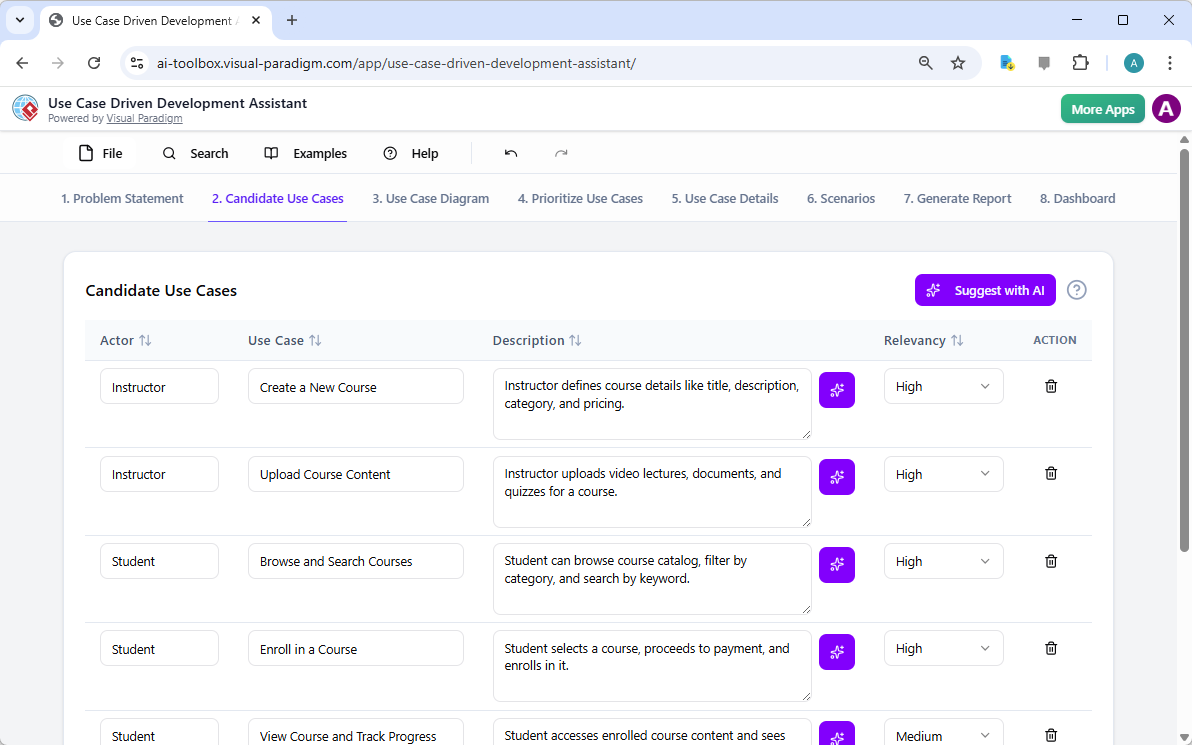
Once the problem is defined, the next logical step is to identify the key functionalities the system must provide. The assistant’s “Candidate Use Cases” tab, shown in Image 2, automates this process. After analyzing the problem statement, the AI suggests a list of use cases, each associated with an actor (like Instructor, Student, or Admin). For our online course platform, the AI proposes use cases such as “Create a New Course,” “Upload Course Content,” “Browse and Search Courses,” and “Enroll in a Course.” This list provides a solid starting point, saving significant time and effort that would otherwise be spent on brainstorming sessions. You can then refine these suggestions, add new ones, or delete irrelevant ones to create a comprehensive list of system functionalities.
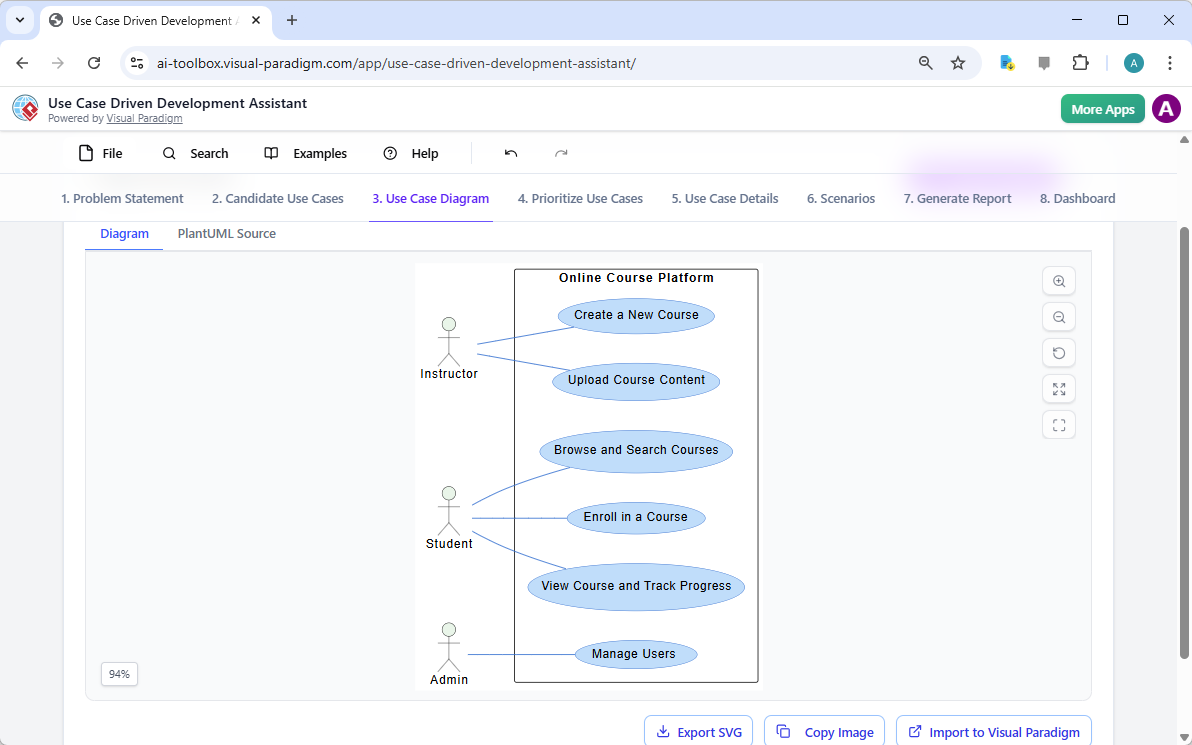
Step 3: Visualizing the System with a Use Case Diagram
After identifying the use cases, it’s crucial to visualize how they interact with the system’s actors. The “Use Case Diagram” tab, illustrated in Image 3, takes the list of use cases and actors and automatically generates a clear, graphical representation. This diagram shows the relationships between the actors (Instructor, Student, Admin) and the system’s functions (Create a New Course, etc.). The AI-powered generation ensures that the diagram is accurate and professionally formatted. This visual aid is invaluable for communication, allowing stakeholders, developers, and designers to quickly grasp the system’s scope and functionality without wading through text-heavy documents.
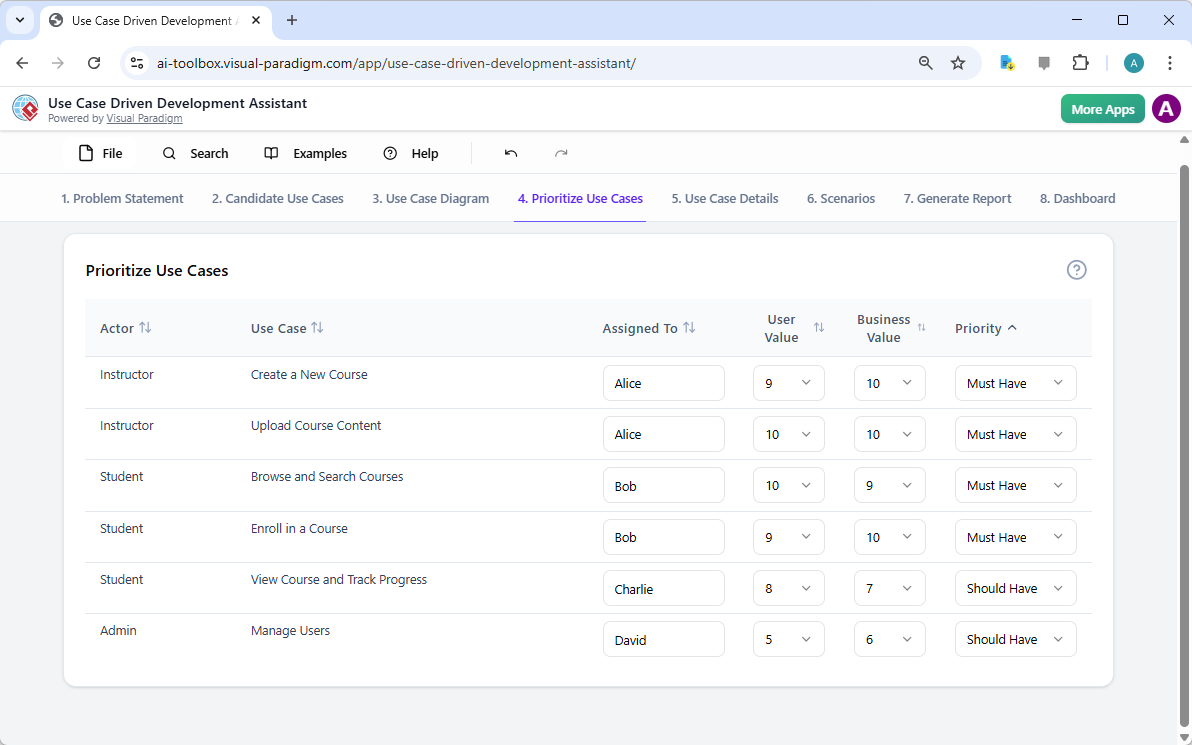
Step 4: Prioritizing Features for Maximum Impact
Not all use cases are created equal. A project’s success often hinges on focusing on the most critical features first. The “Prioritize Use Cases” tab, as shown in Image 4, provides a powerful framework for this. It allows you to assign a user value and business value (on a scale of 0-10) to each use case and then apply the MoSCoW prioritization method (Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, Won’t Have). In our example, the AI has helped identify that “Create a New Course” and “Upload Course Content” are “Must Have” features, as they are essential for the platform’s core function. This structured prioritization ensures that the development team focuses on delivering the highest value to users and the business, avoiding wasted effort on low-priority features.
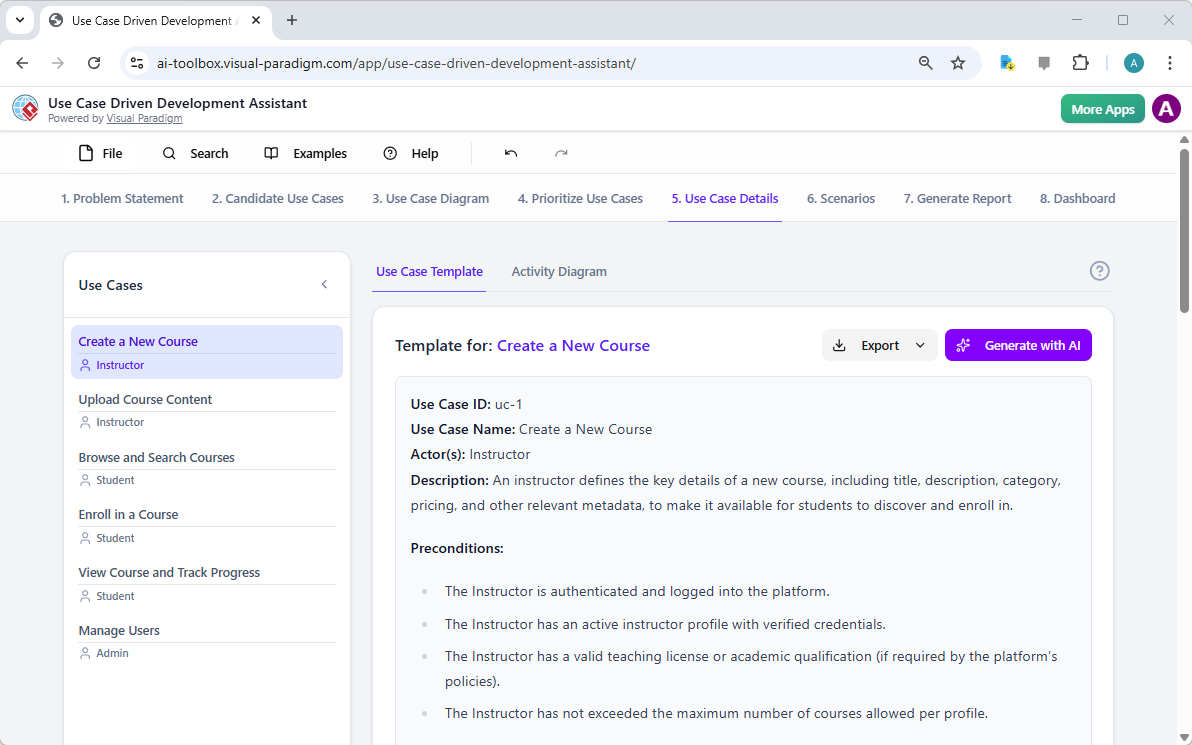
Step 5: Detailing Use Cases and Generating Activity Diagrams
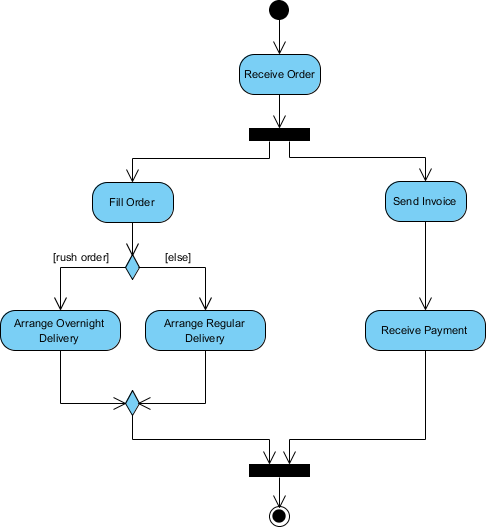
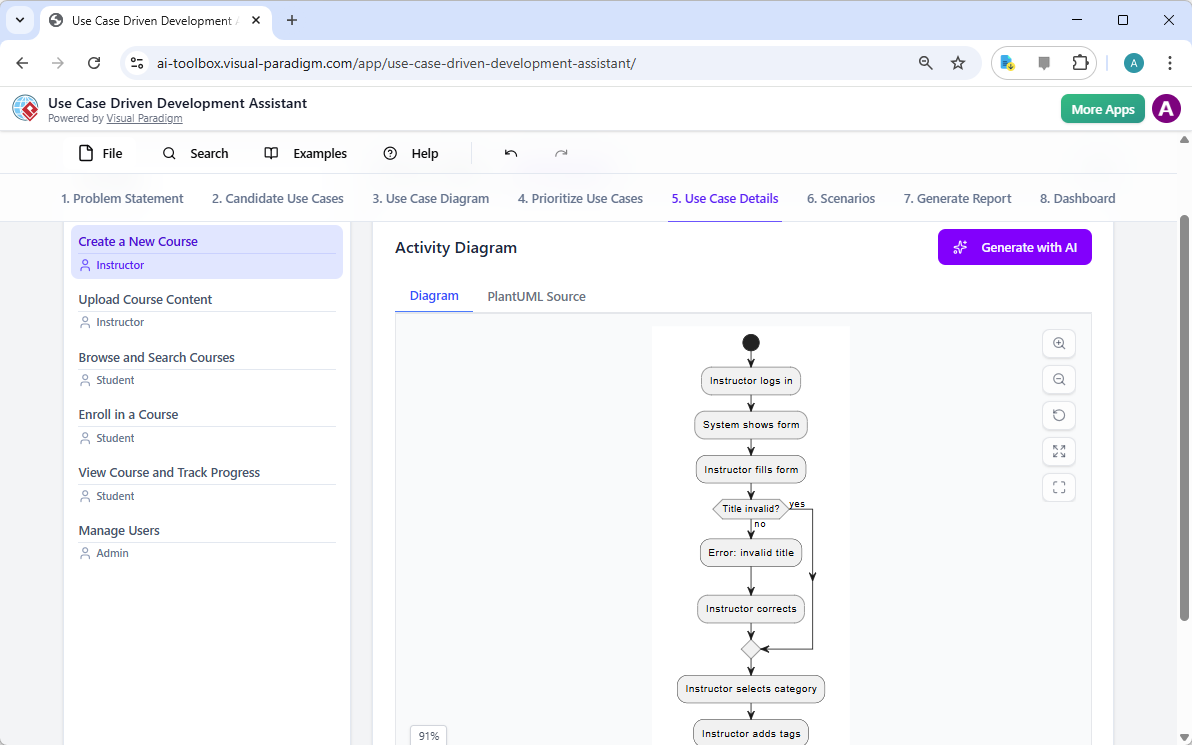
With the high-level view established, the next step is to dive into the details of each use case. The “Use Case Details” tab, shown in Image 5, allows you to create a comprehensive template for a selected use case. The AI can generate a detailed description, including pre-conditions, main flow, and alternative flows. For the “Create a New Course” use case, the AI provides a structured template that outlines the necessary steps. To further enhance understanding, the assistant can generate an “Activity Diagram” for the same use case, as seen in Image 6. This diagram visually maps out the step-by-step workflow, showing the sequence of actions from the instructor logging in to the course being saved. This level of detail is essential for both developers and QA teams.
Step 6: Generating Test Scenarios and Sequence Diagrams
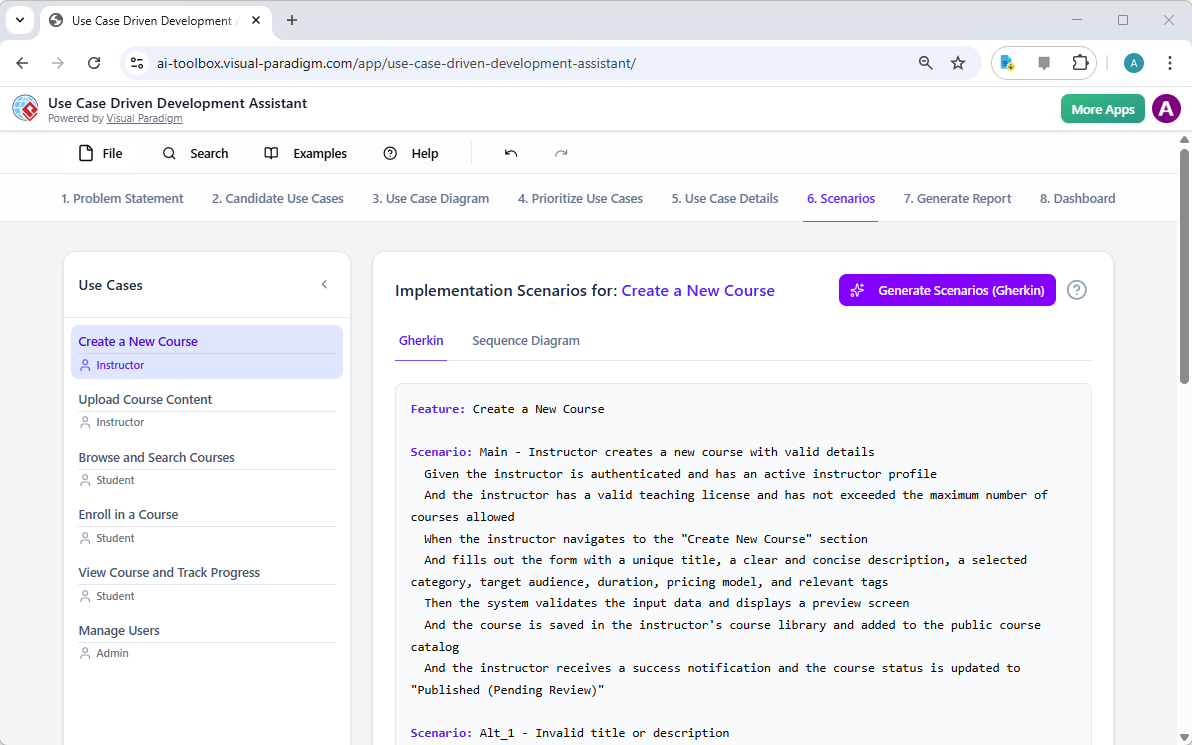
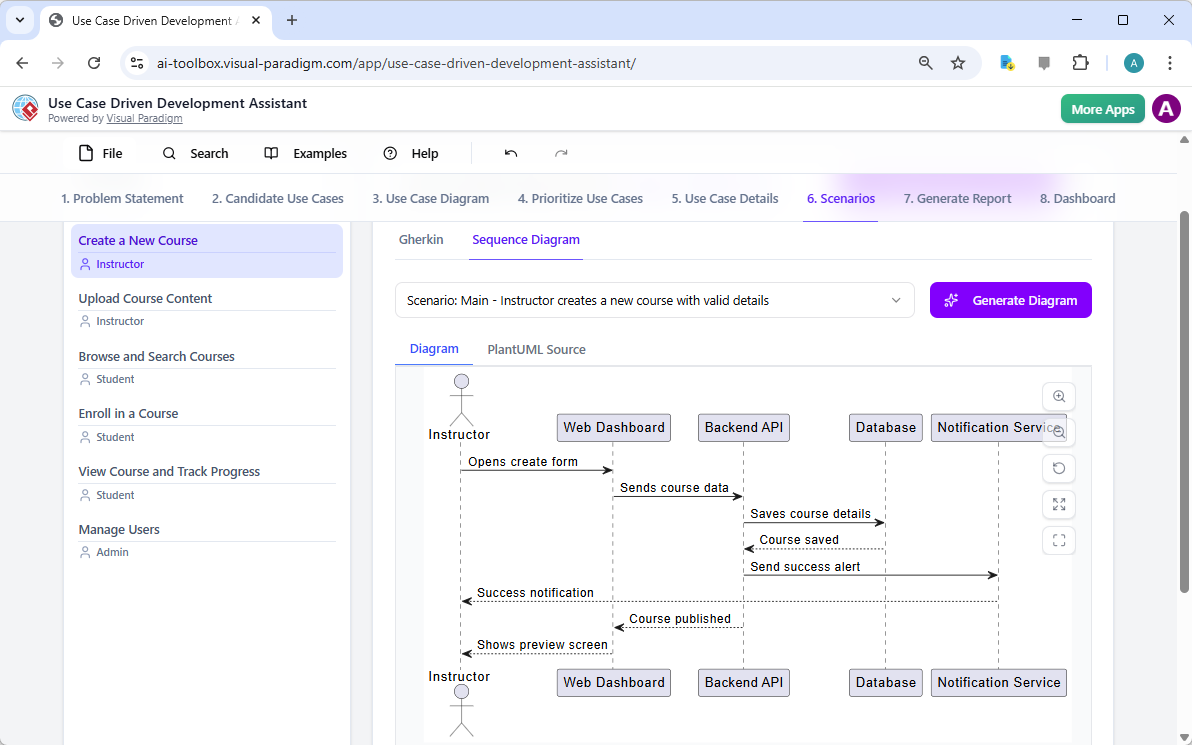
For a development team, the next critical step is to create testable scenarios. The “Scenarios” tab, shown in Image 7, allows you to generate executable Gherkin scenarios directly from your use case descriptions. These scenarios, written in a plain-language format (Given-When-Then), are perfect for automated testing. The AI can generate a main scenario and alternative scenarios, such as one for an invalid title. To further clarify the system’s internal workings, the assistant can generate a “Sequence Diagram,” as seen in Image 8. This diagram shows the interaction between the instructor, the web dashboard, the backend API, the database, and the notification service, providing a clear picture of the system’s architecture and data flow.
Step 7: Creating Comprehensive Project Reports
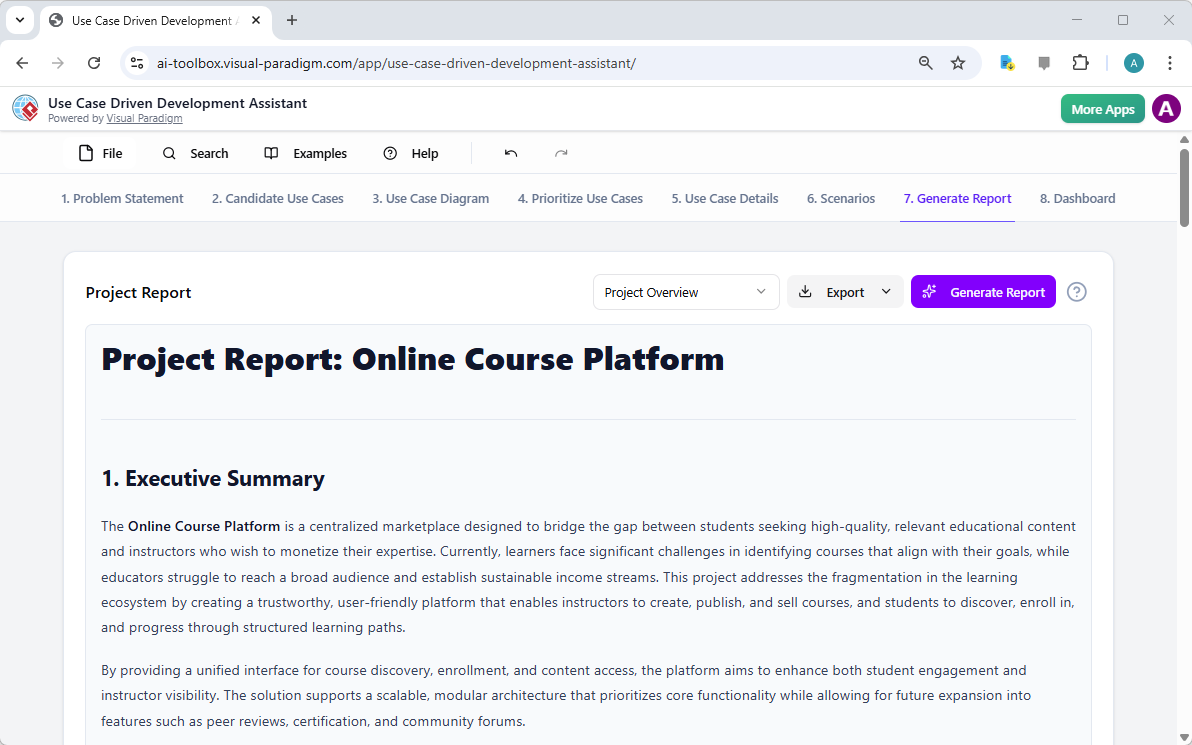
Throughout the development process, it’s essential to communicate the project’s status and plans to various stakeholders. The “Generate Report” tab, as shown in Image 9, makes this easy. You can generate a variety of reports, such as a “Project Overview,” “Implementation Plan,” “QA Test Plan,” or a “Developer Task List.” These reports are generated with AI assistance, ensuring they are consistent and comprehensive. For example, the “Project Overview” report summarizes the entire project, including the executive summary, key features, and the rationale behind the prioritization. This single source of truth ensures everyone is aligned and informed.
Step 8: Tracking Progress with the Dashboard
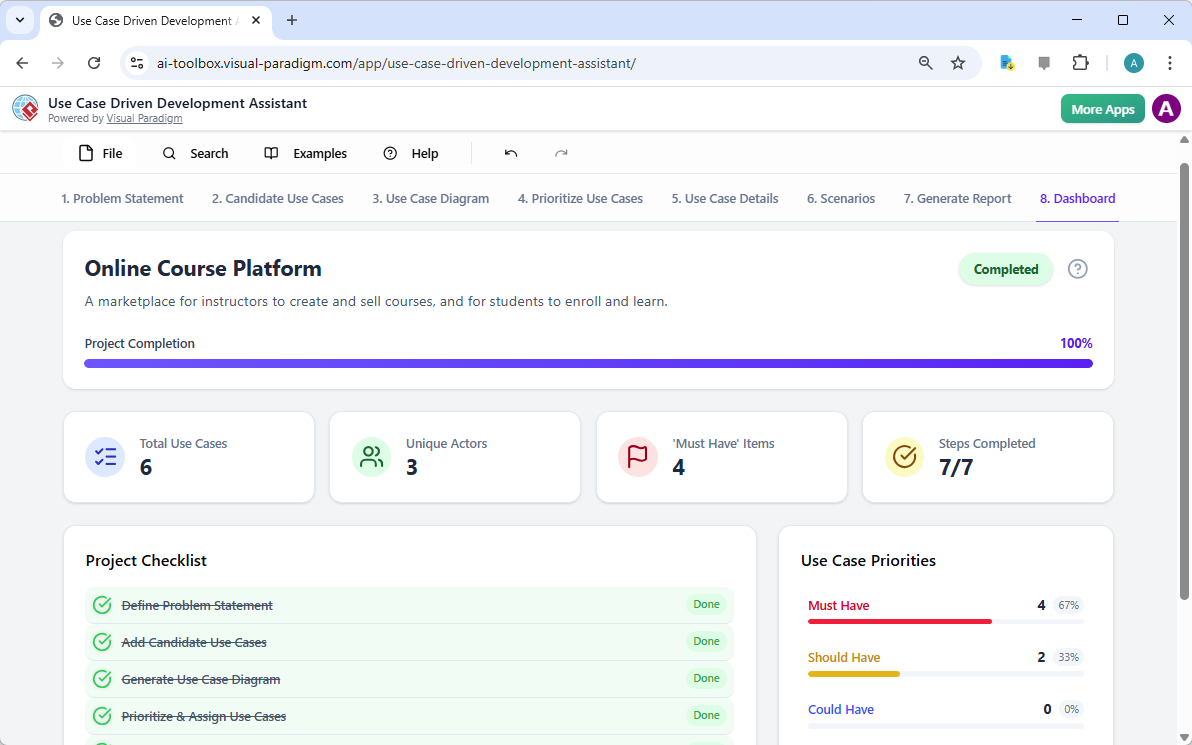
Finally, the journey culminates in the “Dashboard,” as seen in Image 10. This central hub provides a high-level overview of the project’s status. It shows the project completion percentage, the total number of use cases, and the number of “Must Have” items. The project checklist allows you to track your progress, with each completed step marked as “Done.” This real-time visibility into the project’s health is invaluable for project managers and team leads, enabling them to identify bottlenecks and ensure the project stays on track.
The Use Case Driven Development Assistant is more than just a tool; it’s a comprehensive workflow that brings clarity and efficiency to the software development process. By leveraging AI at every stage—from defining the problem to generating reports—it helps teams move from requirements to implementation faster and with greater accuracy. The result is a well-structured, well-documented project that is aligned with business goals and user needs. If you’re looking to streamline your use case development process, this AI-powered tool is a powerful solution.
Ready to see how the Use Case Driven Development Assistant can transform your next project? Try it now.
Related Links
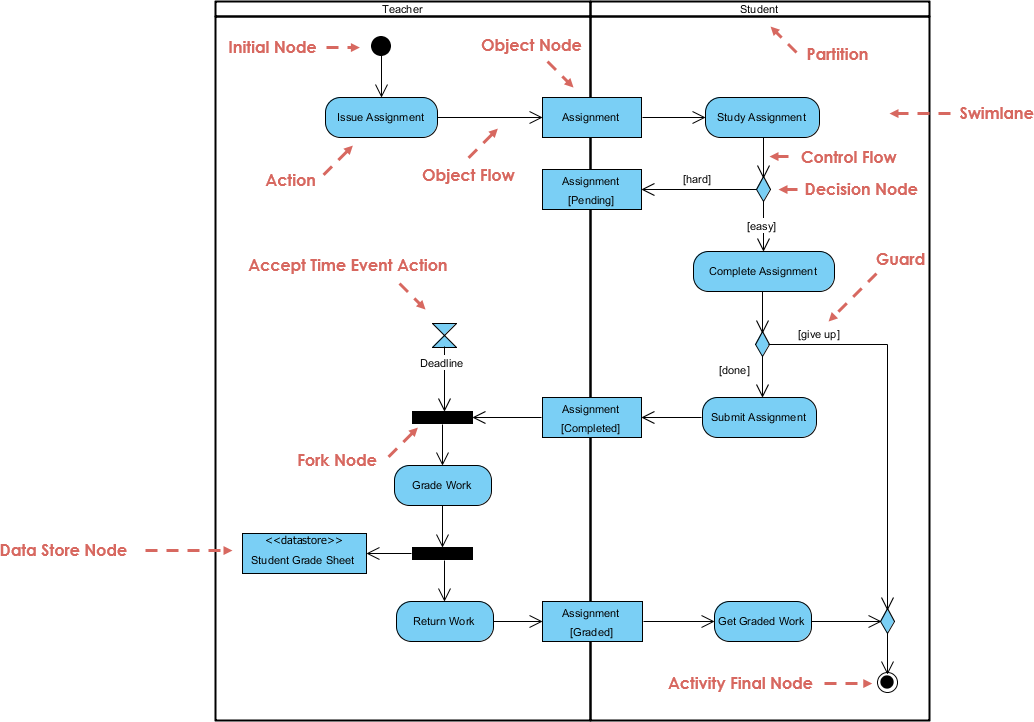
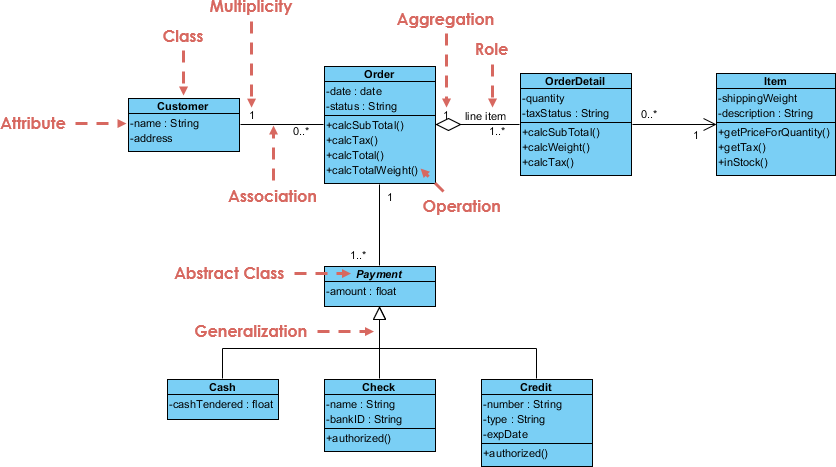
Use case modeling is a fundamental software engineering technique used to capture functional requirements by visualizing the interactions between external actors and a system’s internal functions. Modern platforms now incorporate AI-powered automation to refine diagrams, generate comprehensive use case descriptions, and convert models into test cases or activity diagrams to maintain design consistency and traceability. Advanced tools like the Flow of Events editor and Scenario Analyzer allow development teams to validate and document structured event sequences to improve overall system clarity.
-
What Is a Use Case Diagram? – A Complete Guide to UML Modeling: An in-depth overview covering essential components, purposes, and best practices for requirements modeling.
-
Step-by-Step Use Case Diagram Tutorial – From Beginner to Pro: A practical resource that guides users through foundational to advanced techniques for creating effective use case diagrams.
-
All You Need to Know About Use Case Modeling: A comprehensive exploration of the principles and applications of use case modeling in system design.
-
Visual Paradigm – Use Case Description Features: Details specialized tools used to precisely document user interactions and structured system behavior.
-
Mastering AI-Driven Use Case Diagrams with Visual Paradigm: A tutorial on leveraging AI to create intelligent, dynamic diagrams for modern software systems.
-
Guide to Using the Flow of Events Editor in Visual Paradigm: Step-by-step instructions for documenting structured event sequences within a use case scenario.
-
Unraveling Scenarios with the Use Case Scenario Analyzer: A guide on using analyzers to examine and refine interaction flows for increased system clarity.
-
Convert Use Case to Activity Diagram – AI-Powered Transformation: A resource explaining the automated conversion of use cases into detailed system workflows.
-
Generating Scenarios and Test Cases from Use Case Diagrams Using AI: An exploration of how AI tools automate the creation of requirement-driven test procedures.
-
Use Case Diagram Gallery – Templates & Examples: A curated collection of real-world examples for inspiration, learning, and rapid prototyping.